规约算法
规约算法
-
- 0.引言
- 1.reduction_1
- 2.reduction_2
- 3.reduction_3
- 4.result
0.引言
有的地方也称之为归约算法.
/* asum: sum of all entries of a vector.
* This code only calculates one block to show the usage of shared memory and synchronization */
#include 1.reduction_1
/* sum all entries in x and asign to y */
__global__ void reduction_1(const FLOAT *x, FLOAT *y)
{
__shared__ FLOAT sdata[256];
int tid = threadIdx.x;
/* load data to shared mem
共享内存是块内线程可见的,所以就有竞争问题的存在,也可以通过共享内存进行通信.
为了避免内存竞争,可以使用同步语句:void __syncthreads();语句相当于在线程
块执行时各个线程的一个障碍点,当块内所有线程都执行到本障碍点的时候才能进行下
一步的计算;但是,__syncthreads(); 频繁使用会影响内核执行效率。*/
sdata[tid] = x[tid];//这个x是 FLOAT *x;
__syncthreads();
/* reduction using shared mem 把for循环展开*/
if (tid < 128) sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 128];
__syncthreads();
if (tid < 64) sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 64];
__syncthreads();
if (tid < 32) sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 32];
__syncthreads();
if (tid < 16) sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 16];
__syncthreads();
if (tid < 8) sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 8];
__syncthreads();
if (tid < 4) sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 4];
__syncthreads();
if (tid < 2) sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 2];
__syncthreads();
if (tid == 0) {
*y = sdata[0] + sdata[1];
}
}
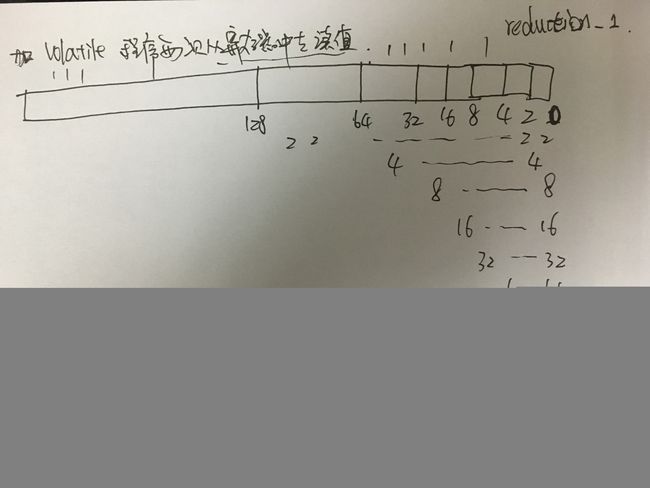
使用__share__共享内存以及__syncthreads()函数进行断句(断句为自己理解命名的).线程理解:

2.reduction_2
__global__ void reduction_2(const FLOAT *x, FLOAT *y)
{
__shared__ volatile FLOAT sdata[256];//加volatile关键字,避免编译器自己进行优化.
int tid = threadIdx.x;
sdata[tid] = x[tid];
__syncthreads();
if(tid < 128) sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 128];
__syncthreads();
if(tid < 64) sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 64];
__syncthreads();
if(tid < 32)
{
sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 32];
sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 16];
sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 8];
sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 4];
sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 2];
sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 1];
}
if(tid == 0) y[0] =sdata[0];
}
这个算法注意点在于:
- 1.共享内存;
- 2.warp机制;
- 3.volatile关键字;
- volatile关键字理解参考1.
- volatile关键字理解参考2
对于第一点,第二节中已经介绍了;对于第二点,GPU中最小的操作为一个warp,一个warp32个线程,这也是程序从if(tid < 32)开始并列写的原因.对于第三点,我尝试用自己的语音讲出来,但是发现还是官方的说法最为贴切中肯,具体的可以参考链接中的文章:
- volatile关键字可以实现线程间的可见性,之所以可以实现这一点,原因在于JVM会保证被volatile修饰的变量,在线程栈中被线程使用时都会主动从共享内存(堆内存/主内存)中以实时的方式同步一次;另一方面,如果线程在工作内存中修改了volatile修饰的变量,也会被JVM要求立马刷新到共享内存中去。因此,即便某个线程修改了该变量,其他线程也可以立马感知到变化从而实现可见性.
大意就是被volatile修饰的变量是实时更新的(可以相反于中断理解),不会被编译器优化误解算法思想.
3.reduction_3
//__device__ 只能在GPU上被调用
__device__ void warpReduce(volatile FLOAT *sdata, int tid)
{
sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 32];
sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 16];
sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 8];
sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 4];
sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 2];
sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 1];
}
__global__ void reduction_3(const FLOAT *x, FLOAT *y)
{
__shared__ FLOAT sdata[256];
int tid = threadIdx.x;
/* load data to shared mem */
sdata[tid] = x[tid];
__syncthreads();
/* reduction using shared mem */
if (tid < 128) sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 128];
__syncthreads();
if (tid < 64) sdata[tid] += sdata[tid + 64];
__syncthreads();
if (tid < 32) warpReduce(sdata, tid);
if (tid == 0) y[0] = sdata[0];
}
reduction_3思想与reduction_2一样,只是为了理解volatile的修饰作用.
4.result
28,结果肯定是小于256的.