基于MATLAB的无线传感器网络定位测量仿真
%|
%| SCRIPT: simMLE
%|
%| PURPOSE: Simulate a relative location system by generating
%| random measurements and maximizing the likelihood fcn.
%| After many trials, show the results vs. the Cramer-Rao Bound.
%|
%| AUTHOR: Neal Patwari
%| http://www.engin.umich.edu/~npatwari/
%|
%| REFERENCE: Relative Location Estimation in Wireless Sensor Networks
%| (N. Patwari, A. O. Hero, M. Perkins, N. S. Correal, R. J. O'Dea),
%| IEEE Trans. Signal Processing, vol. 51, no. 8, Aug. 2003, pp. 2137-2148.
%|
tic
% Use globals to allow minimization functions access to network info,
% debugging info.
global refDevices blindDevices totalDevices linearRefLocs dhat funcEvals dfuncEvals;
% Basic simulation parameters
roomSize = [1,1]; % Room size, meters
gridSize = 5; % How many sensors per side
refDevices = 4; % How many references (must be same length as actualRefLocs)
trials = 20; % How many indep trials to run
measMethod = 'R'; % Use 'R' for RSS, 'T' for TOA
totalDevices = gridSize^2;
blindDevices = totalDevices - refDevices;
blindCoords = 2*blindDevices;
actualRefLocs = [0,0; 0,1; 1,1; 1,0];
linearRefLocs = [actualRefLocs(:,1)', actualRefLocs(:,2)'];
% Optimization parameters
ftol = 0.00001;
if measMethod == 'R',
func = 'calcError'; % Use for RSS
dfunc = 'calcDError'; % Use for RSS
else
func = 'calcErrorTOA'; % Use for TOA
dfunc = 'calcDErrorTOA'; % Use for TOA
end
%| 1. Set up the blindfolded device locations
delta = 1/(gridSize-1);
coords = 0:delta:1;
xMatrix = ones(gridSize,1)*coords;
yMatrix = xMatrix';
xBlind = [xMatrix(2:gridSize-1), ...
xMatrix(gridSize+1:totalDevices-gridSize), ...
xMatrix(totalDevices-gridSize+2:totalDevices-1)];
yBlind = [yMatrix(2:gridSize-1), ...
yMatrix(gridSize+1:totalDevices-gridSize), ...
yMatrix(totalDevices-gridSize+2:totalDevices-1)];
actualBlindLocs = [xBlind', yBlind'];
actualAllLocs = [actualRefLocs; actualBlindLocs];
xActual = actualAllLocs(:,1)';
yActual = actualAllLocs(:,2)';
actualDist = L2_distance(actualAllLocs', actualAllLocs',0);
%| 2. Define the channel model
if measMethod == 'R';
sigmaOverN = 1.7;
% If C==1, then this simulation runs the _true_ MLE.
% If C==exp( 0.5* (log(10)/10 *sigmaOverN)^2), then this runs a
% bias-corrected (pseudo-) MLE.
% C = exp( 0.5* (log(10)/10 *sigmaOverN)^2);
C = 1;
else
sigma_d = 0.2; % Use for TOA
end
for trial = 1:trials,
if measMethod == 'R';
%| 3.0 Generate a random set of RSS-based distance measurements. When RSS
%| is expressed in dB, errors are Gaussian. Here, dhat is an interim
%| variable which has units of distance, and represents an estimate for
%| the range. It is correctly randomly generated as follows:
dhat = actualDist.*10.^(sigmaOverN/10 .*symrandn(totalDevices))./C;
else
%| 3.1 Generate a set of TOA measurements, which are Gaussian around the
%| true value with variance sigma_d.
dhat = actualDist + sigma_d .* symrandn(totalDevices);
end
%| 4. Make an initial guess of the coordinates.
blindLocs0 = [xBlind, yBlind]; % Use the true coordinates (unrealistic but best case)
%| 5. Find optimum locations of neurfons (fixed and relative)
funcEvals = 0; dfuncEvals = 0;
[coordsMLE, iter, errorMin] = frprmn(blindLocs0, ftol, func, dfunc, 0);
disp(sprintf('%d: Function / Deriv. evals: %d / %d.', trial, funcEvals, dfuncEvals));
%| 6. Save the resulting estimated coords
coordEsts(trial, 1:blindCoords) = coordsMLE;
end % for trial
estMean = mean(coordEsts);
estCov = cov(coordEsts);
estVars = diag(estCov);
estStds = sqrt(estVars);
locVars = estVars(1:blindDevices) + estVars((blindDevices+1):(2*blindDevices));
locStd = sqrt(locVars);
toc % show time of execution
% Plot the location estimates for sensors, one at a time.
if 0,
figure
for i=1:blindDevices,
clf
plot(coordEsts(:,i), coordEsts(:,blindDevices+i),'.', ...
estMean(i), estMean(blindDevices+i), 'ro')
hold on
set(gca,'xlim',[-0.2 1.2])
set(gca,'ylim',[-0.2 1.2])
set(gca,'FontSize',20)
set(gca,'DataAspectRatio',[1 1 1])
xlabel('X Position (m)')
ylabel('Y Position (m)')
set(gca,'xTick',0:0.25:1)
set(gca,'yTick',0:0.25:1)
grid;
pause;
end
end
% Calculate and plot CRB vs. estimator performance.
figure; clf;
if measMethod == 'R';
[locstdCRB, coordCRB] = calcLocalizationCRB('R', [xBlind, actualRefLocs(:,1)'], ...
[yBlind, actualRefLocs(:,2)'], blindDevices, totalDevices, sigmaOverN);
else
[locstdCRB, coordCRB] = calcLocalizationCRB('T', [xBlind, actualRefLocs(:,1)'], ...
[yBlind, actualRefLocs(:,2)'], blindDevices, totalDevices, sigma_d);
end
for i=1:blindDevices,
hold on
R = cov(coordEsts(:,i), coordEsts(:,blindDevices+i));
drawOval(estMean(i), estMean(blindDevices+i), R, 'k-','v', 8, 0, 1);
R_CRB = coordCRB([i, i+blindDevices],[i, i+blindDevices]);
drawOval(xBlind(i), yBlind(i), R_CRB, 'r--','.',20, 0, 1);
end
set(gca,'xlim',[-0.2 1.2])
set(gca,'ylim',[-0.2 1.2])
set(gca,'FontSize',18)
set(gca,'DataAspectRatio',[1 1 1])
xlabel('X Position (m)')
ylabel('Y Position (m)')
set(gca,'xTick',0:0.25:1)
set(gca,'yTick',0:0.25:1)
grid;
% Use for comparison
RMS_est_Std = sqrt(mean(locStd.^2))
RMS_crb_Std = sqrt(mean(locstdCRB.^2))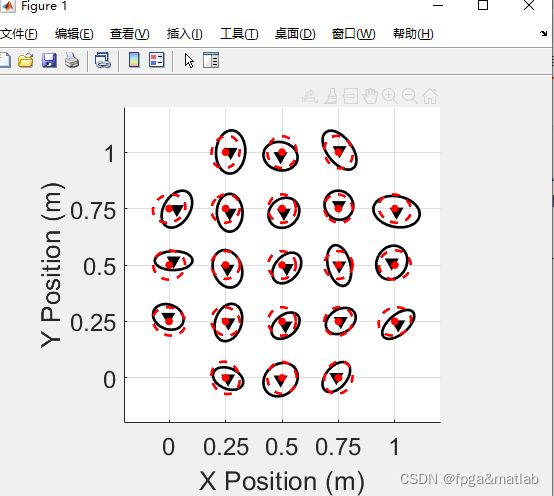
D150