空间坐标变换(Python&C++实现)
空间坐标变换可看作坐标点乘以一个齐次矩阵,其中,齐次矩阵可表示为:

其中:
①区域的3×3矩阵产生三维图形的比例、对称、旋转、错切等基本变换;
②区域产生图形的透视变换;
③区域产生沿X、Y、Z三个轴的平移变换;
④区域产生图形的总比例变换。
平移变换
平移变换可表示为:
[ x y z 1 ] [ 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 l m n 1 ] = [ x + l y + m z + n 1 ] \begin{gathered} \quad \begin{bmatrix} x & y & z & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\ l & m & n & 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x+l & y+m & z+n & 1 \end{bmatrix} \end{gathered} [xyz1] 100l010m001n0001 =[x+ly+mz+n1]
绕X轴旋转
空间立体绕X轴旋转某个角度,实体上个点的X坐标不变,只有Y、Z坐标改变,可表示为:
[ x y z 1 ] [ 1 0 0 0 0 c o s ( θ ) s i n ( θ ) 0 0 − s i n ( θ ) c o s ( θ ) 0 0 0 0 1 ] = [ x y × c o s ( θ ) − z × s i n ( θ ) y × s i n ( θ ) + z × c o s ( θ ) 1 ] \begin{gathered} \quad \begin{bmatrix} x & y & z & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & cos(\theta) & sin(\theta) & 0 \\ 0 & -sin(\theta) & cos(\theta) & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x & y \times cos(\theta) - z \times sin(\theta) & y \times sin(\theta) + z \times cos(\theta) & 1 \end{bmatrix} \end{gathered} [xyz1] 10000cos(θ)−sin(θ)00sin(θ)cos(θ)00001 =[xy×cos(θ)−z×sin(θ)y×sin(θ)+z×cos(θ)1]
绕Y轴旋转
空间立体绕Y轴旋转某个角度,实体上个点的Y坐标不变,只有X、Z坐标改变,可表示为:
[ x y z 1 ] [ c o s ( θ ) 0 − s i n ( θ ) 0 0 1 0 0 s i n ( θ ) 0 c o s ( θ ) 0 0 0 0 1 ] = [ x × c o s ( θ ) + z × s i n ( θ ) y − x × s i n ( θ ) + z × c o s ( θ ) 1 ] \begin{gathered} \quad \begin{bmatrix} x & y & z & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} cos(\theta) & 0 & -sin(\theta) & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ sin(\theta) & 0 & cos(\theta) & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x \times cos(\theta) + z \times sin(\theta) & y & -x \times sin(\theta) + z \times cos(\theta) & 1 \end{bmatrix} \end{gathered} [xyz1] cos(θ)0sin(θ)00100−sin(θ)0cos(θ)00001 =[x×cos(θ)+z×sin(θ)y−x×sin(θ)+z×cos(θ)1]
绕Z轴旋转
空间立体绕Z轴旋转某个角度,实体上个点的Z坐标不变,只有X、Y坐标改变,可表示为:
[ x y z 1 ] [ c o s ( θ ) s i n ( θ ) 0 0 − s i n ( θ ) c o s ( θ ) 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 ] = [ x × c o s ( θ ) − y × s i n ( θ ) x × s i n ( θ ) + y × c o s ( θ ) z 1 ] \begin{gathered} \quad \begin{bmatrix} x & y & z & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} cos(\theta) & sin(\theta) & 0 & 0 \\ -sin(\theta) & cos(\theta) & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x \times cos(\theta) - y \times sin(\theta) & x \times sin(\theta) + y \times cos(\theta) & z & 1 \end{bmatrix} \end{gathered} [xyz1] cos(θ)−sin(θ)00sin(θ)cos(θ)0000100001 =[x×cos(θ)−y×sin(θ)x×sin(θ)+y×cos(θ)z1]
