【C/C++ 数据结构】-就这一篇博客让你玩爆二叉树的各种遍历问题!!!
作者:学Java的冬瓜
冬瓜的主页:☀冬瓜的主页
专栏:【C/C++ 数据结构与算法】
分享:被苦难淬炼过的人,内心真诚。——都靓评宋濂
主要内容:二叉树的递归前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历、层序遍历。以及非递归的前序、中序、后序、层序遍历。线索二叉树的创建和线索化和中序遍历。
文章目录
- 一、前序创建二叉树
- 二、二叉树递归遍历
-
- 1、前序递归遍历
- 2、中序递归遍历
- 3、后序递归遍历
- 4、层序遍历递归
- 三、二叉树非递归遍历
-
- 1、前序遍历非递归
- 2、中序遍历非递归
- 3、后序遍历非递归
- 4、层序遍历非递归
- 四、线索二叉树创建、线索化、遍历
-
- 1、前序创建线索二叉树
- 2、中序线索化线索二叉树
- 3、线索二叉树中序遍历
- 五、完整代码
-
- 1、Traversal.h
- 2、Queue_Stack.c
- 3、orderTraversal.c
- 六、成果演示
-
- 1、创建二叉树
-
- 1.1、递归层序遍历
- 1.2、非递归前序遍历
- 1.3、非递归后序遍历
- 2、创建并线索化线索二叉树
-
- 2.1、线索二叉树中序遍历
- 七、总结
-
- 1、二叉树的创建、遍历
-
- 1.1、关于前序创建二叉树:
- 1.2、关于递归遍历:
- 1.3、关于非递归遍历:
- 2、线索二叉树创建、线索化、遍历
-
- 1.1、关于线索二叉树创建:
- 1.2、关于线索二叉树的线索化:
- 1.3、关于线索二叉树中序遍历:
一、前序创建二叉树
// 前序创建二叉树
TreeNode* createTree(char* str, int* pi) {
if (str[*pi] == '#') {
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
TreeNode* root = (TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
if (root == NULL) {
exit(-1);
}
root->val = str[(*pi)++];
root->left = createTree(str, pi);
root->right = createTree(str, pi);
return root;
}
二、二叉树递归遍历
1、前序递归遍历
// 前序遍历递归
void prevOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
printf("%c ", root->val);
prevOrder(root->left);
prevOrder(root->right);
}
2、中序递归遍历
// 中序遍历递归
void inOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
inOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->val);
inOrder(root->right);
}
3、后序递归遍历
// 后序遍历递归
void postOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
postOrder(root->left);
postOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->val);
}
4、层序遍历递归
// 层次遍历递归
// 函数1
// 打印层序遍历的每一层(递归实现打印)
void printGivenLevel(TreeNode* root, int level) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
if (level == 1) {
printf("%c ", root->val);
}
else {
printGivenLevel(root->left, level - 1);
printGivenLevel(root->right, level - 1);
}
}
// 函数2
// 求整棵树的高度
int hight(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int lhight = hight(root->left);
int rhight = hight(root->right);
return lhight > rhight ? lhight + 1 : rhight + 1;
}
// 函数3
// 层序遍历
void levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
int h = hight(root);
for (int i = 1; i <= h; i++) {
printGivenLevel(root, i);
}
}
三、二叉树非递归遍历
1、前序遍历非递归
//前序遍历非递归
void prevOrderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
// 1、空树
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
// 2、创建并初始化栈
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
// 3、设置一个访问指针,把根节点给它
TreeNode* cur = root;
// 4、操作
while (cur !=NULL || !StackEmpty(&st)) {
if (cur != NULL) {
printf("%c ", cur->val);
StackPush(&st, cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
else{
cur = StackPop(&st);
cur = cur->right;
}
}
// 销毁栈
StackDestroy(&st);
}
2、中序遍历非递归
//中序遍历非递归
void inOrderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur != NULL || !StackEmpty(&st)) {
if (cur != NULL) {
StackPush(&st, cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
else {
cur = StackPop(&st);
printf("%c ", cur->val);
