jieba分词以及LDA主题提取(python)
一、环境配置
在运行分词之前首先要确定Python已经正确安装,这里我安装的是python3.9,但建议安装低一个版本的,如python3.8,因为有些包在pip install安装的时候不支持最新版本。
其次,本文需要用到lda、jieba、numpy、wordcloud等主要的包。如果发现pip安装出现错误,可以上whl官方包手动安装whl格式的包,在网页中利用Ctrl+F快速查找到相应包,如果发现这里面没有,比如lda包,还有个网站提供python官方packagetar.gz后缀的压缩包,具体安装方式百度,主要就是用python setup.py install安装命令。
二、jieba分词-数据预处理
这里采用的是jieba分词,代码如下所示,相关数据及代码文件可以在数据文本下载,在复现时需要根据自己的文件名称修改下面的文件名称。
(3.31补充:有同学反馈github因为某些原因,有时上不去,这里给上网盘地址,一个是只有500个的短文本版本,可以快速复现,另一个是完整的30M长文本-需要久点跑完)文本-提取码1111
import jieba
from os import path #用来获取文档的路径
import jieba.analyse as anls
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#词云生成工具
from wordcloud import WordCloud,ImageColorGenerator
#需要对中文进行处理
import matplotlib.font_manager as fm
#背景图
bg=np.array(Image.open("boy.png"))
#获取当前的项目文件加的路径
d=path.dirname(__file__)
#读取停用词表
stopwords = [line.strip() for line in open('cn_stopwords.txt', encoding='UTF-8').readlines()]
#读取要分析的文本
text_path="answers.txt"
#读取要分析的文本,读取格式
text=open(path.join(d,text_path),encoding="utf8").read()
text_split = jieba.cut(text) # 未去掉停用词的分词结果 list类型
#去掉停用词的分词结果 list类型
text_split_no = []
for word in text_split:
if word not in stopwords:
text_split_no.append(word)
#print(text_split_no)
fW = open('fencioutput.txt','w',encoding = 'UTF-8')
fW.write(' '.join(text_split_no))
fW.close()
text_split_no_str =' '.join(text_split_no) #list类型分为str
with open('fencioutput.txt',"r",encoding = 'UTF-8') as r:
lines =r.readlines()
with open('fencioutput.txt',"w",encoding = 'UTF-8') as w:
for line in lines:
if len(line) > 2:
w.write(line)
fW = open('fencioutput1.txt','w',encoding = 'UTF-8')
fW.write(' '.join(text_split_no))
fW.close()
text_split_no_str =' '.join(text_split_no) #list类型分为str
#基于tf-idf提取关键词
print("基于TF-IDF提取关键词结果:")
keywords = []
for x, w in anls.extract_tags(text_split_no_str, topK=200, withWeight=True):
keywords.append(x) #前200关键词组成的list
keywords = ' '.join(keywords) #转为str
print(keywords)
print("基于词频统计结果")
txt = open("fencioutput1.txt", "r", encoding="UTF-8").read()
words = jieba.cut(txt)
counts = {}
for word in words:
if len(word) == 1:
continue
else:
rword = word
counts[rword] = counts.get(rword, 0) + 1
items = list(counts.items())
items.sort(key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
for i in range(33):
word, count=items[i]
print((word),count)
#生成
wc=WordCloud(
background_color="white",
max_words=200,
mask=bg, #设置词云形状,改为mask =None;默认生成矩形图云
max_font_size=60,
scale=16,
random_state=42,
font_path='simhei.ttf' #中文处理,用国标黑体字体,如果系统没有需将附件的字体文件放到代码目录下
).generate(keywords)
#为图片设置字体
my_font=fm.FontProperties(fname='simhei.ttf.ttf')
#产生背景图片,基于彩色图像的颜色生成器
image_colors=ImageColorGenerator(bg)
#开始画图
plt.imshow(wc,interpolation="bilinear")
