pytorch【数据生成器】【回归数据的生成】【二分类数据集的创建】【小批量切分函数的创建】
文章目录
- 一、回归数据的生成
- 二、二分类数据集的创建
- 三、小批量切分函数的创建
我们创建数据生成器的目的就是便于我们后面pytorch深度学习不同的数据集
首先,导入我们所需要的库
# 随机模块
import random
# 绘图模块
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# numpy
import numpy as np
# pytorch
import torch
from torch import nn,optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils.data import Dataset,TensorDataset,DataLoader
一、回归数据的生成
#生成回归类数据的函数
def tensorGenReg(num_examples = 1000, w = [2, -1, 1], bias = True, delta = 0.01, deg = 1):
"""回归类数据集创建函数。
:param num_examples: 创建数据集的数据量
:param w: 包括截距的(如果存在)特征系数向量
:param bias:是否需要截距(如果需要有截距的话,我们的w的最后一列就是截距)
:param delta:扰动项取值(为了给我们的数据添加一些噪声)
:param deg:方程次数(一元、二元……回归)
:return: 生成的特征张和标签张量
"""
#如果我们的w中是存在了截距bias的
if bias == True:
#那我们输入的特征数就减少了一个
num_inputs = len(w)-1 # 特征张量
#创建正太分布的特征张量,有num_examples行条记录,num_inputs列个特征
features_true = torch.randn(num_examples, num_inputs) # 不包含全是1的列的特征张量
#取出w中除了最后一列的数据,然后将其变形成一列
w_true = torch.tensor(w[:-1]).reshape(-1, 1).float() # 自变量系数
#取出我们w中的最后一列的数据,作为截距
b_true = torch.tensor(w[-1]).float() # 截距
if num_inputs == 1: # 若输入特征只有1个,则不能使用矩阵乘法
#乘上方程次数,然后乘以我们的权重再加上偏置项
#也就是y=wx+b
labels_true = torch.pow(features_true, deg) * w_true + b_true
else:
labels_true = torch.mm(torch.pow(features_true, deg), w_true) + b_true
#将我们的特征和一个全的列拼接起来,并且按照纵向拼接
features = torch.cat((features_true, torch.ones(len(features_true), 1)), 1) # 在特征张量的最后添加一列全是1的列
#labels是给我们正确的标签加上噪声,噪声是正太分布的正确的标签的形状的矩阵然后乘上扰动取值
labels = labels_true + torch.randn(size = labels_true.shape) * delta
#这种情况是没有截距的
else:
#我们的特征就直接是我们的w的长度
num_inputs = len(w)
#创建我们的特征矩阵
features = torch.randn(num_examples, num_inputs)
#将我们的权重矩阵变成一列的
w_true = torch.tensor(w).reshape(-1, 1).float()
# 若输入特征只有1个,则不能使用矩阵乘法
#乘上方程次数,然后乘以我们的权重
#也就是y=wx
if num_inputs == 1:
labels_true = torch.pow(features, deg) * w_true
else:
labels_true = torch.mm(torch.pow(features, deg), w_true)
#labels是给我们正确的标签加上噪声,噪声是正太分布的正确的标签的形状的矩阵然后乘上扰动取值
labels = labels_true + torch.randn(size = labels_true.shape) * delta
return features, labels
这里我们简单验证一下
# 设置随机数种子
torch.manual_seed(420)
# 扰动项取值为0.01
f, l = tensorGenReg(delta=0.01)
# 绘制图像查看结果
plt.subplot(223)
plt.scatter(f[:, 0], l) # 第一个特征和标签的关系
plt.subplot(224)
plt.scatter(f[:, 1], l) # 第二个特征和标签的关系
二、二分类数据集的创建
def tensorGenCla(num_examples = 500, num_inputs = 2, num_class = 3, deg_dispersion = [4, 2], bias = False):
"""分类数据集创建函数。
:param num_examples: 每个类别的数据数量
:param num_inputs: 数据集特征数量
:param num_class:数据集标签类别总数
