Spring MVC【返回数据与请求转发和重定向】
Spring MVC【返回数据与请求转发和重定向】
- 一. 返回数据
-
- 1.1 返回静态页面
- 1.2 返回一个非静态页面
- 1.3 返回text/html类型页面
- 1.4 返回JSON对象
- 1.5 实现计算器功能
- 1.6 使用ajax方式实现登陆功能
- 二.请求转发与请求重定向
-
- 2.1 请求转发(forward)
- 2.2 请求重定向(redirect)
- 三.请求转发和请求重定向有什么区别
-
- 3.1 定义不同
- 3.2 跳转方不同
- 3.3 数据共享不同
- 3.4 最终 URL 地址不同
- 3.5 代码实现不同
- 3.6 转发和重定向的选择
我们知道,默认请求下⽆论是 Spring MVC 或者是 Spring Boot 都是由控制器(Controller)返回的是视图(View)(xxx.html),⽽现在都是前后端分离的,后端只需要返给给前端数据即可,这个时候我们就需要使⽤
@ResponseBody 注解了
一. 返回数据
1.1 返回静态页面
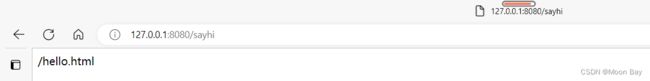
我们先创建一个前端输出的文字的页面,最后来通过Controller来进行访问
hello,spring mvc
Hello,Spring MVC.
//访问静态页面
@RequestMapping("/sayhi")
public String sayHi(){
return "/hello.html";
}
1.2 返回一个非静态页面
@ResponseBody是修饰类或方法的注解,作用是返回当前类中或方法中的非静态页面
//访问非静态页面
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/sayhi")
public String sayHi(){
return "/hello.html";
}
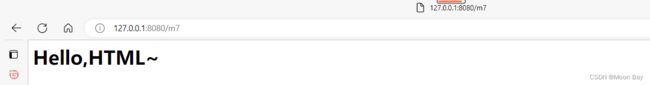
1.3 返回text/html类型页面
这个和返回静态页面的区别就是,需要用@ResponseBody,并且需要使用
前端标题符
@RequestMapping("/m7")
@ResponseBody
public String method_7() {
return "Hello,HTML~
";
}
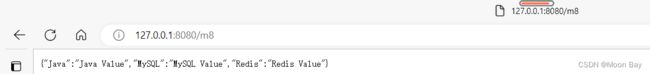
1.4 返回JSON对象
@RequestMapping("/m8")
@ResponseBody
public HashMap method_8() {
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("Java", "Java Value");
map.put("MySQL", "MySQL Value");
map.put("Redis", "Redis Value");
return map;
}
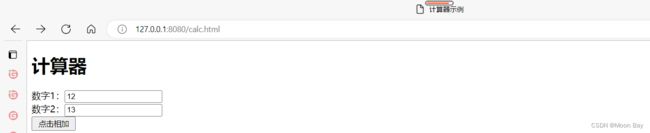
1.5 实现计算器功能
可使⽤ postman 传递参数,或使⽤ form 表单的⽅式提交参数
前端⻚⾯:
计算器示例
后端页面:
@RestController
public class CalcController {
@RequestMapping("/calc")
public String calc(Integer num1,Integer num2){
if (num1 == null || num2==null) {
if (num1 == null || num2 == null) return "参数错误!