#为云图去掉坐标轴
plt.axis("off")
#画云图,显示
#plt.figure()
plt.show()
#为背景图去掉坐标轴
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(bg,cmap=plt.cm.gray)
#plt.show()
#保存云图
wc.to_file("ciyun.png")
print("词云图片已保存")
这里是处理前和处理后的结果


在代码实例中还加入了词云导出的功能,如下所示

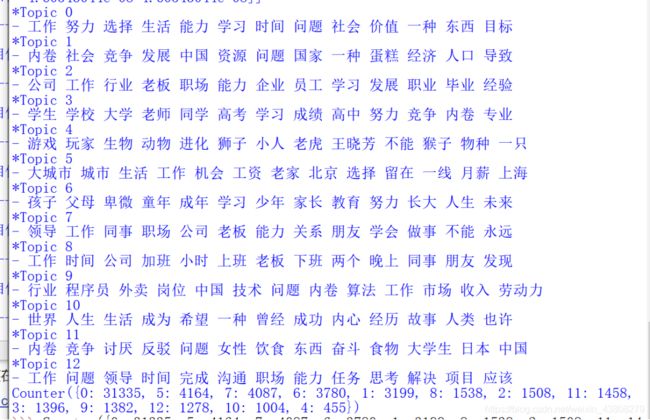
三、LDA主题提取
基于第二步的jieba分词,可以得到分词后的文件,下面进行LDA主题提取。
在LDA模型拟合步骤中,需要修改的参数主要是num_topic和alpha,前者num_topic,即话题数量,通过不断地尝试得到一个合适的值,一般从10到100都可以取,后者一般取成话题数量的倒数,如10个数量,取成0.1,一般偏小较好。
import numpy as np
from gensim import corpora, models
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 读入文本数据
f = open('fencioutput.txt', encoding='utf-8') # 输入已经预处理后的文本
texts = [[word for word in line.split()] for line in f]
f.close()
M = len(texts)
print('文本数目:%d 个' % M)
# 建立词典
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(texts)
V = len(dictionary)
print('词的个数:%d 个' % V)
# 计算文本向量g
corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(text) for text in texts] # 每个text对应的稀疏向量
# 计算文档TF-IDF
corpus_tfidf = models.TfidfModel(corpus)[corpus]
# LDA模型拟合
num_topics = 10 # 定义主题数
lda = models.LdaModel(corpus_tfidf, num_topics=num_topics, id2word=dictionary,
alpha=0.01, eta=0.01, minimum_probability=0.001,
update_every=1, chunksize=100, passes=1)
# 所有文档的主题
doc_topic = [a for a in lda[corpus_tfidf]]
print('Document-Topic:')
print(doc_topic)
# 打印文档的主题分布
num_show_topic = 5 # 每个文档显示前几个主题
print('文档的主题分布:')
doc_topics = lda.get_document_topics(corpus_tfidf) # 所有文档的主题分布
idx = np.arange(M) # M为文本个数,生成从0开始到M-1的文本数组
for i in idx:
topic = np.array(doc_topics[i])
topic_distribute = np.array(topic[:, 1])
topic_idx = topic_distribute.argsort()[:-num_show_topic - 1:-1] # 按照概率大小进行降序排列
print('第%d个文档的前%d个主题:' % (i, num_show_topic))
print(topic_idx)
print(topic_distribute[topic_idx])
# 每个主题的词分布
num_show_term = 15 # 每个主题显示几个词
for topic_id in range(num_topics):
print('主题#%d:\t' % topic_id)
term_distribute_all = lda.get_topic_terms(topicid=topic_id) # 所有词的词分布
term_distribute = term_distribute_all[:num_show_term] # 只显示前几个词
term_distribute = np.array(term_distribute)
term_id = term_distribute[:, 0].astype(np.int)
print('词:', end="")
for t in term_id:
print(dictionary.id2token[t], end=' ')
print('概率:', end="")
print(term_distribute[:, 1])
# 将主题-词写入一个文档 topword.txt,每个主题显示20个词
with open('ldatopic.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as tw:
for topic_id in range(num_topics):
term_distribute_all = lda.get_topic_terms(topicid=topic_id, topn=20)
term_distribute = np.array(term_distribute_all)
term_id = term_distribute[:, 0].astype(np.int)
for t in term_id:
tw.write(dictionary.id2token[t] + " ")
tw.write("\n")
参考
『LDA主题模型』用Python实现主题模型LDA
用WordCloud词云+LDA主题模型,带你读一读《芳华》(python实现)
python–对文本分词去停用词提取关键词并词云展示完整代码示例