EfficientNet网络详解并使用pytorch搭建模型
1.EfficientNet网络设计思想
在原论文中,作者通过网络搜索技术同时探索输入分辨率,网络的深度depth、channel的宽度width对准确率的影响,构建EfficientNet网络。
根据以往的经验,增加网络的深度depth能够得到更加丰富、复杂的特征,但网络的深度过深会面临梯度消失,训练困难的问题。
增加网络的width能够获得更高细粒度的特征并且也更容易训练,但对于width很大而深度较浅的网络往往很难学习到更深层次的特征。
增加输入网络的图像分辨率能够潜在得获得更高细粒度的特征模板,但对于非常高的输入分辨率,准确率的增益也会减小,并且大分辨率图像会增加计算量。
而本论文会同时增加网络的width、网络的深度以及输入网络的分辨率来提升网络的性能:
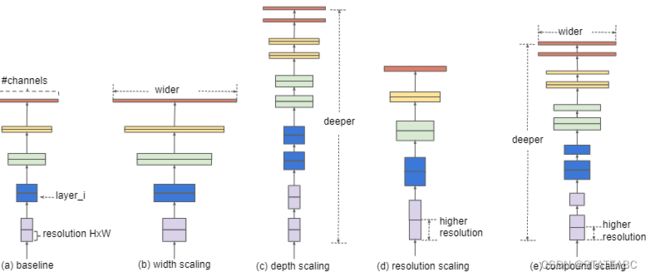
(a)为传统的卷积神经网络
(b)在(a)的基础上增大了特征矩阵的channel(对于每个卷积层使用更多的卷积核
(c.)在(a)的基础上增加了网路网络的深度(增加layer)
(d)在(a)的基础上增加输入图像分辨率,即增加特征矩阵的高和宽
(e)为同时增加网路宽度、深度、输入图像的分辨率。
在EfficientNet模型中,作者使用一组固定的缩放系数统一缩放网络深度、宽度和分辨率。
假设想使用 2N倍的计算资源,可以对网络深度扩大αN倍、宽度扩大βN 、图像尺寸扩大γN倍,这里的α,β,γ都是由原来的小模型上做微小的网格搜索决定的常量系数。
2.EfficientNet网络结构
EfficientNet网络是在EfficientNet-B0的基础上进行不同的调整
EfficientNet-B0 baseline network
分辨率Resolution对应输入每个stage时特征矩阵的高和宽;Channels对应每个stage的输入特征矩阵的channel;Layers为Operator重复的次数;表中的卷积层后默认都跟有BN以及Swish激活函数。
stage1由3x3卷积层组成;
stage2~stage8则是在重复堆叠MBConv,1、6对应1x1卷积层channel的倍率因子;
stage9由1x1卷积层、平均池化层、全连接层组成。
MBConv
与Moblienetv3所使用的block是一样的
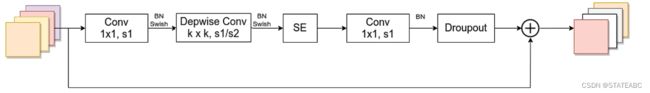
Block是一个结合深度可分离卷积和注意力机制的逆残差结构,每个Block可分为两部分:
主干部分,首先利用1x1卷积升维,再使用3x3或者5x5的逐层卷积进行跨特征点的特征提取,完成特征提取后添加一个通道注意力机制,最后利用1x1卷积降维。
第一个升维的1x1卷积层,卷积核个数是输入特征矩阵channel的n倍;
当n=1时,不要第一个升维的1x1卷积层,即stage2中的MBConv结构都没有第一个升维的1x1卷积层;
残差分支不进行处理。
关于shortcut连接,仅当输入MBConv结构的特征矩阵与输入特征矩阵的shape相同时才存在。
SE模块
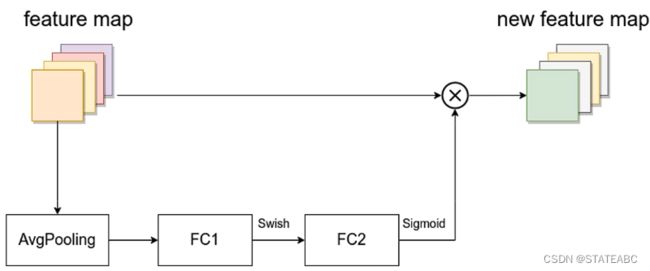
对输入特征矩阵的feature map的每一个channel进行平均池化下采样,通过两个全连接层与原feature map进行乘法操作。
第一个全连接层的节点个数是输入该MBConv特征矩阵channel的1/4,且使用Swish激活函数;
第二个全连接层的节点个数等于Depthwise Conv层输出的特征矩阵channels,且使用Sigmoid激活函数。
注意力机制就是块砖,哪要往哪搬!
