深入底层,spring mvc父子容器初始化过程解析
spring mvc父子容器初始化过程解析
- 1、为什么要学习spring mvc底层?
- 2、Java Web应该学什么?
-
- 1、Tomcat
- 2、servlet
- 3、filter
- 4、listener
- 3、spring mvc容器初始化过程
-
- 1、以WebApplicationInitializer.onStartup()方法作为入口
- 2、registerDispatcherServlet()解析
- 3、ContextLoaderListener.contextInitialized()方法
- 4、DispatcherServlet.init()方法
- 5、总结
- 4、附录
-
- 1、如何验证Bean只存在于一个容器当中?
- 2、本文参考项目下载
1、为什么要学习spring mvc底层?
在大家学习spring mvc之前,一定要学好Java Web才行,什么是Java Web就不用我多说了吧。想必大家也知道,现在流行使用Spring Boot、Spring Cloud这些框架做开发,为什么流行?就是因为框架本身做了很多工作,去除了大量的配置,在没有复杂业务的情况下,构建一个应用也就是分分钟的事,如果我想在我的应用中集成一些其它框架或组件,没问题,引入一个starter,再做一些少量配置。
然而,当我们遇到复杂业务时,往往需要去阅读框架源码,这时候问题就来了,看得让人根本就摸不着头脑,搞不清哪是哪,分不清头和尾,同时也让人不禁感叹到,原来框架做了这么多的事情啊。有没有想过造成这种现象的原因是什么呢,答案不言而喻,是自身基础太薄弱。
框架做的工作再多,但本质还是不变的。就拿spring boot来说,本质就是各种框架构成的,spring boot只是做了自动配置的工作,它的核心jar包是spring-boot-autoconfigure,里面包含了大量的自动配置类,但真正跑起来的,还是spring-core、spring webmvc、mybatis、spring-data等这些框架。
而本文所要介绍的spring mvc,它的本质是Java Web,虽然使用spring mvc开发时感觉和Java Web毫无关系,但只要是Java Web开发,必然绕不开servlet与servlet容器,毕竟它是Java Web的规范,是绕不开的,只不过spring mvc的职责是用来简化web开发的。简化是简化了,但怎么简化的有没有搞清楚呢?比如以下几个问题,你能回答上来吗:
- spring mvc的请求流程?
- 为什么spring mvc不需要web.xml?
- service能不能注入controller?
- spring mvc父子容器的原理?
- 集成spring session后为什么HttpSessionListener失效了?
- servlet3.0中ServletContainerInitializer接口的作用?spring是怎么利用这个接口初始化DispatcherServlet和spring容器的?
其实本文算是我写的 基于servlet3.0搭建spring mvc应用 无web.xml 无spring boot 这篇文章的升级版,欢迎读者看我之前的这篇文章作为铺垫。
2、Java Web应该学什么?
