增广数据集(labelme)
很多时候训练深度神经网络时都是使用transforms来增强数据,这样做通常原始数据集多大,增强后的数据集就多大,但是有时想扩充一下数据集,让数据量大一点,看到roboflow上增强数据集的效果挺不错的,但是对于国内的朋友来说不太友好,有时需要科学上网,上传数据集大一点的话,可能就会像下载某些小片片一样卡在最后几秒,并且还有自己的数据集泄露的风险。
虽然roboflow增强之后的效果很不错,同时还能看增强后的效果和标注信息,但是这些缺点也很明显,所以本着大家一起进步的思想,我写了个程序,可以根据使用者的需求,在训练之前扩充自己的数据集,代码开源在github上,有兴趣的可以试试,觉得不错的话,还望各位不要吝啬小星星,点个star
这里说一下前提,这个代码主要是对labelme标注后的数据集进行增强,不会污染原始标注数据,新生成的图像和json文件会存放在当前文件夹下的create文件中,可以通过labelme可视化
主体代码如下:
class DataAugmentation(object):
to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()
to_image = transforms.ToPILImage()
def __init__(self):
super(DataAugmentation, self).__init__()
self.transforms = transforms
def resize(self, img, boxes, size):
"""
将图像长和宽缩放到指定值size,并且相应调整boxes
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param size:缩放大小
:return:
"""
w, h = img.size
sw = size / w
sh = size / h
label, boxes = boxes[:, :1], boxes[:, 1:5]
boxes = boxes * torch.Tensor([sw, sh, sw, sh])
boxes = torch.cat((label, boxes), dim=1)
return img.resize((size, size), Image.BILINEAR), boxes
def resize_(self, img, boxes, size):
"""
将图像短边缩放到指定值size,保持原有比例不变,并且相应调整boxes
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param size:缩放大小
:return:
"""
w, h = img.size
# min_size = min(w, h)
# sw = sh = size / min_size
sw = size[0] / w
sh = size[1] / h
ow = int(sw * w + 0.5)
oh = int(sh * h + 0.5)
label, boxes = boxes[:, :1], boxes[:, 1:5]
boxes = boxes * torch.Tensor([sw, sh, sw, sh])
boxes = torch.cat((label, boxes), dim=1)
return img.resize((ow, oh), Image.BILINEAR), boxes
def random_flip_horizon(self, img, boxes):
"""
Horizontally flip the given image randomly with a given probability.
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:return:
"""
p = torch.rand(1)
if p > 0.5:
transform = RandomHorizontalFlip()
img = transform(img)
w = img.width
label, boxes = boxes[:, :1], boxes[:, 1:5]
xmin = w - boxes[:, 2]
xmax = w - boxes[:, 0]
boxes[:, 0] = xmin
boxes[:, 2] = xmax
boxes = torch.cat((label, boxes), dim=1)
return img, boxes
def random_flip_vertical(self, img, boxes):
"""
Vertically flip the given image randomly with a given probability.
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:return:
"""
p = torch.rand(1)
if p > 0.5:
transform = RandomVerticalFlip()
img = transform(img)
h = img.height
label, boxes = boxes[:, :1], boxes[:, 1:5]
ymin = h - boxes[:, 3]
ymax = h - boxes[:, 1]
boxes[:, 1] = ymin
boxes[:, 3] = ymax
boxes = torch.cat((label, boxes), dim=1)
return img, boxes
def center_crop(self, img, boxes, size=(600, 600)):
"""
中心裁剪
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param size: 裁剪大小(w,h)
:return:
"""
w, h = img.size
ow, oh = size
max_size = torch.as_tensor([ow - 1, oh - 1], dtype=torch.float32)
i = int(round((h - oh) / 2.))
j = int(round((w - ow) / 2.))
img = img.crop((j, i, j + ow, i + oh))
label, boxes = boxes[:, :1], boxes[:, 1:5]
boxes = boxes - torch.Tensor([j, i, j, i])
boxes = torch.min(boxes.reshape(-1, 2, 2), max_size)
boxes = boxes.clamp(min=0).reshape(-1, 4)
boxes = torch.cat((label, boxes), dim=1)
return img, boxes
def random_equalize(self, img, boxes, p=0.5):
"""
Equalize the histogram of the given image randomly with a given probability.
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param p:probability of the image being equalized
:return:
"""
transform = self.transforms.RandomEqualize(p=p)
img = transform(img)
return img, boxes
def random_autocontrast(self, img, boxes, p=0.5):
"""
Autocontrast the pixels of the given image randomly with a given probability.