cur = cur->right;
}
}
StackDestroy(&st);
}
3、后序遍历非递归
//后序遍历非递归
void postOrderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
// 0、创建栈等准备工作
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
TreeNode* cur = root;
// 前一个访问的节点
TreeNode* prev = NULL;
while (cur || !StackEmpty(&st)) {
// 1、访问左节点直到遇到空
if (cur != NULL) {
StackPush(&st, cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
else {
// 2、此时cur=NULL,取出栈顶元素
TreeNode* top = StackTop(&st);
// 3、若弹出的当前栈顶元素右边为NULL或者已经被访问,
// 则说明该子树的左右均访问完,打印该子树的根节点
if (top->right == NULL || top->right == prev) {
printf("%c ", top->val);
StackPop(&st);
// 把栈顶节点赋值给当前节点cur
cur = top;
// 将当前节点设置为下一次的前一个访问节点
prev = top;
// cur置空,标志以当前节点为根节点的树已经被访问
cur = NULL;
}
else {
cur = top->right;
}
}
}
StackDestroy(&st);
}
4、层序遍历非递归
// 层次遍历非递归
void levelOrderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
// 空树
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
// 树非空
Queue qu;
// 1、初始化队列
QueueInit(&qu);
// 2、把根节点入队
QueuePush(&qu, root);
// 3、队列不空,则把当前节点队头弹出,打印
//再把这个节点的左右子树的非空根,入队列
while (!QueueEmpty(&qu)) {
TreeNode* out = QueuePop(&qu);
printf("%c ", out->val);
if (out->left != NULL) {
QueuePush(&qu, out->left);
}
if (out->right != NULL) {
QueuePush(&qu, out->right);
}
}
// 5、销毁队列
QueueDestroy(&qu);
}
四、线索二叉树创建、线索化、遍历
注意:这里的线索二叉树我用了带头的方式。
二叉树的线索链表有个头节点head,
这个head的lchild指向二叉树的根节点,head的rchild指向中序遍历时访问的最后一个节点(除掉这个根节点的最后一个)
同时,二叉树中序遍历的第一个节点的lchild和最后一个节点的rchild都指向head
1、前序创建线索二叉树
// 前序创建线索二叉树
ThreadNode* createThreadTree(char* str, int* pi) {
if (str[*pi] == '#') {
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
ThreadNode* root = (ThreadNode*)malloc(sizeof(ThreadNode));
if (root == NULL) {
exit(-1);
}
root->val = str[(*pi)++];
root->ltag = Link;
root->rtag = Link;
root->lchild = createThreadTree(str, pi);
root->rchild = createThreadTree(str, pi);
return root;
}
2、中序线索化线索二叉树
// 中序线索化二叉树
// 函数1
void inThreading(ThreadNode** root, ThreadNode** pre) {
if ((*root) == NULL) {
return;
}
inThreading((&(*root)->lchild), pre); // 左子树线索化
if ((*root)->lchild == NULL) { // 前继线索
(*root)->ltag = Thread;
(*root)->lchild = (*pre);
}
if ((*pre)->rchild == NULL) { // 后继线索
(*pre)->rtag = Thread;
(*pre)->rchild = (*root);
}
(*pre) = (*root); // 保存pre指向root的前驱
inThreading((&(*root)->rchild), pre); // 右子树线索化
}
// 函数2
// 二叉树的线索链表有个头节点head,
// 这个head的lchild指向二叉树的根节点,head的rchild指向中序遍历时访问的最后一个节点(除掉这个根节点的最后一个)
// 同时,二叉树中序遍历的第一个节点的lchild和最后一个节点的rchild都指向head
void inOrderThread(ThreadNode** head, ThreadNode** root) {
// 创建头节点
(*head) = (ThreadNode*)malloc(sizeof(ThreadNode));
if ((*head) == NULL) {
exit(-1);
}
(*head)->ltag = Link; //表示lchild为指针
(*head)->rtag = Thread; //表示rchild为线索
(*head)->rchild = (*head); //右线索回指
if ((*root) == NULL) {
(*head)->lchild = (*head); // 若二叉树为空,则左线索回指
}
else {
(*head)->lchild = (*root);
ThreadNode* pre = (*head);
inThreading(root,&pre);
pre->rchild = (*head);
pre->rtag = Thread; // 最后一个节点线索化
(*head)->rchild = pre;
}
}
3、线索二叉树中序遍历
// 线索二叉树中序遍历
void inOrderThreadTraversal(ThreadNode* head) {
ThreadNode* cur = head->lchild;