返回";
}
return "结果:" + (num1+num2) +"
";
}
}
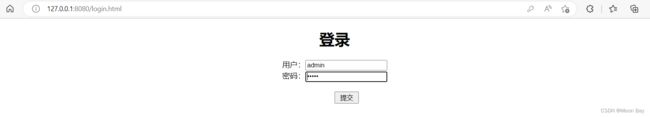
1.6 使用ajax方式实现登陆功能
前端代码:
Document
登录
用户:
密码:
后端代码:
@RequestMapping("/login3")
public HashMap login2(String username, String password){
HashMap result = new HashMap<>();
int state = 200; //状态码
int data = -1; //等于1,登陆成功,否则登陆失败
String msg = "未知错误";
//使用Spring提供的方法tringUtils.hasLength方法就可以同时判断username是否是"空"和null了
if (StringUtils.hasLength(username) && StringUtils.hasLength(password) && username.equals("admin") && password.equals("admin") ){
if ( username.equals("admin") && password.equals("admin")) {
data = 1;
msg = "";
}else {
msg = "用户名或密码错误";
}
}else {
// 参数为空
msg = "非法参数";
}
result.put("state",state);
result.put("data",data);
result.put("msg",msg);
return result;
}
二.请求转发与请求重定向
return 不但可以返回⼀个视图,还可以实现跳转,跳转的⽅式有两种:
● forward 是请求转发
● redirect:请求重定向
forward(请求转发)和 redirect(请求重定向)的区别,举例来说,例如:
你告诉你妈妈,你想吃辣条,如果你妈妈,说好,我帮你去买,这就是 forward 请求转发;
如果你妈妈让你⾃⼰去买,那么就是请求 redirect 重定向
2.1 请求转发(forward)
代码示例:
// [请求转发]
// 实现方法(1)
@RequestMapping("/fw")
public String myForward(){
return "forward:/hello.html";
}
// 实现方法(2)
@RequestMapping("/fw2")
public void myFoward2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.getRequestDispatcher("/hello.html").forward(request,response);
}
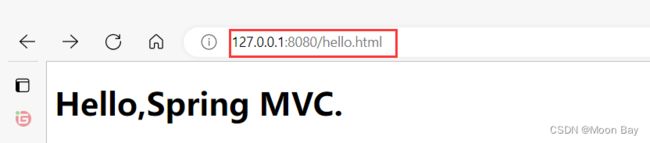
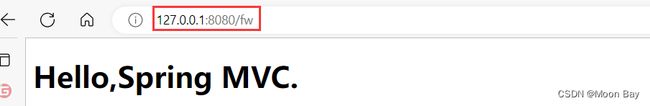
我们可以使用fiddler来进行抓包验证,我们可以发现请求转发客户端只是访问了一次,而转发的过程中是由服务器内部进行访问静态页面后返回数据给服务端的

2.2 请求重定向(redirect)
代码示例:
// [请求重定向]
// 实现方法(1)
@RequestMapping("/rd")
public String myRedirect(){
return "redirect:/hello.html";
}
// 实现方法(2)
@RequestMapping("/rd2")
public void myRedirect(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
response.sendRedirect("/hello.html");
}