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param p:probability of the image being autocontrasted
:return:
"""
transform = self.transforms.RandomAutocontrast(p=p)
img = transform(img)
return img, boxes
def random_adjustSharpness(self, img, boxes, sharpness_factor=1, p=0.5):
"""
Adjust the sharpness of the image randomly with a given probability.
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param sharpness_factor:How much to adjust the sharpness
:param p:probability of the image being color inverted
:return:
"""
transform = self.transforms.RandomAdjustSharpness(sharpness_factor=sharpness_factor, p=p)
img = transform(img)
return img, boxes
def random_solarize(self, img, boxes, threshold=1, p=0.5):
"""
Solarize the image randomly with a given probability by inverting all pixel values above a threshold.
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param threshold:all pixels equal or above this value are inverted
:param p:probability of the image being color inverted
:return:
"""
transform = self.transforms.RandomSolarize(threshold=threshold, p=p)
img = transform(img)
return img, boxes
def random_posterize(self, img, boxes, bits=0, p=0.5):
"""
Posterize the image randomly with a given probability by reducing the number of bits for each color channel.
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param bits:number of bits to keep for each channel (0-8)
:param p:probability of the image being color inverted
:return:
"""
transform = self.transforms.RandomPosterize(bits=bits, p=p)
img = transform(img)
return img, boxes
def random_grayscale(self, img, boxes, p=0.5):
"""
Randomly convert image to grayscale with a probability of p (default 0.1).
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param p:Grayscale version of the input image with probability p and unchanged with probability (1-p).
:return:
"""
transform = self.transforms.RandomGrayscale(p=p)
img = transform(img)
return img, boxes
def gaussian_blur(self, img, boxes, kernel_size=5, sigma=(0.1, 2.0)):
"""
Blurs image with randomly chosen Gaussian blur.
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param kernel_size:Size of the Gaussian kernel
:param sigma:Standard deviation to be used for creating kernel to perform blurring.
:return:
"""
transform = self.transforms.GaussianBlur(kernel_size=kernel_size, sigma=sigma)
img = transform(img)
return img, boxes
def random_invert(self, img, boxes, p=0.5):
"""
Inverts the colors of the given image randomly with a given probability.
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param p:probability of the image being color inverted
:return:
"""
transform = self.transforms.RandomInvert(p=p)
img = transform(img)
return img, boxes
def random_cutout_(self, img, boxes, p=0.5, scale=(0.02, 0.4), ratio=(0.4, 1 / 0.4), value=(0, 255),
pixel_level=False, inplace=False):
"""
Random erase the given CV Image
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param p:probability that the random erasing operation will be performed
:param scale:range of proportion of erased area against input image
:param ratio:range of aspect ratio of erased area
:param value:erasing value
:param pixel_level:filling one number or not. Default value is False
:param inplace:boolean to make this transform inplace. Default set to False
:return:
"""
transform = Cutout(p=p, scale=scale, ratio=ratio, value=value, pixel_level=pixel_level, inplace=inplace)
img = transform(img)
return img, boxes
def random_cutout(self, img, boxes):
img = np.array(img)
img, boxes = cutout(img, boxes)
img = Image.fromarray(img)
return img, boxes
def random_rotate(self, img, boxes, degrees=5, expand=False, center=None, fill=0, resample=None):
degree = torch.randint(0, degrees + 1, (1,))
degree = degree.item()
transform = self.transforms.RandomRotation(degrees=degree, expand=expand, center=center, fill=fill,
resample=resample)
img = transform(img)
return img, boxes
def random_perspective(self, img, boxes, degrees=10, translate=.1, scale=.1, shear=10, perspective=0.0,
border=(0, 0)):
img = np.array(img)
img, boxes = random_perspective(img, boxes.numpy(), degrees=degrees, translate=translate, scale=scale,
shear=shear, perspective=perspective, border=border)
img = Image.fromarray(img)
return img, torch.from_numpy(boxes)
def random_erasing(self, img, boxes, count=3, scale=0.01, ratio=0.4, value=0, inplace=False):
"""
Randomly selects a rectangle region in an torch Tensor image and erases its pixels.
