SpringBoot整合Redis
SpringBoot整合Redis
在SpringBoot中,提供了对Redis的支持:
我们可以使用SpringBoot提供的RedisTemplate对象,操作Redis数据库。
RedisTemplate与StringRedisTemplate
在Redis里面,为了确保数据的安全性以及放便快速存储,任何类型的数据,在Redis内部都是采用二进制的方式存储的,这就导致,当我们存入一个字符串时,可能最终取出的结果会乱掉:
我们在存取的时候,这样的效果显然是不想看到的,如何解决?
SpringBoot给我们提供了两种方式:
其中StringRedisTemplate继承RedisTemplate。
简单来说就是两种序列化的方式,详情参考。
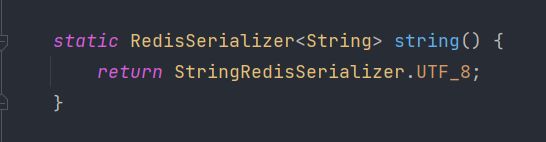
我们发现,在初始化的时候,都调用了.string()方法:
其实就是指定序列化为string的序列化方式。
这里为了测试效果,选用StringRedisTemplate对象。
简单配置
创建一个SpringBoot项目,因为SpringBoot已经整合了Redis,我们只需要引入Redis即可:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.datagroupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
在配置文件中进行一些端口的配置:
# Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=192.168.1.1 #换成你的
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=0
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
#spring.redis.password=
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制) 默认 8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=8
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制) 默认 -1
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=-1
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接 默认 8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=8
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接 默认 0
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0
## 连接超时时间(毫秒)
spring.redis.timeout=30000
Redis命令与StringRedisTemplate方法对应
| 方法 | 返回值 | 对应操作 |
|---|---|---|
| opsForValue() | ValueOperations |
操作string |
| opsForHash() | HashOperations |
操作hash |
| opsForSet() | SetOperations |
操作set |
| opsForList() | ListOperations |
操作list |
| opsForZSet() | ZSetOperations |
操作有序set |
除此之外,还有一些与Key相关的操作,可直接通过RedisTemplate对象去调用。
Key相关
| Redis命令 | StringRedisTemplate/RedisTemplate | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| KEYS * KEYS *key* KEYS *key KEYS key* |
redisTemplate.keys(key); | 获取所有key,模糊查询key(支持通配符*) |
| EXPIRE key 10 | redisTemplate.expire(key,time,TimeUnit.SECONDS); | 指定key缓存失效时间 |
| EXPIREAT key 1293840000 | redisTemplate.expireAt(key, date); | 指定key缓存到期时间 |
| TTL key | redisTemplate.getExpire(key, TimeUnit.SECONDS); | 根据key获取过期时间 |
| EXISTS key | redisTemplate.hasKey(key); | 判断key是否存在 |
| EXISTS key1 key2 key3 | redisTemplate.countExistingKeys(Arrays.asList(key)); | 检查key存在的数量 |
| DEL key | redisTemplate.delete(key); | 删除指定key缓存 |
| DEL key1 key2 key3 | redisTemplate.delete(Arrays.asList(keys)); | 批量删除key |
测试:
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname KeyRedis
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 14:51
*/
@Component
public class KeyRedis {
@Autowired(required = false)
StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public void test(){
ValueOperations<String, String> value = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
HashOperations<String, Object, Object> hash = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
ListOperations<String, String> list = redisTemplate.opsForList();
SetOperations<String, String> set = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
ZSetOperations<String, String> zSet = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
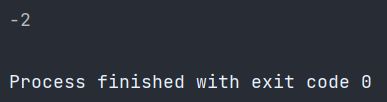
redisTemplate.expire("key",10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(redisTemplate.getExpire("key"));
}
}
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname KeyRedisTest
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 14:53
*/
@SpringBootTest
public class KeyRedisTest {
@Autowired
KeyRedis keyRedis;
@Test
void test1(){
keyRedis.test();
}
}
因为还未过期,所以是 -2
String相关
redisTemplate.opsForValue();//操作字符串
