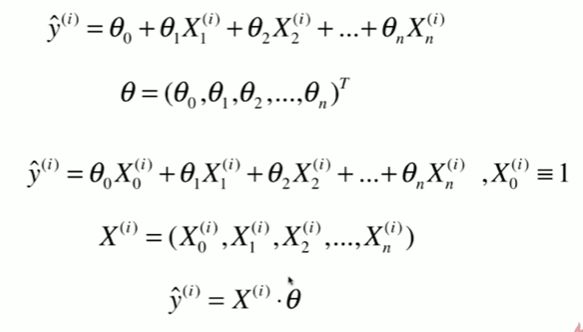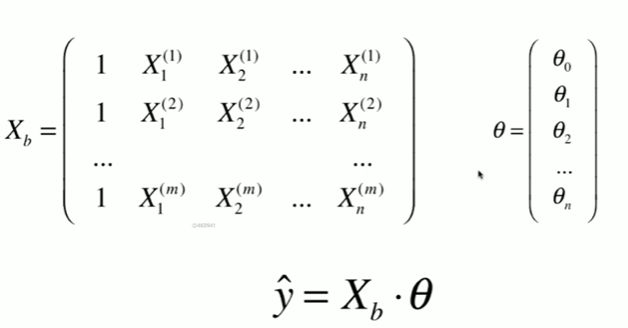第5章下 多元线性回归法
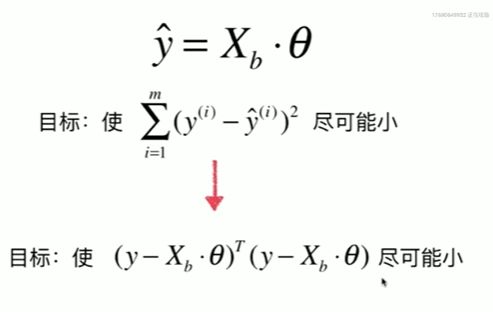
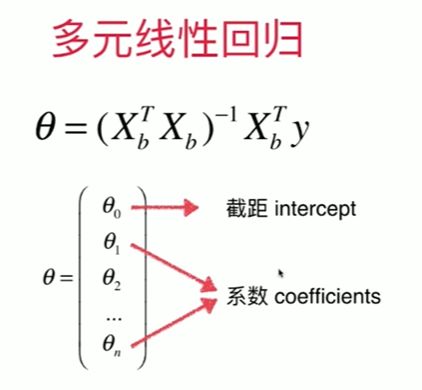
5-7 多元线性回归和正规方程解
5-8 实现多元线性回归
Notbook 示例
Notbook 源码
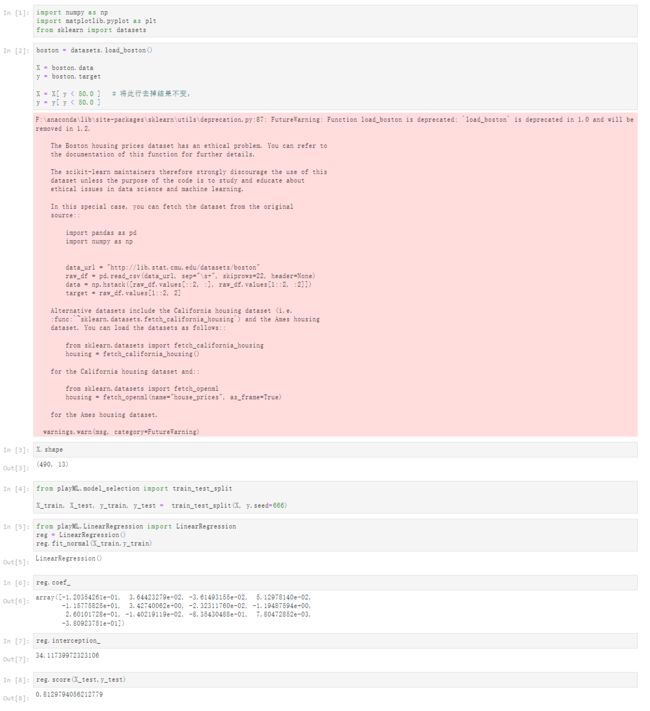
[1]
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
[2]
boston = datasets.load_boston()
X = boston.data
y = boston.target
X = X[ y < 50.0 ] # 将此行去掉结果不变,
y = y[ y < 50.0 ]
F:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\deprecation.py:87: FutureWarning: Function load_boston is deprecated; `load_boston` is deprecated in 1.0 and will be removed in 1.2.
