OpenFOAM自带网格软件——基于snappyHexMesh的圆柱网格画法
0.前言
最近在研究OpenFOAM自带的网格生成软件——snappyHexMesh,并准备拿圆柱绕流算例试试手。主要参考:京东手机的博客和刘楚云知乎的文章。在他们的基础上,学习不同参数对最后网格的影响,并记录下过程。
1.创建圆柱的stl文件
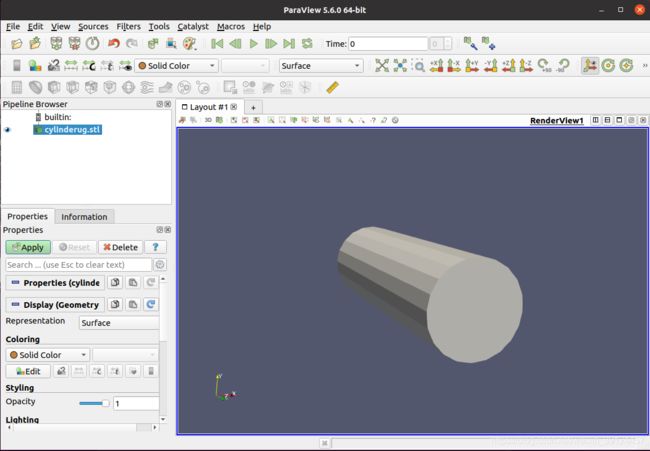
这里用到三维建模软件UG NX6.0。之前用AutoCAD,生成的stl文件的XYZ坐标都会自动拨到正值,这在CFD里是比较麻烦的,所以改用UG。这里忽略画的过程。将stl文件放到OpenFOAM算例的文件夹里,用paraview打开:
2.用AutoSurfacePatch识别不同表面
UG输出的stl文件只带一个表面,所以输入以下指令:
AutoSurfacePatch cylinderug.stl cylinder.stl 130
这里cylinderug.stl是UG输出的stl文件,而后者则是输出的文件。130代表面单元之间超过130度则会被识别成两个面。
输入cat cylinder.stl会看到输出的stl被分成三个patch:
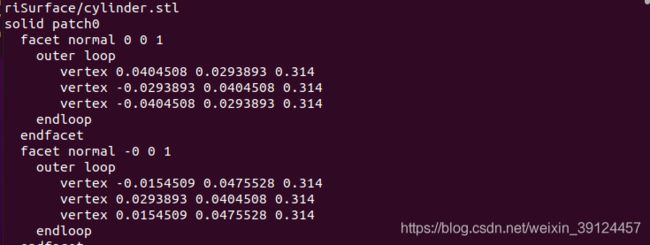


又法向量可知,patch0是顶面,patch1是圆柱的侧面,而patch2则是圆柱的底面。这个信息后面会用到。不同的建模画法可能会导致这些patch的顺序不一样,需要注意。
3.必要文档的准备
在OpenFOAM的tutorials文件夹内搜snappyHexMeshDict即可找到模板,我们稍微修改一下就能用。除此之外还需要meshQualityDict和surfaceFeatureExtractDict两个文档。将3个文档复制到system文件夹中。

4.提取stl的特征
将刚刚得到的cylinder.stl放到constant/triSurface中(没有triSurface就创建一个)。并将system/surfaceFeatureExtractDict中的***.stl改成cylinder.stl,如下:
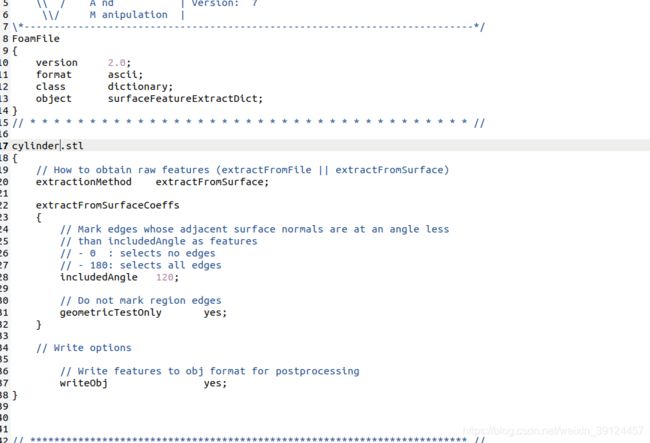
保存退出,然后输入代码:
surfaceFeatureExtract
5.背景网格
用blockMesh画一个背景网格:

需要将圆柱包含在内。这个比较基础就不细讲了。
6.修改snappyhexmeshdict
下面是我修改的snappyHexMeshDict,对一下哪里需要修改:
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
========= |
\\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox
\\ / O peration | Website: https://openfoam.org
\\ / A nd | Version: 7
\\/ M anipulation |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
object snappyHexMeshDict;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
// Which of the steps to run
castellatedMesh true;
snap true;
addLayers true;
// Geometry. Definition of all surfaces. All surfaces are of class
// searchableSurface.