| Redis命令 | StringRedisTemplate/RedisTemplate | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| SET key value | set(key,value) | 设置普通缓存 |
| SET key value time | set(key,value,time) | 设置缓存过期时间 |
| GET key | get(key) | 获取普通股缓存 |
| INCE key | increment(key, delta) | 递增,可设置增量 |
| DECR key | increment(key, -delta) | 递减 |
| SETNX key value | setIfAbsent(key,value) | 将 key 的值设为 value ,当且仅当 key 不存在 |
| SETEX key value | setIfPresent(key,value) | 判断当前的键的值是否为v,是的话不作操作,不是的话进行替换。如果没有这个键也不会做任何操作 |
| GETSET key value | getAndSet(key, value) | key存在设置新值,并返回旧值 |
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname StringRedis
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 11:27
*/
@Component
public class StringRedis {
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public void run() {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "星星");
String name = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println("name = " + name);
}
public void run2() throws InterruptedException {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "soberw", 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
String name = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println("第一次取值:" + name);
Thread.sleep(6 * 1000);
String name2 = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println("第二次取值:" + name2);
}
public void run3() {
ValueOperations<String, String> value = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
System.out.println(value.get("p1"));
}
public void run4() {
Boolean aBoolean = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("name", "soberw");
Boolean aBoolean1 = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("name", "soberw");
System.out.println("aBoolean = " + aBoolean);
System.out.println("aBoolean1 = " + aBoolean1);
}
}
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname StringRedisTest
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 14:37
*/
@SpringBootTest
public class StringRedisTest {
@Autowired
StringRedis stringRedis;
@Test
void stringTest1() {
stringRedis.run(); //星星
}
@Test
void stringTest2() throws InterruptedException {
stringRedis.run2();
//第一次取值:soberw
//第二次取值:null 因为已经过期
}
@Test
void stringTest3(){
stringRedis.run3(); //1
}
@Test
void stringTest4(){
stringRedis.run4();
//aBoolean = true
//aBoolban1 = false
//第一次因为不存在所以进添加进去了 返回true
//第二次因为已经存在了所以不做操作 返回false
}
}
Hash相关
redisTemplate.opsForHash();//操作Hash类型
| Redis命令 | StringRedisTemplate/RedisTemplate | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| HMSET key key1 value1 key2 value2 | putAll(key, map) | 设置缓存 |
| HSET key item value | put(key, item, value) | 向一张hash表中放入数据,如果不存在将创建 |
| HGET key item | get(key, item) | 获取缓存,字段值 |
| HMGET key | entries(key) | 获取hashKey对应的所有键值 |
| HVALS | values(key) | 获取hashKey对应的所有键值 |
| HEXISTS key item | hasKey(key, item) | 判断hash表中是否有该项的值 |
| HINCRBY key item by | increment(key, item, by) | hash递增 如果不存在,就会创建一个 并把新增后的 |
| HLEN | lengthOfValue(key,hashkey) | 获取指定hash键指定键值的长度 |
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname HashRedis
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 15:01
*/
@Component
public class HashRedis {
private final String key = "student#01";
@Autowired(required = false)
StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public void test(){
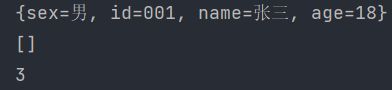
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key,"id","001");
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key,"name","张三");
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key,"age","18");
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key,"sex","男");
Map<Object, Object> entries = redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key);