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param scale:range of proportion of erased area against input image
:param ratio:range of aspect ratio of erased area
:param value:erasing value
:param inplace:boolean to make this transform inplace. Default set to False
:return:
"""
scale = (scale, scale)
ratio = (ratio, 1. / ratio)
if count != 0:
for num in range(count):
transform = RandomErasing(scale=scale, ratio=ratio, value=value, inplace=inplace)
img = transform(self.to_tensor(img))
img = self.to_image(img)
return img, boxes
transform = RandomErasing(scale=scale, ratio=ratio, value=value, inplace=inplace)
img = transform(self.to_tensor(img))
return self.to_image(img), boxes
def random_bright(self, img, boxes, u=32):
"""
随机亮度
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param u:
:return:
"""
img = self.to_tensor(img)
alpha = np.random.uniform(-u, u) / 255
img += alpha
img = img.clamp(min=0.0, max=1.0)
return self.to_image(img), boxes
def random_contrast(self, img, boxes, lower=0.5, upper=1.5):
"""
随机对比度
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param lower:
:param upper:
:return:
"""
img = self.to_tensor(img)
alpha = np.random.uniform(lower, upper)
img *= alpha
img = img.clamp(min=0, max=1.0)
return self.to_image(img), boxes
def random_saturation(self, img, boxes, lower=0.5, upper=1.5):
"""
随机饱和度
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param lower:
:param upper:
:return:
"""
img = self.to_tensor(img)
alpha = np.random.uniform(lower, upper)
img[1] = img[1] * alpha
img[1] = img[1].clamp(min=0, max=1.0)
return self.to_image(img), boxes
def add_gasuss_noise(self, img, boxes, mean=0, std=0.1):
"""
随机高斯噪声
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:param mean:
:param std:
:return:
"""
img = self.to_tensor(img)
noise = torch.normal(mean, std, img.shape)
img += noise
img = img.clamp(min=0, max=1.0)
return self.to_image(img), boxes
def add_salt_noise(self, img, boxes):
"""
随机盐噪声
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:return:
"""
img = self.to_tensor(img)
noise = torch.rand(img.shape)
alpha = np.random.random()
img[noise[:, :, :] > alpha] = 1.0
return self.to_image(img), boxes
def add_pepper_noise(self, img, boxes):
"""
随机椒噪声
:param img: Image
:param boxes: bbox坐标
:return:
"""
img = self.to_tensor(img)
noise = torch.rand(img.shape)
alpha = np.random.random()
img[noise[:, :, :] > alpha] = 0
return self.to_image(img), boxes
def mixup(self, img1, img2, box1, box2, alpha=32.):
"""
mixup
:param img1: Image
:param img2: Image
:param box1: bbox1坐标
:param box2: bbox2坐标
:param alpha:
:return:
"""
p = torch.rand(1)
if p > 0.5:
max_w = max(img1.size[0], img2.size[0])
max_h = max(img1.size[1], img2.size[1])
img1, box1 = self.resize_(img1, box1, (max_w, max_h))
img2, box2 = self.resize_(img2, box2, (max_w, max_h))
img1 = self.to_tensor(img1)
img2 = self.to_tensor(img2)
weight = np.random.beta(alpha, alpha)
miximg = weight * img1 + (1 - weight) * img2
return self.to_image(miximg), torch.cat([box1, box2])
return img1, box1
def mosaic(self, imgpath, cls, imgfile, img_size=640):
p = torch.rand(1)
if p > 0.5:
return load_mosaic(imgpath, cls, imgfile, img_size=img_size)
else:
img = Image.open(imgpath)
jsonpath = '.'.join(imgpath.split('.')[:-1]) + '.json'
return img, load_json_points(jsonpath, cls)
def draw_img(self, img, boxes):
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
for box in boxes:
draw.rectangle(list(box[1:]), outline='yellow', width=2)
img.show()当然这只是代码的一部分,这里将增强方法写成一个类,基本包含了主流的数据增强手段,可以满足大部分日常训练需求
示例:
假设这是目标数据集,将enhance.py文件放在该目录下
先安装requirement中的包,运行enhance.py
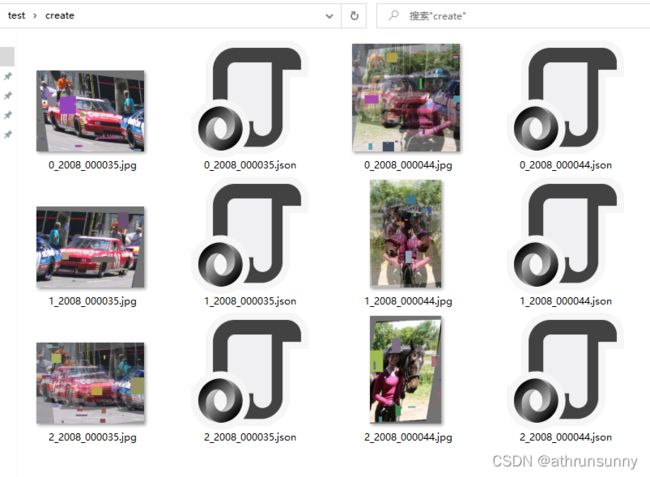
增强的数据会存放在create文件夹中
这里的图片是随便挑了几张voc数据集进行标注,可以看一下增强后的效果
增强之后与原始数据合并,之后就可以根据自己的需要转换成模型输入所需要的数据格式