// Surfaces are used
// - to specify refinement for any mesh cell intersecting it
// - to specify refinement for any mesh cell inside/outside/near
// - to 'snap' the mesh boundary to the surface
geometry
{
cylinder.stl
{
type triSurfaceMesh;
name inner_cylinder;
regions
{
patch0 // STL文件中的表面名称
{
name surface0;//z=-0.157 surface
}
patch1
{
name cylinder;// 定义圆柱体侧表面为cylinder,这样其他的文件不用改。
}
patch2
{
name surface2;//z=0.157 surface
}
}
}
//- Refine a bit extra around the small centre hole
refinementBox
{
type searchableBox;
min (-0.2 -0.2 0);
max (1.2 0.2 0.314);
}
};
// Settings for the castellatedMesh generation.
castellatedMeshControls
{
// Refinement parameters
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// If local number of cells is >= maxLocalCells on any processor
// switches from from refinement followed by balancing
// (current method) to (weighted) balancing before refinement.
maxLocalCells 100000;
// Overall cell limit (approximately). Refinement will stop immediately
// upon reaching this number so a refinement level might not complete.
// Note that this is the number of cells before removing the part which
// is not 'visible' from the keepPoint. The final number of cells might
// actually be a lot less.
maxGlobalCells 2000000;
// The surface refinement loop might spend lots of iterations refining just a
// few cells. This setting will cause refinement to stop if <= minimumRefine
// are selected for refinement. Note: it will at least do one iteration
// (unless the number of cells to refine is 0)
minRefinementCells 0;
// Number of buffer layers between different levels.
// 1 means normal 2:1 refinement restriction, larger means slower
// refinement.
nCellsBetweenLevels 2;
// Explicit feature edge refinement
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Specifies a level for any cell intersected by its edges.
// This is a featureEdgeMesh, read from constant/triSurface for now.
features
(
{
file "cylinder.eMesh";
level 0;
}
);
// Surface based refinement
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Specifies two levels for every surface. The first is the minimum level,
// every cell intersecting a surface gets refined up to the minimum level.
// The second level is the maximum level. Cells that 'see' multiple
// intersections where the intersections make an
// angle > resolveFeatureAngle get refined up to the maximum level.
refinementSurfaces//细化表面
{
inner_cylinder//与上面的name对应
{
level (2 2);//表面网格细化的最小和最大等级,即网格被分割的最小和最大次数。
regions//局部细化
{
patch1
{
level (2 4);
patchInfo//patch信息
{
type wall;//类型只能为wall或者patch
}
}
patch0//patch1和patch2在生成外部网格时会被去除,可以不用定义。
{
level (2 2);
patchInfo
{
type patch;
}
}
patch2
{
level (2 2);
patchInfo
{
type patch;
}
}
}
}
}
resolveFeatureAngle 30;
// Region-wise refinement
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Specifies refinement level for cells in relation to a surface. One of
// three modes
// - distance. 'levels' specifies per distance to the surface the
// wanted refinement level. The distances need to be specified in
// descending order.
// - inside. 'levels' is only one entry and only the level is used. All
// cells inside the surface get refined up to the level. The surface
// needs to be closed for this to be possible.
// - outside. Same but cells outside.
refinementRegions
{
refinementBox
{
mode inside;
levels ((1E15 1));
}
}
// Mesh selection
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// After refinement patches get added for all refinementSurfaces and
// all cells intersecting the surfaces get put into these patches. The
// section reachable from the locationInMesh is kept.
// NOTE: This point should never be on a face, always inside a cell, even
// after refinement.
// This is an outside point locationInMesh (-0.033 -0.033 0.0033);
locationInMesh (0.1 0 0.157); // Inside point
// Whether any faceZones (as specified in the refinementSurfaces)
// are only on the boundary of corresponding cellZones or also allow
// free-standing zone faces. Not used if there are no faceZones.
allowFreeStandingZoneFaces true;
}
// Settings for the snapping.
snapControls
{
//- Number of patch smoothing iterations before finding correspondence
// to surface
nSmoothPatch 3;
//- Relative distance for points to be attracted by surface feature point
// or edge. True distance is this factor times local
// maximum edge length.
tolerance 1.0;
//- Number of mesh displacement relaxation iterations.
nSolveIter 300;
//- Maximum number of snapping relaxation iterations. Should stop
// before upon reaching a correct mesh.
nRelaxIter 5;
// Feature snapping
//- Number of feature edge snapping iterations.