System.out.println(entries);
}
public void test1(){
redisTemplate.opsForHash().values("key");
}
public void test2(){
redisTemplate.opsForHash().lengthOfValue(key,"id");
}
}
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname HashRedisTest
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 15:05
*/
@SpringBootTest
public class HashRedisTest {
@Autowired
HashRedis hashRedis;
@Test
void test(){
hashRedis.test();
hashRedis.test1();
hashRedis.test2();
}
}
List相关
redisTemplate.opsForList();//操作List类型
| Redis命令 | StringRedisTemplate/RedisTemplate | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| RPUSH key value | rightPush(key, value) | 将list放入缓存,从右边添加 |
| LPUSH key value | leftPush(key, value) | 将list放入缓存,从左边添加 |
| LRANGE key 0 -1 | range(key, start, end) | 获取list缓存指定范围的内容 |
| LLEN key | size(key) | 获取list缓存的长度 |
| LINDEX key index | index(key, index) | 通过索引 获取list中的值 |
| LSET key index value | set(key, index, value) | 根据索引修改list中的某条数据 |
| LREM key count value | remove(key, count, value) | 移除N个值为value |
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname ListRedis
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 20:29
*/
@Component
public class ListRedis {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
private final String key = "onewayroad";
public void test() {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(key, "周星星");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(key, "张敏");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(key, "李大锤");
String value = stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop(key);
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().size(key));
}
}
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname ListRedisTest
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 20:33
*/
@SpringBootTest
public class ListRedisTest {
@Autowired
ListRedis listRedis;
@Test
void test(){
listRedis.test();
}
}
Set相关
redisTemplate.opsForSet();//操作Set类型
| Redis命令 | StringRedisTemplate/RedisTemplate | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| SMEMBEredisTemplate key | memberedisTemplate(key) | 根据key获取Set中的所有值 |
| SISMEMBER key value | isMember(key, value) | 根据value从一个set中查询,是否存在 |
| SADD key value1 value2 | add(key, values) | 将数据放入set缓存 |
| SCARD key | size(key) | 获取set缓存的长度 |
| SREM key value1 value2 | remove(key, values) | 移除值为value的 |
| SDIFF key1, key2 | difference(key1, key2) | 求两个key对应的set的差集(不包括右边的) |
| SINTER key1, key2 | intersect(key1, key2) | 求两个key对应的set的交集 |
| SUNION key1, key2 | set.union(key1, key2) | 求两个key对应的set的并集 |
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.SetOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname SetRedis
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 15:09
*/
@Component
public class SetRedis {
private final String key1 = "stu#01";
private final String key2 = "stu#02";
@Autowired(required = false)
StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public void test(){
SetOperations<String, String> set = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
set.add(key1,"a");
set.add(key1,"b");
set.add(key1,"c");
set.add(key2,"b");
set.add(key2,"c");
set.add(key2,"d");
System.out.println("key1 = " + set.members(key1));
System.out.println("key2 = " + set.members(key2));
System.out.println("set.difference(key1,key2) = " + set.difference(key1, key2));
System.out.println("set.intersect(key1,key2) = " + set.intersect(key1, key2));
System.out.println("set.union(key1,key2) = " + set.union(key1, key2));
}
}
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname SetRedisTest