while (cur != head) {
while (cur->ltag == Link) {
cur = cur->lchild;
}
printf("%c ", cur->val);
while (cur->rtag == Thread && cur->rchild != head) {
cur = cur->rchild;
printf("%c ", cur->val);
}
cur = cur->rchild;
}
}
五、完整代码
1、Traversal.h
#pragma once
#include 2、Queue_Stack.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "Traversal.h"
//关于队列函数
//队列初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = NULL;
pq->tail = NULL;
}
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//队尾入队(尾插)
QNode* QueuePush(Queue* pq, TreeNode x)
{
assert(pq);
//注意1:创建新节点
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
//1、空间申请失败
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
//2、空间申请成功
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//注意2:连接链表
//3、处理队列链表头节点
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
//4、处理其它节点
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
return newnode;
}
//队头出队(头删)
QNode* QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//注意1:若队列中没有数据了,就不能出队了,会中止程序
assert(pq->head);
//重点:注意2:要把只有一个节点单独提出来,否则tail始终指向最后一个节点,它变成野指针
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
QNode* ret = pq->head;
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
return ret;
}
else
{
//注意3:free()前,记录第一个节点的下一个节点
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
QNode* ret = pq->head;
pq->head = next;
return ret;
}
}
// 获取队列有效数据的个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur != NULL)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
return pq->head == NULL;
}
// 关于栈部分函数
//初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//注意:动态申请数组空间
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)malloc(4 * sizeof(STDataType));
//1、申请失败
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
//2、申请成功
else
{
ps->data = tmp;
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0;
}
}
//销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->data);
ps->data = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
//压栈/入栈
STDataType StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType x)
{
//1、断言,确保ps不等于NULL。
assert(ps);
//2、判断空间是否已满,满了就先增容
if (ps->capacity == ps->top)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->data, 2 * ps->capacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
ps->data = tmp;
ps->capacity *= 2;
}
}
//3、尾插
ps->data[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
return x;
}
//出栈
STDataType StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//注意:确保top不越界,栈空时,直接终止程序报错
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
return ps->data[ps->top];
}
//获取栈顶数据
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//注意:若栈中没有数据了,ps->top=0,没有下面这步断言,会导致数组越界
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->data[ps->top - 1];
}
//判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
3、orderTraversal.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "Traversal.h"
void menu() {
printf("**********************************************************************\n");
printf("************ 1.前序创建二叉树 *****************\n");