在分析spring mvc容器初始化过程之前,先把Java Web的知识体系梳理一遍,以及哪些应该学,哪些已经过时。
重点要学的:
- tomcat(servlet容器)
- servlet
- filter
- listener
- session和cookie机制
- ajax
已经过时的:
- jsp
- el
- jstl
- struts2
其它:
- 模板技术(如freemarker):现在都流行前后端分离,可不学
- hibernate:现在比较流行轻量级的mybatis,可不学
1、Tomcat
Tomcat作为servlet容器,它的使命就是加载应用中的servlet、filter和listener等组件,在传统的Java Web应用程序中,这些组件都是需要配置在应用的web.xml中的,但是servlet3.0规范出来之后,应用可以通过实现ServletContainerInitializer接口来注册servlet、filter和listener等组件,这使得我们无需web.xml。
另外,为了简化 Servlet 的配置,Servlet 3.0 中增加了注解支持,例如:@WebServlet、@WebInitParm、@WebFilter和@WebLitener等,这使得除了web.xml和ServletContainerInitializer接口外,还可以通过注解的方式来注册servlet、filter和listener等组件。值得一提的是,ServletContainerInitializer接口实现类以及这些注解是由servlet容器直接扫描的,并不需要声明为Spring的Bean。
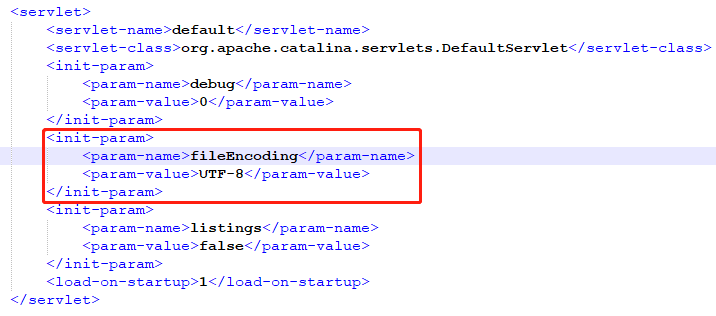
Tomcat静态资源中文乱码问题:
spring mvc有一个核心的DispatcherServlet,而Tomcat也有一个servlet叫DefaultServlet,静态资源一般由DefaultServlet处理而无法到达DispatcherServlet,因此如果在应用中配置了字符编码过滤器,实际上对静态资源请求是不生效的。
我们可以在Tomcat的conf目录下找到web.xml文件,然后搜索DefaultServlet,添加编码配置,如下图所示。
2、servlet
如何编写servlet?
- 实现Servlet接口:需要重写5个方法
- 继承GenericServlet类:只需要重写核心的service方法
- 继承HttpServlet类:针对HTTP协议重写doGet、doPost等方法
由于大部分都是用servlet处理http协议请求,因此继承HttpServlet类最方便。
如何配置servlet?
- web.xml
- 实现ServletContainerInitializer接口
- @webServlet注解
自定义servlet如下代码所示。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebInitParam;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
@WebServlet(
asyncSupported = true,
name = "myServlet",
description = "自定义servlet",
loadOnStartup = 1,
urlPatterns = {"/myservlet"},
initParams = {
@WebInitParam(name = "编程帮", value = "www.biancheng.net", description = "init参数1"),
@WebInitParam(name = "京东", value = "www.jd.com", description = "init参数2")
}
)
@Slf4j
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
log.info("请求到达MyServlet");
log.info("init参数1:{}",getServletConfig().getInitParameter("编程帮"));
log.info("init参数2:{}",getServletConfig().getInitParameter("京东"));
response.setContentType("text/plain");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.write("自定义servlet处理成功");
writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
}
3、filter
核心接口:
- Filter
- FilterConfig
- FilterChain:过滤器传递工具
可通过实现Filter接口来编写一个过滤器,配置过滤器的方式与配置servlet方法类似。
自定义filter如下代码所示。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/*")
@Slf4j
public class MyCharacterEncodingFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
log.info("请求经过MyCharacterEncodingFilter");
((HttpServletRequest)request).setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
((HttpServletResponse)response).setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
4、listener
在servlet技术中已经定义了一些事件,并且可以针对这些事件编写相应的监听器,例如可以在web应用程序启动或关闭时执行一些任务(数据库连接的建立与释放),或监听session的创建与销毁。
自定义session监听器如下代码所示。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionEvent;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener;
@WebListener
@Slf4j
public class MySessionListener implements HttpSessionListener {
@Override
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se) {
log.info("session创建");
}
@Override
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent se) {
log.info("session销毁");
}
}
| Listener接口 | Event类 |
|---|---|
| ServletContextListener | ServletContextEvent |
| ServletContextAttributeListener | ServletContextAttributeEvent |
| HttpSessionListener | HttpSessionEvent |