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 15:16
*/
@SpringBootTest
public class SetRedisTest {
@Autowired
SetRedis setRedis;
@Test
void test(){
setRedis.test();
}
}
ZSet相关
redisTemplate.opsForZSet();//操作ZSet(有序集合)类型
大致上与set相似,额外增加了权重值。
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ZSetOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname ZSetRedis
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 20:46
*/
@Component
public class ZSetRedis {
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
private final String key ="zhouxingxing";
public void test(){
//添加周星星同学成绩
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(key,"语文",98);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(key,"数学",87);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(key,"英语",75);
//获取分数最高的成绩
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> values = stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().popMax(key);
//打印值
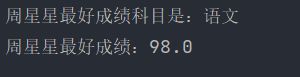
System.out.println("周星星最好成绩科目是:"+values.getValue());
System.out.println("周星星最好成绩:"+values.getScore());
}
}
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname ZSetRedisTest
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 20:47
*/
@SpringBootTest
public class ZSetRedisTest {
@Autowired
ZSetRedis zSetRedis;
@Test
void test(){
zSetRedis.test();
}
}
BitMap相关 *
严格来说,BitMap并不是一个单独的类型,而是数据string类型里面的。
bitmap也叫位图,也就是⽤⼀个bit位来表⽰⼀个东西的状态,我们都知道bit位是⼆进制,所以只有两种状态,0和1。
bitmap的出现就是为了⼤数据量⽽来的,但是前提是统计的这个⼤数据量每个的状态只能有两种,因为每⼀个bit位只能表⽰两种状态。
| Redis命令 | StringRedisTemplate/RedisTemplate | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| SETBIT key offest value | setBit(key,offest,boolean) | 给key指定偏移量设置值 |
| GETBIT key offest | getBit(key,offest) | 获取key指定偏移量的值 |
| BITCOUNT key [start] [end] | bitCount(key,start,end) | 计算给定字符串中,被设置为 1 的比特位的数量 |
| BITOP operation destkey key [key …] | bitOp(op,dest,key) | 对一个或多个保存二进制位的字符串 key 进行位元操作,并将结果保存到 destkey 上 |
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisCallback;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname BitMapRedis
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 21:00
*/
@Component
public class BitMapRedis {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
private final String key ="singin#2022#zhouxingxing";
public void test(){
//设置签到
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setBit(key,2,true);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setBit(key,85,true);
//获取周星星同学的签到天数
RedisCallback<Long> callback = connection -> connection.bitCount(key.getBytes(),0,365);
Long count = stringRedisTemplate.execute(callback);
//打印周星星2022年签到天数
System.out.println("周星星2022年一共签到天数:"+count);
}
}
package com.soberw.redis_quickstart.redis;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
/**
* @author soberw
* @Classname ZSetRedisTest
* @Description
* @Date 2022-05-26 20:47
*/
@SpringBootTest
public class BitMapRedisTest {
@Autowired
BitMapRedis bitMapRedis;
@Test
void test(){
bitMapRedis.test();
}
}
场景使用举例
BitMap
签到:
offset= dayofYear 今年的第几天
setbit 2020#UserId#6 5 1
setbit 2020#UserId#6 168 1
setbit 2020#UserId#13 256 1
bitcount 2020#UserId#6 0 -1 获取某人的具体登录天数
366天/8 ≈ 46 byte ≈ 0.0449219(kb) *10万 ≈ 4492.19 (kb)/1024 ≈ 4.3869(mb)
活跃用户:
setbit 20200601 6 1
setbit 20200602 6 1
setbit 20200602 13 1
bitop and jieguo1 20200601 20200602 一直在线人数统计
bitop or jieguo2 20200601 20200602 时间段总的活跃用户数
bitcount jieguo1
bitop 参与的运算有
| 操作 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| and与 | 有0出0;全1出1 |
| or 或 | 有1出1;全0出0 |
| not 非 | 有1出0;有0出1。 |
| xor 异或 | 相同得0;相异得1 |
SET
好友的交际
ZSET
排行榜, 热搜,今日头条 推荐
RedisTemplate
前面所使用的StringRedisTemplate其实就是RedisTemplate的一个子类,他们只是实现序列化的方式不同罢了。
