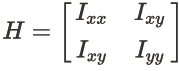harris角点检测算法实现
算法流程:
1、将图像转换为灰度图像;
2、利用Sobel滤波器求出 海森矩阵 (Hessian matrix) :
3、将高斯滤波器分别作用于Ix²、Iy²、IxIy;
4、计算每个像素的 R= det(H) - k(trace(H))²。det(H)表示矩阵H的行列式,trace表示矩阵H的迹。通常k的取值范围为[0.04,0.16];
5、满足 R>=max(R) * th 的像素点即为角点。th常取0.1。
python代码实现:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding: utf-8
import cv2
import copy
import numpy as np
def bgr2gray(img):
gray = 0.2126 * img[..., 2] + 0.7152 * img[..., 1] + 0.0722 * img[..., 0]
gray = gray.astype(np.uint8)
return gray
def sobel_filtering(gray):
# get shape
img_h, img_w = gray.shape
# sobel kernel
sobel_y = np.array(((1, 2, 1),
(0, 0, 0),
(-1, -2, -1)), dtype=np.float32)
sobel_x = np.array(((1, 0, -1),
(2, 0, -2),
(1, 0, -1)), dtype=np.float32)
# padding
tmp = np.pad(gray, (1, 1), 'edge')
# prepare
ix = np.zeros_like(gray, dtype=np.float32)
iy = np.zeros_like(gray, dtype=np.float32)
# get differential
for y in range(img_h):
for x in range(img_w):
ix[y, x] = np.mean(tmp[y: y + 3, x: x + 3] * sobel_x)
iy[y, x] = np.mean(tmp[y: y + 3, x: x + 3] * sobel_y)
ix2 = ix ** 2
iy2 = iy ** 2
ixy = ix * iy
return ix2, iy2, ixy
def gaussian_filtering(I, k_size=3, sigma=3):
# get shape
img_h, img_w = I.shape
# gaussian
i_t = np.pad(I, (k_size // 2, k_size // 2), 'edge')
# gaussian kernel
K = np.zeros((k_size, k_size), dtype=np.float32)
for x in range(k_size):
for y in range(k_size):
_x = x - k_size // 2
_y = y - k_size // 2
K[y, x] = np.exp(-(_x ** 2 + _y ** 2) / (2 * (sigma ** 2)))
K /= (sigma * np.sqrt(2 * np.pi))
K /= K.sum()
# filtering
for y in range(img_h):
for x in range(img_w):
I[y, x] = np.sum(i_t[y: y + k_size, x: x + k_size] * K)
return I
def corner_detect(img, ix2, iy2, ixy, k=0.04, th=0.1):
# prepare output image
out = copy.deepcopy(img)
# get R
R = (ix2 * iy2 - ixy ** 2) - k * ((ix2 + iy2) ** 2)
# detect corner
out[R >= np.max(R) * th] = [255, 0, 0]
out = out.astype(np.uint8)
return out
def harris_corner(img):
# 1. grayscale
gray = bgr2gray(img)
# 2. get difference image
ix2, iy2, ixy = sobel_filtering(gray)
# 3. gaussian filtering
ix2 = gaussian_filtering(ix2, k_size=3, sigma=3)
iy2 = gaussian_filtering(iy2, k_size=3, sigma=3)
ixy = gaussian_filtering(ixy, k_size=3, sigma=3)
# 4. corner detect
out = corner_detect(img, ix2, iy2, ixy)
return out
def main():
# Read image
img = cv2.imread("test.jpg")
img = cv2.resize(img, (512, 512))
img = img.astype(np.float32)
# Harris corner detection
out = harris_corner(img)
cv2.imwrite("out.jpg", out)
print("proc ok.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()结果:
opencv python版本实现:
对于每一个像素(x,y),在(blockSize*blockSize)邻域内,计算梯度图的协方差矩阵M(x,y) ,然后通过上面第二步中的角点响应函数得到结果图。图像中的角点可以为该结果图的局部最大值。即可以得到输出图中的局部最大值,这些值就对应图像中的角点。
Harris 角点检测函数:
cv2.cornerHarris(src, blockSize, ksize, k, dst, borderType)src:数据类型为float32的输入图像
blockSize:角点检测中要考虑的领域大小
ksize:Sobel求导中使用的窗口大小
k:Harris 角点检测方程中的自由参数,取值参数为 [0,04,0.06].
dst:目标图像
borderType:边界类型
import cv2
import numpy as np
def test():
img = cv2.imread("test.jpg")
img = cv2.resize(img, (512, 512))
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray = np.float32(gray)
# 输入图像必须是 float32,最后一个参数在 0.04 到 0.05 之间
dst = cv2.cornerHarris(gray, 3, 3, 0.04)
# result is dilated for marking the corners, not important
# dst = cv2.dilate(dst, None)
# Threshold for an optimal value, it may vary depending on the image.
img[dst > 0.1 * dst.max()] = [255, 0, 0]
cv2.imwrite("out2.jpg", img)
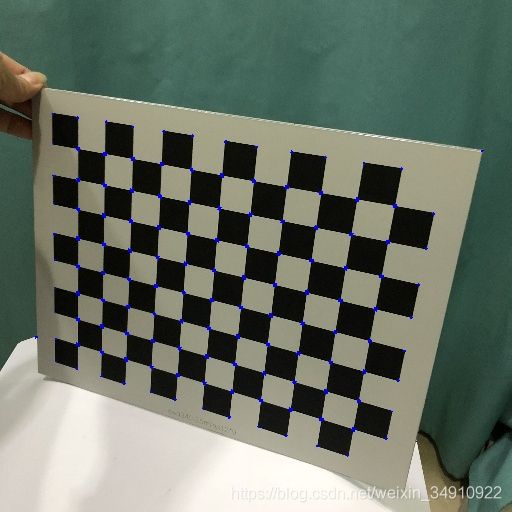
print("proc ok.")结果:
相关链接:
1、harris角点检测原理
2、SHI-TOMASI角点检测
参考文章:
1、python实现Harris角点检测算法(本文代码来源)
https://www.jb51.net/article/201957.htm
2、opencv实现版本python
https://blog.csdn.net/yukinoai/article/details/88759615
3、opencv c++版本实现
https://blog.csdn.net/zhu_hongji/article/details/81235643