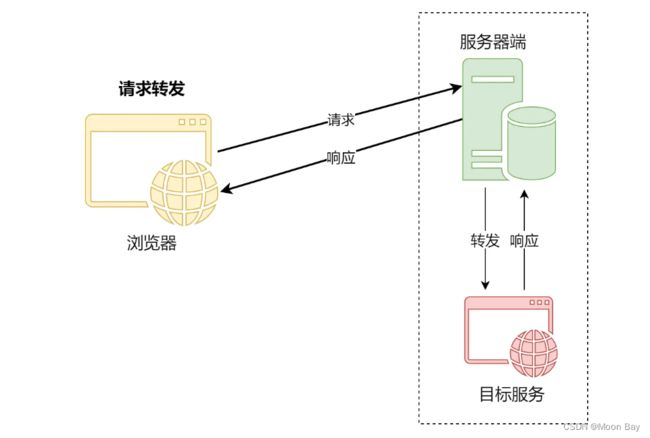
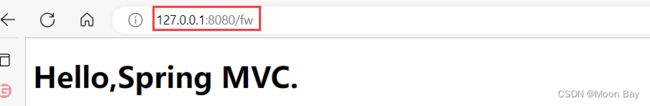
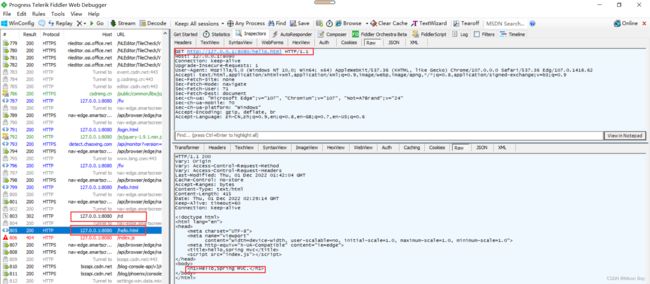
我们可以使用fiddler来进行抓包验证,我们可以发现请求1转发客户端是先访问服务器,而服务器内部会响应客户端的请求1,之后客户端会进行请求2,服务器进行进行访问静态页面后返回数据给客户端的,我们看到页面就了解了,重定向会将页面地址最后跳转到我们需要访问的静态页面地址
三.请求转发和请求重定向有什么区别
请求转发和请求重定向主要区别,包含以下 5 点:
● 定义不同
● 跳转方不同
● 数据共享不同
● 最终 URL 地址不同
● 代码实现不同
3.1 定义不同
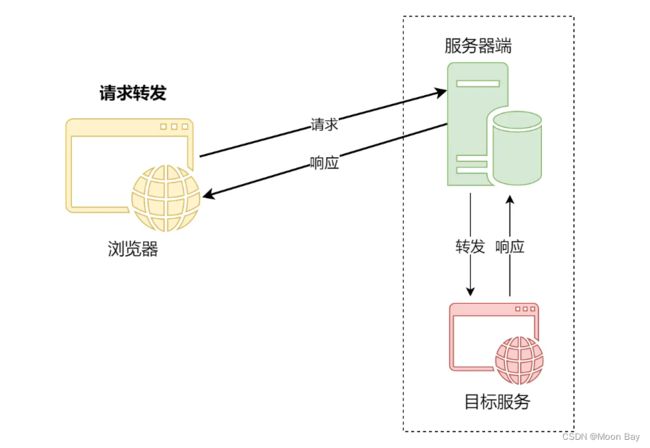
请求转发(Forward):发生在服务端程序内部,当服务器端收到一个客户端的请求之后,会先将请求,转发给目标地址,再将目标地址返回的结果转发给客户端
请求重定向(Redirect):请求重定向指的是服务器端接收到客户端的请求之后,会给客户端返回了一个临时响应头,这个临时响应头中记录了,客户端需要再次发送请求(重定向)的 URL 地址,客户端再收到了地址之后,会将请求发送到新的地址上,这就是请求重定向
3.2 跳转方不同
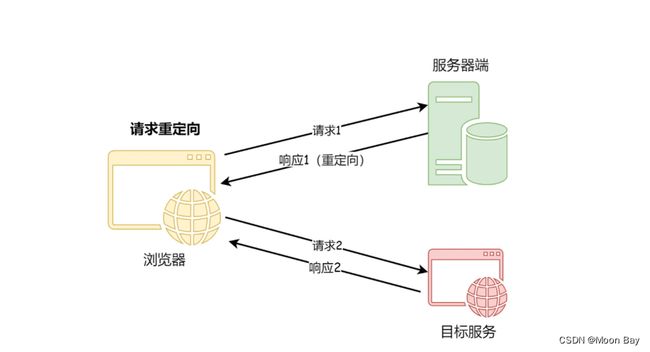
请求转发是服务器端的行为,服务器端代替客户端发送请求,并将结果返回给客户端;
而请求重定向是客户端的行为,它们的交互流程
如下图所示:
3.3 数据共享不同
请求转发是服务器端实现的,所以整个执行流程中,客户端(浏览器端)只需要发送一次请求,因此整个交互过程中使用的都是同一个 Request 请求对象和一个 Response 响应对象,所以整个请求过程中,请求和返回的数据是共享的;而请求重定向客户端发送两次完全不同的请求,所以两次请求中的数据是不同的
3.4 最终 URL 地址不同
请求转发是服务器端实现的,所以整个执行流程中,客户端(浏览器端)只需要发送一次请求,因此整个交互过程中使用的都是同一个 Request 请求对象和一个 Response 响应对象,所以整个请求过程中,请求和返回的数据是共享的;而请求重定向客户端发送两次完全不同的请求,所以两次请求中的数据是不同的
3.5 代码实现不同
// [请求转发]
// 实现方法(1)
@RequestMapping("/fw")
public String myForward(){
return "forward:/hello.html";
}
// 实现方法(2)
@RequestMapping("/fw2")
public void myFoward2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.getRequestDispatcher("/hello.html").forward(request,response);
}
// [请求重定向]
// 实现方法(1)
@RequestMapping("/rd")
public String myRedirect(){
return "redirect:/hello.html";
}
// 实现方法(2)
@RequestMapping("/rd2")
public void myRedirect(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
response.sendRedirect("/hello.html");
}
3.6 转发和重定向的选择
1、重定向的速度比转发慢,因为浏览器还得发出一个新的请求,如果在使用转发和重定向都无所谓的时候建议使用转发
2、因为转发只能访问当前web的应用程序,所以不同web应用程序之间的访问,特别是要访问到另外一个web站点上的资源的情况,这个时候就只能使用重定向了