泛型约束的使用
而在使用RedisTemplate的时候,是可以指定泛型的,有了泛型的约束,可以让我们在操作的使用更加规范化。
看下面一段代码:
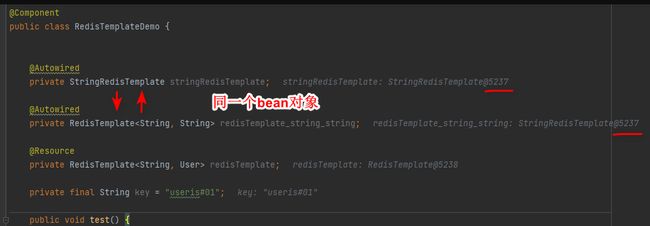
@Component
public class RedisTemplateDemo {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate_string_string;
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, User> redisTemplate;
@Resource(name="redisTemplate")
private ValueOperations<String,User> valueOperations;
private final String key = "useris#01";
public void test() {
User user = User.builder().id(1).name("李四").build();
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key,user );
User value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
valueOperations.set(key,user );
User value2 = valueOperations.get(key);
System.out.println(value);
}
}
因为@Autowired是按照类型自动注入IOC的,因此注入的第一个和第二个对象,虽然一个是StringRedisTemplate、一个是RedisTemplate,但是实际上在容器中确实一个bean对象:
这显然不是我们想要的,如何解决:
SpringBoot官方例子推荐我们使用@Resource注解:
@Autowired 与 @Resource 区别
区别:
1:
@Autowired注解由Spring提供,只按照byType注入;
@Resource注解由J2EE提供,默认按照byName自动注入。
2:
@Autowired默认按类型进行装配,
@Resource默认按照名称进行装配。
序列化
前面都是直接使用的StringRedisTemplate去操作的Redis,说过是因为其使用的是string的序列化方式,而RedisTemplate则是使用的JDK的序列化方式,在使用起来不太友好,直接使用时字符串是会出现乱码的,如何解决呢:
JdkSerializationRedisSerializer serializer = new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer();
byte[] serialize = serializer.serialize("user#01");
System.out.println(new String(serialize));
自定义序列化工具
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean(name = "redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
// 在使用注解@Bean返回RedisTemplate的时候,同时配置hashKey与hashValue的序列化方式。
// key采用String的序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
// value序列化方式采用jackson
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
// hash的key也采用String的序列化方式
template.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
// hash的value序列化方式采用jackson
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
}
可以设置自定义的序列化工具来解决,这里采用的是Jackson工具,当然也可以使用阿里的FastJSON工具。
XXXOperations
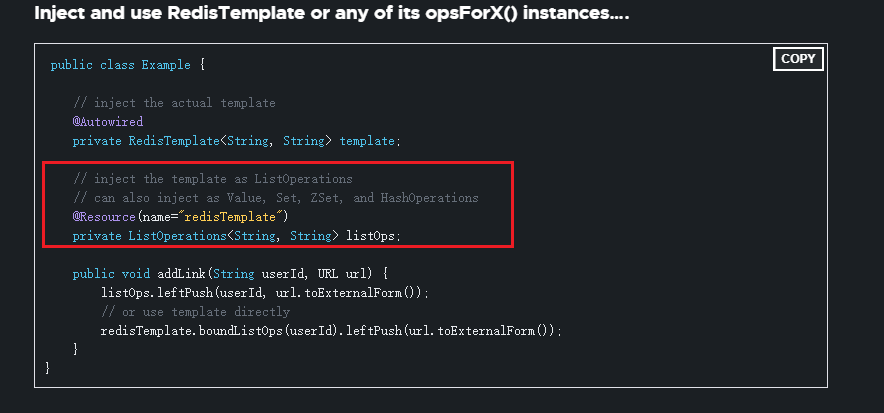
在前面操作的时候,我们都是需要频繁的通过StringRedisTemplate.opsForXXX()来过去对应的Redis数据类型以操作Redis,这样未免很麻烦,下面介绍解决方案:
RedisTemplate中还有一系列的XXXOperations对应着不同的Redis数据类型,我们可以根据不同的类型自动注入获取:
为什么ValueOperations可以自动注入呢?
spring源码分析:
<T> T adaptBeanInstance(String name, Object bean, @Nullable Class<?> requiredType) {
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
Object convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return (T) convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
String targetTypeName = targetType.getName();
String editorName = targetTypeName + "Editor";
try {
Class<?> editorClass = cl.loadClass(editorName);
if (editorClass != null) {
if (!PropertyEditor.class.isAssignableFrom(editorClass)) {
unknownEditorTypes.add(targetType);
return null;
}
return (PropertyEditor) instantiateClass(editorClass);
}
// Misbehaving ClassLoader returned null instead of ClassNotFoundException
// - fall back to unknown editor type registration below
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Ignore - fall back to unknown editor type registration below
}
Redis客户端
除了SpringBoot给出的操作Redis的解决方案RedisTemplate,还有很多开源的Redis客户端供我们选择使用,目前比较流行的几款有:
-
Jedis
Jedis是Redis的Java实现的客户端,其API提供了比较全面的Redis命令的支持;Jedis中的方法调用是比较底层的暴露的Redis的API,也即Jedis中的Java方法基本和Redis的API保持着一致,了解Redis的API,也就能熟练的使用Jedis。
-
Redisson
Redisson实现了分布式和可扩展的Java数据结构,提供很多分布式相关操作服务,例如,分布式锁,分布式集合,可通过Redis支持延迟队列。和Jedis相比,功能较为简单,不支持字符串操作,不支持排序、事务、管道、分区等Redis特性。Redisson的宗旨是促进使用者对Redis的关注分离,从而让使用者能够将精力更集中地放在处理业务逻辑上。Redisson中的方法则是进行比较高的抽象,每个方法调用可能进行了一个或多个Redis方法调用。
-
Lettuce
Lettuce:高级Redis客户端,用于线程安全同步,异步和响应使用,支持集群,Sentinel,管道和编码器。目前springboot默认使用的客户端。