| HttpSessionActivationListener | HttpSessionEvent |
| HttpSessionAttributeListener | HttpSessionBindingEvent |
| HttpSessionBindingListener | HttpSessionBindingEvent |
| ServletRequestListener | ServletRequestEvent |
| ServletRequestAttributeListener | ServletRequestAttributeEvent |
3、spring mvc容器初始化过程
千呼万唤始出来,犹抱琵琶半遮面!下面开始正式解析spring mvc容器初始化过程。
解析过程将通过DEBUG截图结合源码注释的方式进行。
在 基于servlet3.0搭建spring mvc应用 无web.xml 无spring boot 这篇文章中我已经提到了很关键的一点:
- 在servlet3.0环境中,容器会在类路径中查找实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口的类,如果能发现的话就会用它来配置Servlet容器。Spring提供了这个接口的实现,名为SpringServletContainerInitializer,这个类会查找实现WebApplicationInitializer的类并将配置的任务交给他们来完成,Spring3.2引入了一个便利的WebApplicationInitializer基础实现,就是AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer。
1、以WebApplicationInitializer.onStartup()方法作为入口
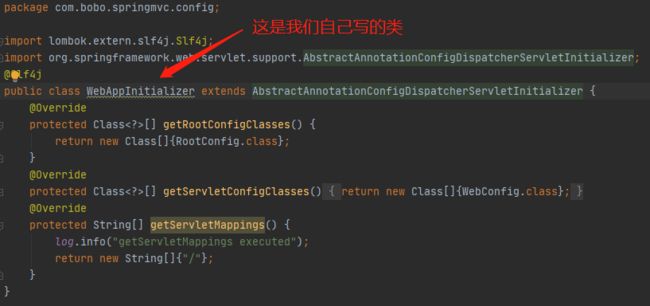
寻找onStartup方法:
SpringServletContainerInitializer会调用WebApplicationInitializer的onStartup方法进行初始化,我们一般在应用中会实现WebApplicationInitializer的子类AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer,如下图所示,如果我们的实现没有重写onStartup方法的话,那么应该先到AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer寻找onStartup方法,但是也没有,因此再找它的父类AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer,此时找到了onStartup方法。
打断点,开始debug:
在AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer的onStartup方法上打断点,并以debug方式启动Tomcat,如下图所示。如果有不会搭建应用或不会在IDEA中配置Tomcat的,就请先看 基于servlet3.0搭建spring mvc应用 无web.xml 无spring boot 这篇文章,或者你们自行搭建,方法多种多样怎么搞都行,我也会将我的项目打成压缩包上传,文末可直接下载。
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
// 注册ContextLoaderListener,是ServletContextListener的子类,主要用于监听servlet上下文初始化事件和销毁事件
// 本文主要分析初始化事件
registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext);
}
registerContextLoaderListener()方法点进去。
protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 创建RootApplicationContext,spring mvc应用实际上有两个ApplicationContext
// 其中一个就是RootApplicationContext,而另一个称为ServletApplicationContext,它们俩是父子关系,即父子容器
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext();
if (rootAppContext != null) {
// new一个ContextLoaderListener,并传入rootAppContext
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
// 向servlet上下文注册ContextLoaderListener
servletContext.addListener(listener);
}
}
上面这段代码接下来重点要分析两个地方:
- 点进createRootApplicationContext()方法查看如何创建RootApplicationContext
- 对ContextLoaderListener的contextInitialized()方法打上断点,servlet上下文初始化时会产生该事件,断点就会进来
先看createRootApplicationContext()方法。
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
// getRootConfigClasses()会调用到我们自己重写的方法
Class<?>[] configClasses = getRootConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
// new一个上下文
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.register(configClasses);
return context;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
RootApplicationContext会根据getRootConfigClasses()来决定将哪些Bean纳入自己的容器中。
顾名思义,RootApplicationContext为根上下文,主要存放的是@service、@Repository、@Component等这些Bean,而下面要讲的ServletRootApplicationContext主要存放的是控制器@Controller、视图解析器等web组件。
根据spring父子容器的特性:子容器可以获取父容器的bean,而反过来不可以,因此spring mvc会将RootApplicationContext设置为ServletRootApplicationContext的父容器,从而导致@Service等组件无法注入@Controller。
由于我重写的getRootConfigClasses()方法返回RootConfig.class,因此下面给出我的RootConfig的示例。
重点是@ComponentScan,如何确保某些组件不被重复扫描
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(