printf("************ 递归: *****************\n");
printf("************ 2.前序遍历递归 3.中序遍历递归 *****************\n");
printf("************ 4.后序遍历递归 5.层序遍历递归 *****************\n");
printf("************ 非递归: *****************\n");
printf("************ 6.前序遍历非递归 7.中序遍历非递归 *****************\n");
printf("************ 8.后序遍历非递归 9.层序遍历非递归 *****************\n");
printf("**********************************************************************\n");
printf("************ 10.前序创建线索二叉树并中序线索化 *****************\n");
printf("************ 11.线索二叉树中序遍历 *****************\n");
printf("**********************************************************************\n");
printf("************ 0.退出 *****************\n");
printf("**********************************************************************\n");
}
// 前序遍历递归
void prevOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
printf("%c ", root->val);
prevOrder(root->left);
prevOrder(root->right);
}
// 中序遍历递归
void inOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
inOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->val);
inOrder(root->right);
}
// 后序遍历递归
void postOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
postOrder(root->left);
postOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->val);
}
// 层次遍历递归
// 函数1
// 打印层序遍历的每一层(递归实现打印)
void printGivenLevel(TreeNode* root, int level) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
if (level == 1) {
printf("%c ", root->val);
}
else {
printGivenLevel(root->left, level - 1);
printGivenLevel(root->right, level - 1);
}
}
// 函数2
// 求整棵树的高度
int hight(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int lhight = hight(root->left);
int rhight = hight(root->right);
return lhight > rhight ? lhight + 1 : rhight + 1;
}
// 函数3
// 层序遍历
void levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
int h = hight(root);
for (int i = 1; i <= h; i++) {
printGivenLevel(root, i);
}
}
//前序遍历非递归
void prevOrderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
// 1、空树
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
// 2、创建并初始化栈
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
// 3、设置一个访问指针,把根节点给它
TreeNode* cur = root;
// 4、操作
while (cur !=NULL || !StackEmpty(&st)) {
if (cur != NULL) {
printf("%c ", cur->val);
StackPush(&st, cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
else{
cur = StackPop(&st);
cur = cur->right;
}
}
// 销毁栈
StackDestroy(&st);
}
//中序遍历非递归
void inOrderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur != NULL || !StackEmpty(&st)) {
if (cur != NULL) {
StackPush(&st, cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
else {
cur = StackPop(&st);
printf("%c ", cur->val);
cur = cur->right;
}
}
StackDestroy(&st);
}
//后序遍历非递归
void postOrderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
// 0、创建栈等准备工作
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
TreeNode* cur = root;
// 前一个访问的节点
TreeNode* prev = NULL;
while (cur || !StackEmpty(&st)) {
// 1、访问左节点直到遇到空
if (cur != NULL) {
StackPush(&st, cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