// Leave out altogether to disable.
nFeatureSnapIter 10;
//- Detect (geometric) features by sampling the surface
implicitFeatureSnap false;
//- Use castellatedMeshControls::features
explicitFeatureSnap true;
//- Detect features between multiple surfaces
// (only for explicitFeatureSnap, default = false)
multiRegionFeatureSnap true;
}
// Settings for the layer addition.
addLayersControls
{
// Are the thickness parameters below relative to the undistorted
// size of the refined cell outside layer (true) or absolute sizes (false).
relativeSizes true;
// Per final patch (so not geometry!) the layer information
layers
{
"cylinder.*"
{
nSurfaceLayers 3;
}
}
// Expansion factor for layer mesh
expansionRatio 1.0;
// Wanted thickness of final added cell layer. If multiple layers
// is the thickness of the layer furthest away from the wall.
// Relative to undistorted size of cell outside layer.
// See relativeSizes parameter.
finalLayerThickness 0.3;
// Minimum thickness of cell layer. If for any reason layer
// cannot be above minThickness do not add layer.
// See relativeSizes parameter.
minThickness 0.25;
// If points get not extruded do nGrow layers of connected faces that are
// also not grown. This helps convergence of the layer addition process
// close to features.
nGrow 0;
// Advanced settings
// When not to extrude surface. 0 is flat surface, 90 is when two faces
// are perpendicular
featureAngle 30;
// Maximum number of snapping relaxation iterations. Should stop
// before upon reaching a correct mesh.
nRelaxIter 5;
// Number of smoothing iterations of surface normals
nSmoothSurfaceNormals 1;
// Number of smoothing iterations of interior mesh movement direction
nSmoothNormals 3;
// Smooth layer thickness over surface patches
nSmoothThickness 10;
// Stop layer growth on highly warped cells
maxFaceThicknessRatio 0.5;
// Reduce layer growth where ratio thickness to medial
// distance is large
maxThicknessToMedialRatio 0.3;
// Angle used to pick up medial axis points
minMedianAxisAngle 90;
// Create buffer region for new layer terminations
nBufferCellsNoExtrude 0;
// Overall max number of layer addition iterations. The mesher will exit
// if it reaches this number of iterations; possibly with an illegal
// mesh.
nLayerIter 50;
// Max number of iterations after which relaxed meshQuality controls
// get used. Up to nRelaxIter it uses the settings in meshQualityControls,
// after nRelaxIter it uses the values in meshQualityControls::relaxed.
nRelaxedIter 20;
}
// Generic mesh quality settings. At any undoable phase these determine
// where to undo.
meshQualityControls
{
#include "meshQualityDict"
// Optional : some meshing phases allow usage of relaxed rules.
// See e.g. addLayersControls::nRelaxedIter.
relaxed
{
//- Maximum non-orthogonality allowed. Set to 180 to disable.
maxNonOrtho 75;
}
}
// Advanced
// Write flags
writeFlags
(
scalarLevels // write volScalarField with cellLevel for postprocessing
layerSets // write cellSets, faceSets of faces in layer
layerFields // write volScalarField for layer coverage
);
// Merge tolerance. Is fraction of overall bounding box of initial mesh.
// Note: the write tolerance needs to be higher than this.
mergeTolerance 1E-6;
// ************************************************************************* //
最后终端运行:
snappyHexMesh
运行结束后会生成几个时间步的文件夹:
我们打开paraview查看网格:
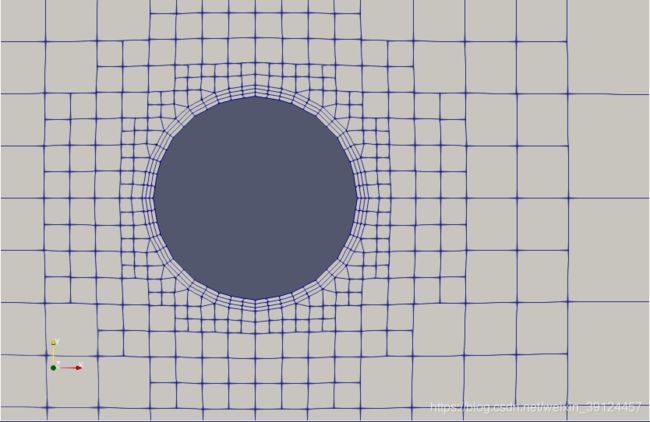
我们在实际计算的时候,将时间步里面的polyMesh文件夹放到constant内,覆盖原来的,就可以参加计算了。
网格质量的好坏决定了仿真结果是否准确有效。在snappyHexMeshDict中有许多需要调节的参数,将在后面的博客中记录。