basePackages = {"com.bobo.springmvc"},
excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class, RestController.class}),
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,classes = {WebConfig.class})
}
)
public class RootConfig {
}
由于ContextLoaderListener的contextInitialized()方法是通过事件触发的,因此我们先打上断点即可,接着代码回到AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer.onStartup()方法。
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
// 上面已经介绍过了
super.onStartup(servletContext);
// 注册DispatcherServlet
registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext);
}
2、registerDispatcherServlet()解析
断点进到registerDispatcherServlet()方法里面。
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
String servletName = getServletName();
// 创建ServletApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = createServletApplicationContext();
// 创建DispatcherServlet(其实就是new了一个DispatcherServlet),并传入ServletApplicationContext
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(getServletApplicationContextInitializers());
// 注册DispatcherServlet
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, dispatcherServlet);
if (registration == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to register servlet with name '" + servletName + "'. " +
"Check if there is another servlet registered under the same name.");
}
// 设置servle容器启动时就加载DispatcherServlet
// 这一步是必须的,因为DispatcherServlet的init()方法会做一些重要的事情,这个下面会讲
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping(getServletMappings());
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
Filter[] filters = getServletFilters();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(filters)) {
for (Filter filter : filters) {
registerServletFilter(servletContext, filter);
}
}
customizeRegistration(registration);
}
上面这段代码接下来重点要分析两个地方:
- 点进createServletApplicationContext()方法查看如何创建ServletApplicationContext
- DispatcherServlet的init()方法
createServletApplicationContext()方法如下所示。
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
// new一个上下文
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
// getServletConfigClasses()会调用到我们自己重写的方法
Class<?>[] configClasses = getServletConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
context.register(configClasses);
}
return context;
}
由于我重写的getServletConfigClasses()方法返回WebConfig.class,因此下面给出我的WebConfig的示例。
重点是@ComponentScan,如何确保某些组件不被重复扫描
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan(
basePackages = {"com.bobo.springmvc"},
includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class, RestController.class})
},
useDefaultFilters = false
)
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver(){
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
resolver.setSuffix(".html");
resolver.setExposeContextBeansAsAttributes(true);
return resolver;
}
/**
* 配置静态资源的处理.将静态资源的请求转发到servlet容器中的默认servlet,而不是让DispathcerServlet去处理
*/
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
}
介绍到这里,总结一下,也就是AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer的onStartup()方法就跑完了,另外两个重要的初始化分别是ContextLoaderListener的contextInitialized()和DispatcherServlet的init(),这两个分别由servlet容器初始化事件和DispatcherServlet初始化事件触发的,因此我们分别打上断点,下面继续。
3、ContextLoaderListener.contextInitialized()方法
断点进入到contextInitialized()方法,标志着servlet上下文已经初始化,到如下图所示。
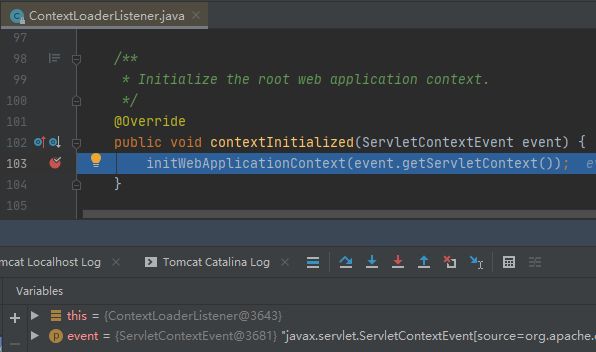
点进去之后,如下图所示。