EfficientNet-B1~B7
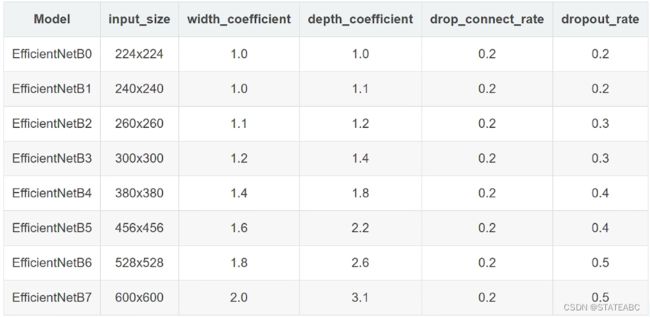
width_coefficient代表Channel维度上的倍率因子,如EfficientNetB0中stage1的3x3卷积层所使用的卷积核个数为32,bane在B6中就是32x1.8=57.6,取整到理它最近的8的整数倍即56,其他stage同理;
depth_corfficient代表depth维度上倍率因子(因针对stage2到stage8),如EfficientNetB0中stage7的L=4,那么在B6中就是4x2.6=10.4,向上取整即11,将stage7的MBConv重复堆叠11次。
drop_connect_rate是在MBConv结构中dropout层使用的drop_rate,在官方keras模块的实现中MBConv结构的drop_rate是从0递增到drop_connect_rate的。还需要注意的是,这里的Dropout层是Stochastic Depth,即会随机丢掉整个block的主分支(只剩捷径分支,相当于直接跳过了这个block)也可以理解为减少了网络的深度。
dropout_rate是最后一个全连接层前的dropout层(在stage9的Pooling与FC之间)的dropout_rate。
EfficientNet网络准确率很高且参数个数很少,但非常占GPU显存。
3.使用Pytorch搭建MobileNetv3网络
卷积+BN+激活函数模块
class ConvBNActivation(nn.Sequential): #卷积+BN+激活函数
def __init__(self,
in_planes: int, #输入特征矩阵channel
out_planes: int, #输出特征矩阵channel
kernel_size: int = 3, #卷积核大小
stride: int = 1, #步距
groups: int = 1, #g=1使用dw卷积,g=2使用普通卷积
norm_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None, #BN结构
activation_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None): #BN结构后的激活函数
padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 #根据kernel_size计算padding
if norm_layer is None: #如果没有传入norm_layer则使用BN
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
if activation_layer is None: #如果没有传入activation_layer则使用SiLU激活函数(和swish激活函数一样)
activation_layer = nn.SiLU # alias Swish (torch>=1.7)
#传入所需要构建的一系列层结构
super(ConvBNActivation, self).__init__(nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_planes, #传入卷积层所需要参数
out_channels=out_planes,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
groups=groups,
bias=False), #使用BN结构则不使用bias
norm_layer(out_planes), #BN结构,传入的参数为上一层的输出channel
activation_layer()) #不传入参数默认使用SiLU激活函数
注意力模块
class SqueezeExcitation(nn.Module): #SE模块
def __init__(self,
input_c: int, # block input channel 对应MBConv输入特征矩阵的channel
expand_c: int, # block expand channel 对应第一个1x1卷积层升维后的channel(dw卷积不改变channel)
squeeze_factor: int = 4): #对应第一个全连接层的节点个数,论文中默认等于4
super(SqueezeExcitation, self).__init__()
squeeze_c = input_c // squeeze_factor #squeeze_c的计算公式
self.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(expand_c, squeeze_c, 1) #构建第一个全连接层
self.ac1 = nn.SiLU() # alias Swish
self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(squeeze_c, expand_c, 1) #构建第二个全连接层
self.ac2 = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor: #前向传播过程
scale = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, output_size=(1, 1)) #对输入进行平均池化
scale = self.fc1(scale)
scale = self.ac1(scale)
scale = self.fc2(scale)
scale = self.ac2(scale)
return scale * x
MBConv模块
class InvertedResidualConfig: #残差结构配置,与mobilenetv3类似
# kernel_size, in_channel, out_channel, exp_ratio, strides, use_SE, drop_connect_rate
def __init__(self,
kernel: int, # 3 or 5
input_c: int,
out_c: int,
expanded_ratio: int, # 1 or 6
stride: int, # 1 or 2
use_se: bool, # True
drop_rate: float,
index: str, # 1a, 2a, 2b, ...
width_coefficient: float):