python代码
绕X轴旋转
def rotate_X(x, y, z, alpha):
alpha = alpha * (np.pi / 180)
x_r = x
y_r = np.cos(alpha) * y - np.sin(alpha) * z
z_r = np.sin(alpha) * y + np.cos(alpha) * z
return round(x_r, 4), round(y_r, 4), round(z_r, 4)
绕Y轴旋转
def rotate_Y(x, y, z, beta):
beta = beta * (np.pi / 180)
x_r = np.cos(beta) * x + np.sin(beta) * z
y_r = y
z_r = -np.sin(beta) * x + np.cos(beta) * z
return round(x_r, 4), round(y_r, 4), round(z_r, 4)
绕Z轴旋转
def rotate_Z(x, y, z, gamma):
gamma = gamma * (np.pi / 180)
x_r = np.cos(gamma) * x - np.sin(gamma) * y
y_r = np.sin(gamma) * x + np.cos(gamma) * y
z_r = z
return round(x_r, 4), round(y_r, 4), round(z_r, 4)
为了更直观的显示,使用matplotlib将旋转前后的点显示出来
def plot_3D(x, y, z, x1, y1, z1):
a, b, c = [0, x, x1], \
[0, y, y1], \
[0, z, z1]
d, e, f, g, h, i = [0], [0], [0], [0], [0], [0]
d.append(x)
e.append(y)
f.append(z)
g.append(x1)
h.append(y1)
i.append(z1)
dd, ee, ff = [x, 0, 0, x, x, x], \
[y, y, 0, 0, y, y], \
[z, z, z, z, z, 0]
dd1, ee1, ff1 = [0, x, x, 0, 0, 0], \
[0, 0, y, y, 0, 0], \
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, z]
dd2, ee2, ff2 = [x, x], \
[0, 0], \
[0, z]
dd3, ee3, ff3 = [0, 0], \
[y, y], \
[0, z]
gg, hh, ii = [x1, 0, 0, x1, x1, x1], \
[y1, y1, 0, 0, y1, y1], \
[z1, z1, z1, z1, z1, 0]
gg1, hh1, ii1 = [0, x1, x1, 0, 0, 0], \
[0, 0, y1, y1, 0, 0], \
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, z1]
gg2, hh2, ii2 = [x1, x1], \
[0, 0], \
[0, z1]
gg3, hh3, ii3 = [0, 0], \
[y1, y1], \
[0, z1]
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d') # 创建一个三维的绘图工程
ax.scatter3D(a, b, c, c='r') # 绘制数据点 c: 'r'红色,'y'黄色,等颜色
ax.text(x, y, z, (x, y, z), c='r') # 显示点坐标
ax.text(x1, y1, z1, (x1, y1, z1), c='r')
ax.plot3D(d, e, f, c='b')
ax.plot3D(dd, ee, ff, c='b', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(dd1, ee1, ff1, c='b', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(dd2, ee2, ff2, c='b', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(dd3, ee3, ff3, c='b', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(g, h, i, c='y')
ax.plot3D(gg, hh, ii, c='y', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(gg1, hh1, ii1, c='y', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(gg2, hh2, ii2, c='y', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(gg3, hh3, ii3, c='y', linestyle='--')
ax.set_xlabel('X') # 设置x坐标轴
ax.set_ylabel('Y') # 设置y坐标轴
ax.set_zlabel('Z') # 设置z坐标轴
ax.grid(False) # 关闭网格
plt.show()
现设初始点为P0(0,0,6),P0先绕X轴旋转6°,再绕Y轴旋转45°得到P2
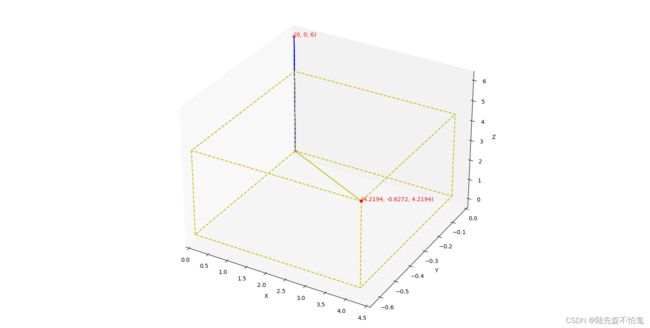
完整代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1、绕Z周旋转gamma角