The Boston housing prices dataset has an ethical problem. You can refer to
the documentation of this function for further details.
The scikit-learn maintainers therefore strongly discourage the use of this
dataset unless the purpose of the code is to study and educate about
ethical issues in data science and machine learning.
In this special case, you can fetch the dataset from the original
source::
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data_url = "http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/datasets/boston"
raw_df = pd.read_csv(data_url, sep="\s+", skiprows=22, header=None)
data = np.hstack([raw_df.values[::2, :], raw_df.values[1::2, :2]])
target = raw_df.values[1::2, 2]
Alternative datasets include the California housing dataset (i.e.
:func:`~sklearn.datasets.fetch_california_housing`) and the Ames housing
dataset. You can load the datasets as follows::
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
housing = fetch_california_housing()
for the California housing dataset and::
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
housing = fetch_openml(name="house_prices", as_frame=True)
for the Ames housing dataset.
warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning)
[3]
X.shape
(490, 13)
[4]
from playML.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y,seed=666)
[5]
from playML.LinearRegression import LinearRegression
reg = LinearRegression()
reg.fit_normal(X_train,y_train)
LinearRegression()
[6]
reg.coef_
array([-1.20354261e-01, 3.64423279e-02, -3.61493155e-02, 5.12978140e-02,
-1.15775825e+01, 3.42740062e+00, -2.32311760e-02, -1.19487594e+00,
2.60101728e-01, -1.40219119e-02, -8.35430488e-01, 7.80472852e-03,
-3.80923751e-01])
[7]