else {
// 2、此时cur=NULL,取出栈顶元素
TreeNode* top = StackTop(&st);
// 3、若弹出的当前栈顶元素右边为NULL或者已经被访问,
// 则说明该子树的左右均访问完,打印该子树的根节点
if (top->right == NULL || top->right == prev) {
printf("%c ", top->val);
StackPop(&st);
// 把栈顶节点赋值给当前节点cur
cur = top;
// 将当前节点设置为下一次的前一个访问节点
prev = top;
// cur置空,标志以当前节点为根节点的树已经被访问
cur = NULL;
}
else {
cur = top->right;
}
}
}
StackDestroy(&st);
}
// 层次遍历非递归
void levelOrderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
// 空树
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
// 树非空
Queue qu;
// 1、初始化队列
QueueInit(&qu);
// 2、把根节点入队
QueuePush(&qu, root);
// 3、队列不空,则把当前节点队头弹出,打印
//再把这个节点的左右子树的非空根,入队列
while (!QueueEmpty(&qu)) {
TreeNode* out = QueuePop(&qu);
printf("%c ", out->val);
if (out->left != NULL) {
QueuePush(&qu, out->left);
}
if (out->right != NULL) {
QueuePush(&qu, out->right);
}
}
// 5、销毁队列
QueueDestroy(&qu);
}
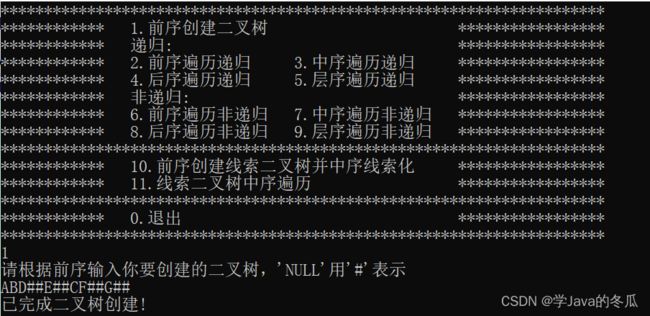
// ABD##E##CF##G##
// 前序创建二叉树
TreeNode* createTree(char* str, int* pi) {
if (str[*pi] == '#') {
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
TreeNode* root = (TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
if (root == NULL) {
exit(-1);
}
root->val = str[(*pi)++];
root->left = createTree(str, pi);
root->right = createTree(str, pi);
return root;
}
// 前序创建线索二叉树
ThreadNode* createThreadTree(char* str, int* pi) {
if (str[*pi] == '#') {
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
ThreadNode* root = (ThreadNode*)malloc(sizeof(ThreadNode));
if (root == NULL) {
exit(-1);
}
root->val = str[(*pi)++];
root->ltag = Link;
root->rtag = Link;
root->lchild = createThreadTree(str, pi);
root->rchild = createThreadTree(str, pi);
return root;
}
// 中序线索化二叉树
// 函数1
void inThreading(ThreadNode** root, ThreadNode** pre) {
if ((*root) == NULL) { // 不能这样截至递归,会造成叶子节点后继无法线索化
return;
}
inThreading((&(*root)->lchild), pre); // 左子树线索化
if ((*root)->lchild == NULL) { // 前继线索
(*root)->ltag = Thread;
(*root)->lchild = (*pre);
}
if ((*pre)->rchild == NULL) { // 后继线索
(*pre)->rtag = Thread;
(*pre)->rchild = (*root);
}
(*pre) = (*root); // 保存pre指向root的前驱
inThreading((&(*root)->rchild), pre); // 右子树线索化
}
// 函数2
// 二叉树的线索链表有个头节点head,
// 这个head的lchild指向二叉树的根节点,head的rchild指向中序遍历时访问的最后一个节点(除掉这个根节点的最后一个)
// 同时,二叉树中序遍历的第一个节点的lchild和最后一个节点的rchild都指向head
void inOrderThread(ThreadNode** head, ThreadNode** root) {
// 创建头节点
(*head) = (ThreadNode*)malloc(sizeof(ThreadNode));
if ((*head) == NULL) {
exit(-1);
}
(*head)->ltag = Link; //表示lchild为指针
(*head)->rtag = Thread; //表示rchild为线索
(*head)->rchild = (*head); //右线索回指
if ((*root) == NULL) {
(*head)->lchild = (*head); // 若二叉树为空,则左线索回指
}
else {
(*head)->lchild = (*root);
ThreadNode* pre = (*head);
inThreading(root,&pre);
pre->rchild = (*head);
pre->rtag = Thread; // 最后一个节点线索化
(*head)->rchild = pre;
}
}
// 线索二叉树中序遍历
void inOrderThreadTraversal(ThreadNode* head) {
ThreadNode* cur = head->lchild;
while (cur != head) {
while (cur->ltag == Link) {
cur = cur->lchild;
}
printf("%c ", cur->val);
while (cur->rtag == Thread && cur->rchild != head) {
cur = cur->rchild;