def rotate_Z(x, y, z, gamma):
gamma = gamma * (np.pi / 180)
x_r = np.cos(gamma) * x - np.sin(gamma) * y
y_r = np.sin(gamma) * x + np.cos(gamma) * y
z_r = z
return round(x_r, 4), round(y_r, 4), round(z_r, 4)
# 2、绕Y轴旋转beta角
def rotate_Y(x, y, z, beta):
beta = beta * (np.pi / 180)
x_r = np.cos(beta) * x + np.sin(beta) * z
y_r = y
z_r = -np.sin(beta) * x + np.cos(beta) * z
return round(x_r, 4), round(y_r, 4), round(z_r, 4)
# 3、绕X轴旋转alpha角
def rotate_X(x, y, z, alpha):
alpha = alpha * (np.pi / 180)
x_r = x
y_r = np.cos(alpha) * y - np.sin(alpha) * z
z_r = np.sin(alpha) * y + np.cos(alpha) * z
return round(x_r, 4), round(y_r, 4), round(z_r, 4)
def plot_3D(x, y, z, x1, y1, z1):
a, b, c = [0, x, x1], \
[0, y, y1], \
[0, z, z1]
d, e, f, g, h, i = [0], [0], [0], [0], [0], [0]
d.append(x)
e.append(y)
f.append(z)
g.append(x1)
h.append(y1)
i.append(z1)
dd, ee, ff = [x, 0, 0, x, x, x], \
[y, y, 0, 0, y, y], \
[z, z, z, z, z, 0]
dd1, ee1, ff1 = [0, x, x, 0, 0, 0], \
[0, 0, y, y, 0, 0], \
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, z]
dd2, ee2, ff2 = [x, x], \
[0, 0], \
[0, z]
dd3, ee3, ff3 = [0, 0], \
[y, y], \
[0, z]
gg, hh, ii = [x1, 0, 0, x1, x1, x1], \
[y1, y1, 0, 0, y1, y1], \
[z1, z1, z1, z1, z1, 0]
gg1, hh1, ii1 = [0, x1, x1, 0, 0, 0], \
[0, 0, y1, y1, 0, 0], \
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, z1]
gg2, hh2, ii2 = [x1, x1], \
[0, 0], \
[0, z1]
gg3, hh3, ii3 = [0, 0], \
[y1, y1], \
[0, z1]
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d') # 创建一个三维的绘图工程
ax.scatter3D(a, b, c, c='r') # 绘制数据点 c: 'r'红色,'y'黄色,等颜色
ax.text(x, y, z, (x, y, z), c='r') # 显示点坐标
ax.text(x1, y1, z1, (x1, y1, z1), c='r')
ax.plot3D(d, e, f, c='b')
ax.plot3D(dd, ee, ff, c='b', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(dd1, ee1, ff1, c='b', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(dd2, ee2, ff2, c='b', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(dd3, ee3, ff3, c='b', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(g, h, i, c='y')
ax.plot3D(gg, hh, ii, c='y', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(gg1, hh1, ii1, c='y', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(gg2, hh2, ii2, c='y', linestyle='--')
ax.plot3D(gg3, hh3, ii3, c='y', linestyle='--')
ax.set_xlabel('X') # 设置x坐标轴
ax.set_ylabel('Y') # 设置y坐标轴
ax.set_zlabel('Z') # 设置z坐标轴
ax.grid(False) # 关闭网格
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
x, y, z = 0, 0, 6
x1, y1, z1 = rotate_X(x, y, z, 6)
x2, y2, z2 = rotate_Y(x1, y1, z1, 45)
print(x2, y2, z2)
plot_3D(x, y, z, x2, y2, z2)
C++代码:
#include