python 抽样方法
概率和统计的PYTHON(PYTHON FOR PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS)
为什么我们需要采样? (Why do we need Sampling?)
Sampling is used when we try to draw a conclusion without knowing the population. Population refers to the complete collection of observations we want to study, and a sample is a subset of the target population. Here’s an example. A Gallup poll¹, conducted between July 15 to 31 last year, found that 42% of Americans approve of the way Donald Trump is handling his job as president. The results were based on telephone interviews of a random sample of ~4500 calls (assuming one adult per call. ~4500 adults), aged 18 and older, living in the U.S. The poll was conducted during a period of controversy over Trump’s social media comments. For this survey, the population is ALL the U.S citizens aged 18 and older, and the sample is 4500 adults.
当我们尝试在不知道总体的情况下得出结论时,将使用抽样。 人口是指我们要研究的观测资料的完整集合,样本是目标人口的子集。 这是一个例子。 去年7月15日至31日进行的盖洛普民意调查¹发现,有42%的美国人赞成唐纳德·特朗普处理总统职位的方式。 结果基于电话采访,随机抽样了约4500个电话(假设每个电话约一个成年人。约4500个成年人),他们居住在美国,年龄在18岁及以上。该调查是在特朗普社交媒体评论引起争议的一段时间内进行的。 在本次调查中,人口为18岁及以上的所有美国公民,样本为4500名成人。
If sampling is done wrong, it will lead to biases that affect the accuracy of your research/survey results. To avoid selection biases, we have to carefully choose a subset of a population that can be representative of the group as a whole.
如果采样做错了,将导致偏差,从而影响您的研究/调查结果的准确性。 为了避免选择偏见,我们必须仔细选择总体的一个子集 可以代表整个团体。
概率抽样的类型 (Types of Probability Sampling)
简单随机抽样(Simple Random Sampling)
Image by Author using Powerpoint 图片作者使用PowerpointSimple random sampling means we randomly select samples from the population where every unit has the same probability of being selected.
简单随机抽样意味着我们从总体中随机选择样本,每个样本单元都有相同的被选择概率。
Pros: there’s no need to divide the population into subgroups or take any other additional steps before selecting members of the population at random.
优点:在随机选择总体成员之前,无需将总体划分为子组或采取任何其他其他步骤。
Cons: the samples might not be representative, and it could be time-consuming for large populations.
缺点:样本可能不具有代表性,并且对于大量人群可能很耗时。
Use Case: it’s used when we don’t know too much about the population.
用例:当我们对人口不太了解时使用。
#let's create a dataframe first!
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from numpy.random import randn
# Define total number of customers
number_of_customers = 10
# Create data dictionary
data = {'customer_id':np.arange(1, number_of_customers+1).tolist(),
'customer_life_time_value':randn(10)}
# Transform dictionary into a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# View data frame
df#only using random(), we can generate 4 samples from this dataset
# Obtain simple random samplesimple_random_sample = df.sample(n=4).sort_values(by='customer_id')
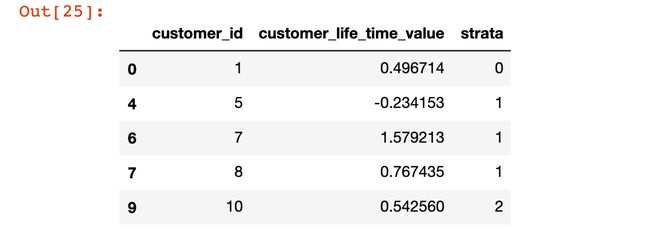
simple_random_sample分层抽样 (Stratified Sampling)
Image by Author using Powerpoint 图片作者使用PowerpointFor stratified sampling the population is divided into subgroups (called strata), then randomly select samples from each stratum.
对于分层抽样,将总体分为子组(称为分层),然后从每个分层中随机选择样本。
Pros: it captures key population characteristics, so the sample is more representative of the population.