printf("%c ", cur->val);
}
cur = cur->rchild;
}
}
int main()
{
TreeNode* root = NULL;
ThreadNode* threadRoot = NULL;
ThreadNode* threadHead = NULL;
int input = 0;
do {
menu();
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input) {
case 0:
break;
case 1:
printf("请根据前序输入你要创建的二叉树,'NULL'用'#'表示\n");
char str1[100];
scanf("%s", str1);
int i1 = 0;
root = createTree(str1, &i1);
break;
case 2:
prevOrder(root);
printf("\n");
break;
case 3:
inOrder(root);
printf("\n");
break;
case 4:
postOrder(root);
printf("\n");
break;
case 5:
levelOrder(root);
printf("\n");
break;
case 6:
prevOrderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
break;
case 7:
inOrderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
break;
case 8:
postOrderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
break;
case 9:
levelOrderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
break;
case 10:
printf("请根据前序输入你要创建的二叉树,'NULL'用'#'表示\n");
char str2[100];
scanf("%s", str2);
int i2 = 0;
threadRoot = createThreadTree(str2, &i2); // 创建二叉树
inOrderThread(&threadHead, &threadRoot); // 线索化二叉树
break;
case 11:
{
inOrderThreadTraversal(threadHead);
printf("\n");
break;
}
default:
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
六、成果演示
在这里我就只选部分遍历或者代码较为复杂的部分,给出成果展示:
1、创建二叉树
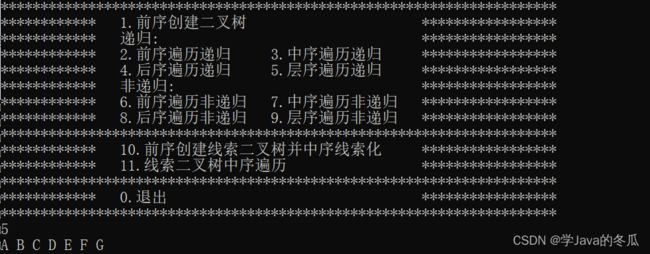
1.1、递归层序遍历
1.2、非递归前序遍历
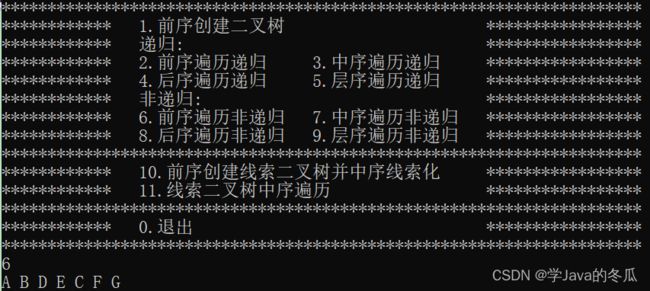
1.3、非递归后序遍历
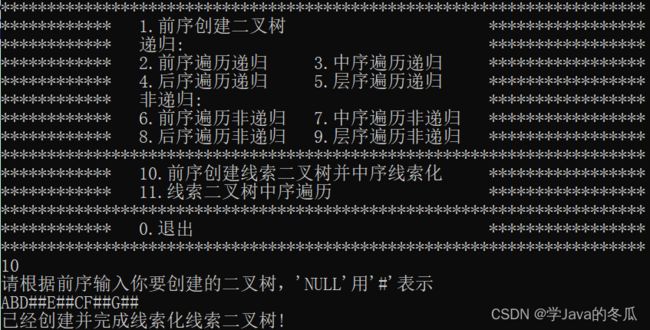
2、创建并线索化线索二叉树
2.1、线索二叉树中序遍历
七、总结
1、二叉树的创建、遍历
1.1、关于前序创建二叉树:
- 给了一个字符串,和取地址的i(防止递归时出错,确保按照字符顺序一个一个访问),先判断当前节点是否为空,空则返回,不空则申请空间,并给它赋值,然后进入左子树,右子树递归创建二叉树。
1.2、关于递归遍历:
- 二叉树的递归遍历的前序,中序、后序模板一模一样,最简单。
- 二叉树的递归遍历的层序遍历,在levelOrder函数中,可以用hight求树的高度,再根据层数,用printGivenLevel打印指定层的节点
1.3、关于非递归遍历:
-
前序、中序、后序的非递归都用到栈,层序非递归用到队列
-
前序非递归和中序非递归:它们的模板一样,cur!=NULL || !StackEmpty(&st),满足两者中的一个就继续进入循环操作。其中前序非递归是先cur!=NULL时,并打印。而中序遍历则是刚好cur==NULL时打印。且前序非递归和中序非递归都是满足cur!=NULL时入栈,cur=NULL时出栈。
-
后序非递归:要增加一个prev指针来判断是否已经访问右孩子。它同样要 cur!=NULL || !StackEmpty(&st) 才循环。具体操作是:先cur!=NULL一直入栈。当cur=NULL时,用StackTop取出栈顶元素top,如果top->right=NULL(右孩子为空)或者top->right=prev(右孩子已经被访问),那就出栈并打印栈顶元素top。否则(top->right!=NULL && top->right!=prev),那就访问右孩子,即cur=top->right。
-
层序遍历非递归:先把根节点入队列,满足!QueueEmpty,即队列不空时反复循环。进入循环时,先把队头出队并打印,再判断这个节点有没有左孩子,有则入队,再判断有没有有孩子,有则入队。
2、线索二叉树创建、线索化、遍历
1.1、关于线索二叉树创建:
- 给了一个字符串,和取地址的i(防止递归时出错,确保按照字符顺序一个一个访问)
- 先判断当前节点是否为空,空则返回,不空则申请空间,并给它赋值,注意:赋值时,把当前节点的前驱标志(ltag)和后继标志(rtag)都赋值为Link(设置了一个枚举,Link为第一个元素,故Link=0)
- 然后进入左子树,右子树递归创建二叉树。
1.2、关于线索二叉树的线索化:
- 注意使用二级指针,因为创建了树之后,线索化就是还要改变节点,因此需要二级指针去操作。
- 这里也需要设置一个pre,用来方便线索化前驱后继的操作。
- 在inOrderThread函数里,先创建头节点并给它赋值。再判断将要线索化的树是否为空,如果空则头节点head左lchild和rchild都指向自己。不空则head的左指针指向树的根节点。然后用pre记录第一个head这个头节点。
- 再一步就是进入中间部分的线索化,用inThreading中序递归去实现中间部分的前驱后继的线索化。
- 最后就把中序的最后一个节点右(pre)指针指向head,head的右指针指向最后一个节点(pre),完成线索化
1.3、关于线索二叉树中序遍历:
- 当cur!=head时,进入第一个循环
- 然后当cur->ltag=Link时,循环一直访问左孩子,直到退出里面一层循环(此时cur->ltag=head),先打印。这个里面的循环是打印每棵子树最左边的节点。
- 然后判断cur->rtag=Thread && cur->rchild!=head cur=cur->rchild,打印cur的值。这个循环是打印每棵子树的根节点
- 然后再cur=cur->rchild,看cur的右边是否还有孩子,有的话继续返回大循环操作。