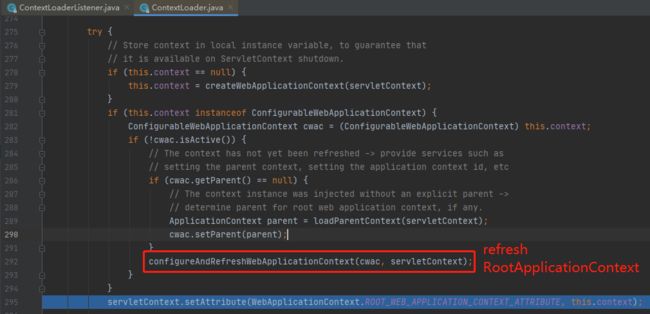
核心代码就是刷新上下文了,还记得上面在new ContextLoaderListener()的时候,构造器传的是RootApplicationContext,因此ContextLoaderListener是用来加载RootApplicationContext的。然后刷新上下文就是Spring IOC容器内部的逻辑了,与Spring MVC无关。
4、DispatcherServlet.init()方法
其实DispatcherServlet并未直接实现Servlet接口的init()方法,而是它的父类GenericServlet实现的,如下所示。
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
this.init();
}
GenericServlet的子类,也是DispatcherServlet的父类HttpServletBean实现了无参的init()方法,如下所示。
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
initServletBean();
}
然后就是HttpServletBean的子类,DispatcherServlet的父类FrameworkServlet实现了initServletBean()方法,如下所示。
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
// 删了很多代码,只留下这两行核心代码
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
// 暂无实现
initFrameworkServlet();
}
点进initWebApplicationContext()方法。
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 获取RootApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// 上面在new DispatherServlet的时候,构造器传入了ServletApplicationContext,也就是这里的this.webApplicationContext
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// 设置spring mvc父子容器的关系的源码就在这里,可以看到RootApplicationContext是父
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
// 刷新ServletApplicationContext,是Spring IOC容器的逻辑,与Spring MVC无关
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
return wac;
}
5、总结
以下是对各个组件主要职责的总结:
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer:
- 根据RootConfig创建了一个上下文:RootApplicationContext
- 向ServletContext注册了ContextLoaderListener,传入了RootApplicationContext
- 根据ServletConfig创建了一个上下文:ServletApplicationContext
- 向ServletContext注册了DispatcherServlet,传入了ServletApplicationContext
ContextLoadListener:
- 刷新RootApplicationContext:refresh
DispatcherServlet:
- 执行Servlet.init()->FrameworkServlet.initServletBean()方法
- 设置parent:ServletApplicationContext.setParent(RootApplicationContext)
- 刷新ServletApplicationContext:refresh
spring mvc容器初始化过程就解析到这里了,怎么样,还是学到了不少东西的吧。
4、附录
1、如何验证Bean只存在于一个容器当中?
由于Spring MVC父子容器的存在,无疑增加了复杂性,有时候会有这样一个问题:某个Bean既存在于父容器,又存在于子容器,这不仅浪费了内存,还有可能造成程序逻辑错误。
就拿控制器Controller来说,我们希望它只存在于子容器,如何验证呢?可以通过实现ApplicationContextAware接口,如下代码所示。
import com.bobo.springmvc.service.ChatService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
@Controller
@Slf4j
public class ChatController implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Autowired
private ChatService chatService;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET,value = "/toChat")
public String toChat(HttpServletRequest request){
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
String sessionId = session.getId();
if(null == session.getAttribute("viewCount")){
session.setAttribute("viewCount",1);
}else{
session.setAttribute("viewCount",((int)(session.getAttribute("viewCount")))+1);
}
log.info("请求到达ChatController.toChat方法,sessionId:{},viewCount:{}",sessionId,session.getAttribute("viewCount"));
chatService.doChat(request);
return "chat";
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
log.info("ChatController,applicationContext:{},parent:{}",applicationContext,applicationContext.getParent());
}
}
在setApplicationContext方法中打印了日志,如果控制台打印了多次,则说明ChatController被多个容器初始化了,这显然是不对的。
如何保证只存在于一个容器呢?这就要合理使用组件扫描@ComponentScan啦,可以参照上面RootConfig和WebConfig的代码。
2、本文参考项目下载
完完全全是一个spring mvc项目,无spring boot,无web.xml、spring.xml。
spring mvc项目