优点:它捕获了关键的人口特征,因此样本更能代表人口。
Cons: it’s ineffective if subgroups cannot be formed.
缺点:如果不能形成小组,这是无效的。
Use Case: it’s commonly used in geographic sampling where strata can be states, countries, or ecoregions.
用例:通常用于地层可以是州,国家或生态区的地理采样。
#Let's add subgroup labels to the datasetdf['strata']=[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2]sss = StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=5, test_size=0.5, random_state=0)for x, y in sss.split(df, df['strata']):
stratified_random_sample = df.iloc[y].sort_values(by='customer_id')
stratified_random_sample整群抽样 (Cluster Sampling)
Image by Author using Powerpoint 图片作者使用PowerpointFor clustering sampling, the population is divided into different clusters. Then a fixed number of clusters are randomly sampled and all units within each of the selected clusters are included in the sample.
对于聚类抽样,将总体分为不同的聚类。 然后,对固定数量的聚类进行随机采样,并将每个选定聚类内的所有单元包括在样本中。
Pros: it reduces variability, and it’s easy to conduct.
优点:它减少了可变性,并且易于操作。
Cons: it is possible to introduce bias during sampling.
缺点:在采样过程中可能会引入偏差。
Use Case: it’s used when all individuals in each cluster can be representative of the populations.
用例:当每个群集中的所有个人都可以代表总体时使用。
#create 4 different clusters based on customers' lift time valuesdf['cluster'] = pd.cut(df['customer_life_time_value'], bins=4, labels=False) +1# predefine which clusters/groups we want to select samples fromn=[2,4]def clustering_sampling(df,n):
df_list=[]
for i in range(len(n)):
df1=df[df['cluster']==n[i]]
df_list.append(df1)
final_df=pd.concat(df_list, ignore_index=True)
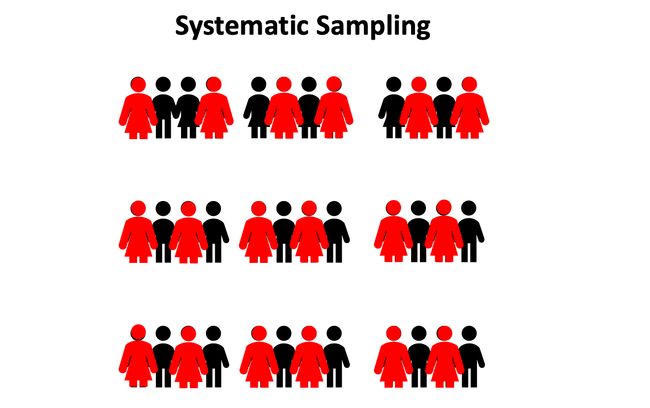
return final_dfclustering_sampling(df,n)系统采样 (Systematic Sampling)
Select every other person from the population (Image by Author using Powerpoint) 从人口中选择其他所有人(作者使用Powerpoint拍摄)A systematic sample is drawn by selecting units systematically from a sample frame. (i.e every other unit is included in the sample)
通过从样本框架中系统选择单位来绘制系统样本。 (即样本中包含其他所有单位)
Pros: it can eliminate clustered selection, and it’s simple to execute.
优点:它可以消除集群选择,并且执行简单。
Cons: we need to predetermine the estimated population size. It doesn’t work well if the population has a type of standardized pattern.
缺点:我们需要预先确定估计的人口规模。 如果总体具有某种标准化模式,则效果不佳。
Use Case: it’s used when the relevant data does not exhibit patterns.
用例:当相关数据不显示模式时使用。
def systematic_sampling(df, step):
indexes = np.arange(0,len(df),step=step)
systematic_sample = df.iloc[indexes]
return systematic_sample
systematic_sampling(df, 1)翻译自: https://towardsdatascience.com/probability-sampling-methods-explained-with-python-4c0a19a59456
python 抽样方法