:param deg_dispersion:数据分布离散程度参数,需要输入一个列表,其中第一个参数表示每个类别数组均值的参考、第二个参数表示随机数组标准差。
:param bias:建立模型逻辑回归模型时是否带入截距
:return: 生成的特征张量和标签张量,其中特征张量是浮点型二维数组,标签张量是长正型二维数组。
"""
#首先创建一个空的张量,一列的,作为我们下面特征的模板(特征使用full_like创建和我们这个模板同形状的张量)
cluster_l = torch.empty(num_examples, 1) # 每一类标签张量的形状
mean_ = deg_dispersion[0] # 每一类特征张量的均值的参考值
std_ = deg_dispersion[1] # 每一类特征张量的方差
lf = [] # 用于存储每一类特征张量的列表容器
ll = [] # 用于存储每一类标签张量的列表容器
k = mean_ * (num_class-1) / 2 # 每一类特征张量均值的惩罚因子,也就是为了让我们的每一个类别最好都是对称地分布在0的两侧,所以这里的mean仅仅是一个步长,(num_class-1)/2也就是一半的点在0的一侧,另一半点在0的另外一侧,比方说-4,0,4就是一个例子
for i in range(num_class):
#这里的i*mean_-k就是加上了惩罚因子然后让我们的类别分布在0的两侧
#然后我们创建正态分布,其均值为i*mean_-k,然后标准差就直接取std_,矩阵的大小是需要的记录的数量乘以特征的数量
data_temp = torch.normal(i*mean_-k, std_, size=(num_examples, num_inputs)) # 生成每一类张量
lf.append(data_temp) # 将每一类张量添加到lf中
#第i类的标签就是i
labels_temp = torch.full_like(cluster_l, i) # 生成类一类的标签
ll.append(labels_temp) # 将每一类标签添加到ll中
#将我们的标签和特征列表分别拼接
features = torch.cat(lf).float()
labels = torch.cat(ll).long()
#如果需要生成偏置项的话,我们就生成全1的一列偏置项拼接给我们的特征矩阵,按照列(1)进行拼接
if bias == True:
features = torch.cat((features, torch.ones(len(features), 1)), 1) # 在特征张量中添加一列全是1的列
return features, labels
举例查看
# 设置随机数种子
torch.manual_seed(420)
# 创建数据
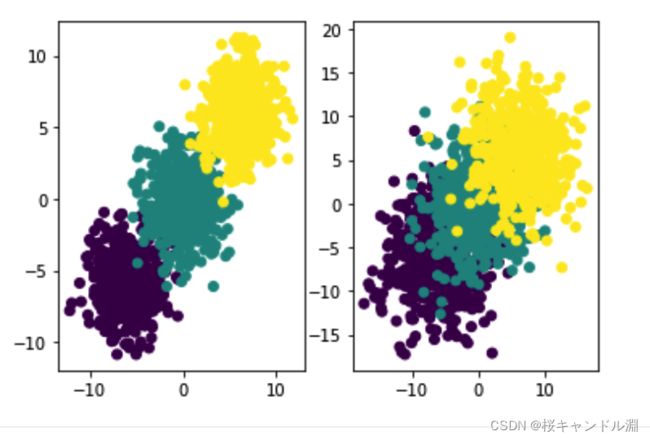
f, l = tensorGenCla(deg_dispersion = [6, 2]) # 离散程度较小
f1, l1 = tensorGenCla(deg_dispersion = [6, 4]) # 离散程度较大
# 绘制图像查看
plt.subplot(121)
plt.scatter(f[:, 0], f[:, 1], c = l)
plt.subplot(122)
plt.scatter(f1[:, 0], f1[:, 1], c = l1)
三、小批量切分函数的创建
def data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
"""
数据切分函数
:param batch_size: 每个子数据集包含多少数据
:param featurs: 输入的特征张量
:param labels:输入的标签张量
:return l:包含batch_size个列表,每个列表切分后的特征和标签所组成
"""
#特征的个数
num_examples = len(features)
#生成索引列表
#exp:[0,1,2,3,4,5]
indices = list(range(num_examples))
#打乱索引
#exp:[5,4,2,3,1,0]
random.shuffle(indices)
l = []
#从0到num_examples,步长为batch_size
#exp:[0,2,4],步长为2
for i in range(0, num_examples, batch_size):
#索引i到batch_size的的数据
#这里min(i + batch_size, num_examples)的话可以防止越界访问
#依次取出0-1,2-3,4-5的索引
#这个索引对应的是我们打乱的数据
#exp:[5,4,2,3,1,0]
j = torch.tensor(indices[i: min(i + batch_size, num_examples)])
#取出索引所对应的特征和标签
#index_select可以根据我们的向量,批量索引出对应的记录,这里的参数0表示的是维度
#exp:[5,4,2,3,1,0]
#0-1就是5,4
#2-3就是2,3
#4-5就是1,0
#然后再根据5,4和2,3和1,0的索引去我们的原特征矩阵features中找出对应的特征
#去我们对应的标签中找出对应的标签
#将标签拼接在特征后面,进行返回
l.append([torch.index_select(features, 0, j), torch.index_select(labels, 0, j)])
return l
简单测试
l = data_iter(10, features, labels)
plt.scatter(l[0][0][:, 0], l[0][0][:, 1], c = l[0][1])