self.input_c = self.adjust_channels(input_c, width_coefficient)
self.kernel = kernel
self.expanded_c = self.input_c * expanded_ratio
self.out_c = self.adjust_channels(out_c, width_coefficient)
self.use_se = use_se
self.stride = stride
self.drop_rate = drop_rate
self.index = index
@staticmethod
def adjust_channels(channels: int, width_coefficient: float):
return _make_divisible(channels * width_coefficient, 8)
class InvertedResidual(nn.Module): #MBConv模块
def __init__(self,
cnf: InvertedResidualConfig, #残差结构配置
norm_layer: Callable[..., nn.Module]): #BN结构
super(InvertedResidual, self).__init__()
if cnf.stride not in [1, 2]: #判断dw卷积的步长是否在1和2中
raise ValueError("illegal stride value.")
self.use_res_connect = (cnf.stride == 1 and cnf.input_c == cnf.out_c) #根据步长判断是否使用shortcut连接
layers = OrderedDict() #定义有序字典来搭建MBConv结构
activation_layer = nn.SiLU # alias Swish
# expand 搭建第一个1x1卷积层 注意当n=1时不需要第一个1x1卷积层
if cnf.expanded_c != cnf.input_c: #当expanded_c = input_c时n=1,跳过
layers.update({"expand_conv": ConvBNActivation(cnf.input_c, #调用ConvBNActivation并传入相关参数
cnf.expanded_c,
kernel_size=1,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
activation_layer=activation_layer)})
# depthwise 搭建DW卷积
layers.update({"dwconv": ConvBNActivation(cnf.expanded_c, #dw卷积输入和输出特征矩阵的channel不发生变化
cnf.expanded_c,
kernel_size=cnf.kernel,
stride=cnf.stride,
groups=cnf.expanded_c,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
activation_layer=activation_layer)})
if cnf.use_se: #判断是否使用SE模块
layers.update({"se": SqueezeExcitation(cnf.input_c, #这里注意,输入特征矩阵为输入MBConv模块的特征矩阵的channel
cnf.expanded_c)})
# project 搭建最后的1x1卷积层
layers.update({"project_conv": ConvBNActivation(cnf.expanded_c,
cnf.out_c,
kernel_size=1,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
activation_layer=nn.Identity)}) #在最后1x1卷积层后没有激活函数,因此不做任何处理,传入nn.Identity
self.block = nn.Sequential(layers)
self.out_channels = cnf.out_c
self.is_strided = cnf.stride > 1
# 只有在使用shortcut连接时才使用dropout层
if self.use_res_connect and cnf.drop_rate > 0:
self.dropout = DropPath(cnf.drop_rate)
else:
self.dropout = nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
result = self.block(x)
result = self.dropout(result)
if self.use_res_connect:
result += x
return result
实现EfficientNet
class EfficientNet(nn.Module): #实现EfficientNet
def __init__(self,
width_coefficient: float, #网络宽度的倍率因子
depth_coefficient: float, #网络深度的倍率因子
num_classes: int = 1000, #分类的类别个数
dropout_rate: float = 0.2, #MB模块中的dropout的随机失活比例
drop_connect_rate: float = 0.2, #最后一个全连接层的dropout的随机失活比例
block: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None, #MBConv模块
norm_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None #BN结构
):
super(EfficientNet, self).__init__()
# kernel_size, in_channel, out_channel, exp_ratio, strides, use_SE, drop_connect_rate, repeats
default_cnf = [[3, 32, 16, 1, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 1], #以B0构建的默认配置表,stage2~stage8
[3, 16, 24, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 2],
[5, 24, 40, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 2],
[3, 40, 80, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 3],
[5, 80, 112, 6, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 3],
[5, 112, 192, 6, 2, True, drop_connect_rate, 4],
[3, 192, 320, 6, 1, True, drop_connect_rate, 1]]
def round_repeats(repeats): #depth_coefficient * repeats向上取整
"""Round number of repeats based on depth multiplier."""
return int(math.ceil(depth_coefficient * repeats))
if block is None: #如果block为空就默认等于MBConv
block = InvertedResidual
if norm_layer is None: #如果norm_layer为空就默认为BN结构
norm_layer = partial(nn.BatchNorm2d, eps=1e-3, momentum=0.1)
adjust_channels = partial(InvertedResidualConfig.adjust_channels, #对传入的channel乘倍率因子再调整到离它最近的8的整数倍
width_coefficient=width_coefficient)
# build inverted_residual_setting
bneck_conf = partial(InvertedResidualConfig,
width_coefficient=width_coefficient)
b = 0 #统计搭建MBblock的次数
num_blocks = float(sum(round_repeats(i[-1]) for i in default_cnf)) #遍历default_cnf列表获取重复次数
inverted_residual_setting = [] #定义空列表存储MBConv的配置文件
for stage, args in enumerate(default_cnf): #遍历default_cnf列表
cnf = copy.copy(args) #后面会对数据进行修改,为了不影响原数据
for i in range(round_repeats(cnf.pop(-1))): #遍历每个stage中的MBConv模块
if i > 0:
# strides equal 1 except first cnf
cnf[-3] = 1 # strides
cnf[1] = cnf[2] # input_channel equal output_channel
cnf[-1] = args[-2] * b / num_blocks # update dropout ratio
index = str(stage + 1) + chr(i + 97) # 1a, 2a, 2b, ...
inverted_residual_setting.append(bneck_conf(*cnf, index))
b += 1
# create layers
layers = OrderedDict()
# first conv
layers.update({"stem_conv": ConvBNActivation(in_planes=3,
out_planes=adjust_channels(32),
kernel_size=3,
stride=2,
norm_layer=norm_layer)})
# building inverted residual blocks
for cnf in inverted_residual_setting:
layers.update({cnf.index: block(cnf, norm_layer)})
# build top
last_conv_input_c = inverted_residual_setting[-1].out_c
last_conv_output_c = adjust_channels(1280)
layers.update({"top": ConvBNActivation(in_planes=last_conv_input_c,
out_planes=last_conv_output_c,
kernel_size=1,
norm_layer=norm_layer)})
self.features = nn.Sequential(layers)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
classifier = []
if dropout_rate > 0:
classifier.append(nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate, inplace=True))
classifier.append(nn.Linear(last_conv_output_c, num_classes))
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(*classifier)
# initial weights
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode="fan_out")
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.ones_(m.weight)
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
def _forward_impl(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
x = self.features(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
return self._forward_impl(x)