reg.interception_
34.11739972323106
[8]
reg.score(X_test,y_test)
0.81297940562127795-9 使用scikit-learn解决回归问题
Notbook 示例
Notbook 源码
Scikit-learn 中的回归问题
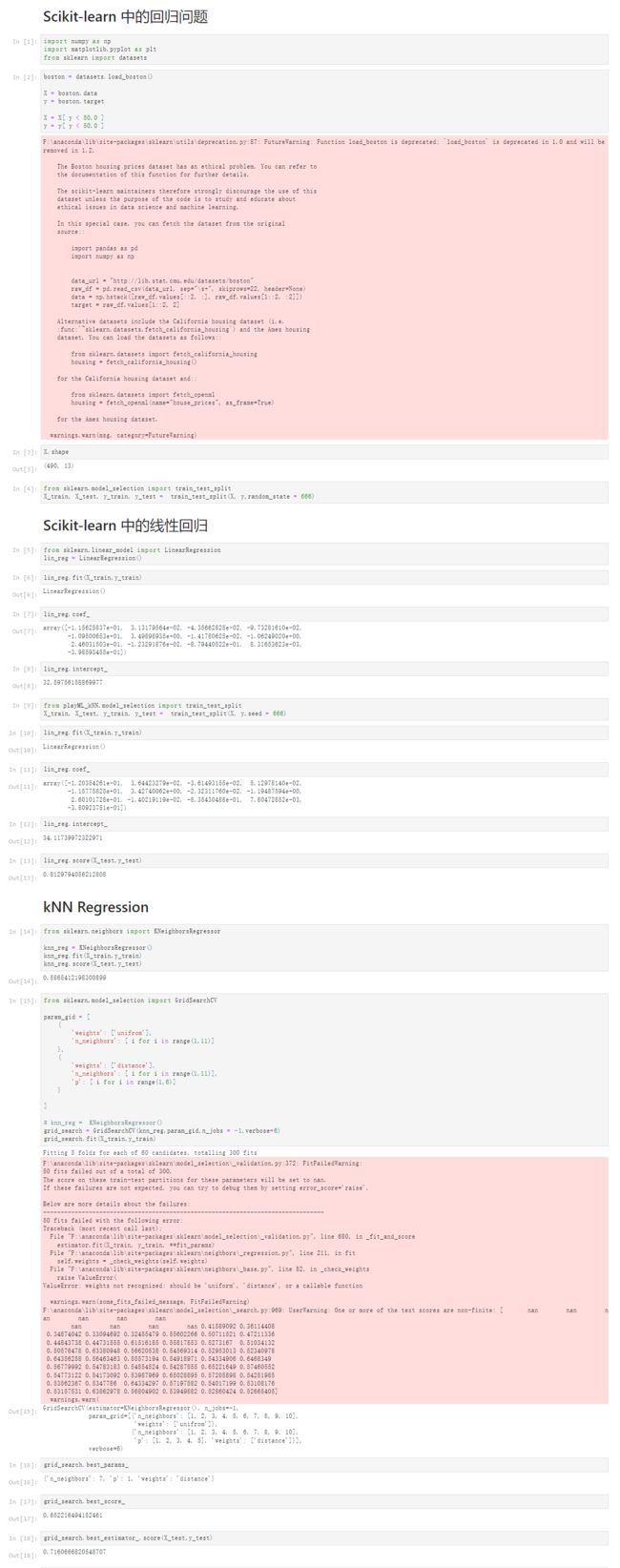
[1]
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
[2]
boston = datasets.load_boston()
X = boston.data
y = boston.target
X = X[ y < 50.0 ]
y = y[ y < 50.0 ]
F:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\deprecation.py:87: FutureWarning: Function load_boston is deprecated; `load_boston` is deprecated in 1.0 and will be removed in 1.2.
The Boston housing prices dataset has an ethical problem. You can refer to
the documentation of this function for further details.
The scikit-learn maintainers therefore strongly discourage the use of this
dataset unless the purpose of the code is to study and educate about
ethical issues in data science and machine learning.
In this special case, you can fetch the dataset from the original
source::
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data_url = "http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/datasets/boston"
raw_df = pd.read_csv(data_url, sep="\s+", skiprows=22, header=None)
data = np.hstack([raw_df.values[::2, :], raw_df.values[1::2, :2]])
target = raw_df.values[1::2, 2]
Alternative datasets include the California housing dataset (i.e.
:func:`~sklearn.datasets.fetch_california_housing`) and the Ames housing
dataset. You can load the datasets as follows::
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
housing = fetch_california_housing()
for the California housing dataset and::
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
housing = fetch_openml(name="house_prices", as_frame=True)
for the Ames housing dataset.
warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning)
[3]
X.shape
(490, 13)
[4]
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y,random_state = 666)
Scikit-learn 中的线性回归
[5]
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
lin_reg = LinearRegression()
[6]
lin_reg.fit(X_train,y_train)
LinearRegression()
[7]
lin_reg.coef_
array([-1.15625837e-01, 3.13179564e-02, -4.35662825e-02, -9.73281610e-02,
-1.09500653e+01, 3.49898935e+00, -1.41780625e-02, -1.06249020e+00,
2.46031503e-01, -1.23291876e-02, -8.79440522e-01, 8.31653623e-03,
-3.98593455e-01])
[8]
lin_reg.intercept_
32.59756158869977
[9]
from playML_kNN.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y,seed = 666)
[10]
lin_reg.fit(X_train,y_train)
LinearRegression()
[11]
lin_reg.coef_
array([-1.20354261e-01, 3.64423279e-02, -3.61493155e-02, 5.12978140e-02,
-1.15775825e+01, 3.42740062e+00, -2.32311760e-02, -1.19487594e+00,
2.60101728e-01, -1.40219119e-02, -8.35430488e-01, 7.80472852e-03,
-3.80923751e-01])
[12]
lin_reg.intercept_
34.11739972322971
[13]
lin_reg.score(X_test,y_test)
0.8129794056212808
kNN Regression
[14]
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressor
knn_reg = KNeighborsRegressor()
knn_reg.fit(X_train,y_train)
knn_reg.score(X_test,y_test)
0.5865412198300899
[15]
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
param_gid = [
{
'weights': ['unifrom'],
'n_neighbors': [ i for i in range(1,11)]
},
{
'weights': ['distance'],
'n_neighbors': [ i for i in range(1,11)],
'p': [ i for i in range(1,6)]
}
]
# knn_reg = KNeighborsRegressor()
grid_search = GridSearchCV(knn_reg,param_gid,n_jobs = -1,verbose=6)
grid_search.fit(X_train,y_train)
Fitting 5 folds for each of 60 candidates, totalling 300 fits
F:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\sklearn\model_selection\_validation.py:372: FitFailedWarning:
50 fits failed out of a total of 300.
The score on these train-test partitions for these parameters will be set to nan.
If these failures are not expected, you can try to debug them by setting error_score='raise'.
Below are more details about the failures:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
50 fits failed with the following error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "F:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\sklearn\model_selection\_validation.py", line 680, in _fit_and_score
estimator.fit(X_train, y_train, **fit_params)
File "F:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\sklearn\neighbors\_regression.py", line 211, in fit
self.weights = _check_weights(self.weights)
File "F:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\sklearn\neighbors\_base.py", line 82, in _check_weights
raise ValueError(
ValueError: weights not recognized: should be 'uniform', 'distance', or a callable function
warnings.warn(some_fits_failed_message, FitFailedWarning)
F:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\sklearn\model_selection\_search.py:969: UserWarning: One or more of the test scores are non-finite: [ nan nan nan nan nan nan
nan nan nan nan 0.41589092 0.36114408
0.34874042 0.33094692 0.32455479 0.55602266 0.50711521 0.47211336
0.44843738 0.44731555 0.61516185 0.55817853 0.5273167 0.51034132
0.50576478 0.63380948 0.56620538 0.54569314 0.52953013 0.52340978
0.64356258 0.56463463 0.55573194 0.54918971 0.54334906 0.6468349
0.56779992 0.54783183 0.54854524 0.54287855 0.65221649 0.57460552
0.54773122 0.54173092 0.53987969 0.65028895 0.57205898 0.54251985
0.53562367 0.5347786 0.64334297 0.57197582 0.54017199 0.53108176
0.53157531 0.63862978 0.56804902 0.53949882 0.52860424 0.52665405]
warnings.warn(
GridSearchCV(estimator=KNeighborsRegressor(), n_jobs=-1,
param_grid=[{'n_neighbors': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
'weights': ['unifrom']},
{'n_neighbors': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
'p': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], 'weights': ['distance']}],
verbose=6)
[16]
grid_search.best_params_
{'n_neighbors': 7, 'p': 1, 'weights': 'distance'}
[17]
grid_search.best_score_
0.652216494152461
[18]
grid_search.best_estimator_.score(X_test,y_test)
0.71606668205487075-10 线性回归的可解性和更多思考
Notbook 示例
Notbook 源码
更多关于线性回归模型的讨论
[1]
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
[2]
boston = datasets.load_boston()
X = boston.data
y = boston.target
X = X[ y < 50.0 ]
y = y[ y < 50.0 ]
F:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\deprecation.py:87: FutureWarning: Function load_boston is deprecated; `load_boston` is deprecated in 1.0 and will be removed in 1.2.
The Boston housing prices dataset has an ethical problem. You can refer to
the documentation of this function for further details.
The scikit-learn maintainers therefore strongly discourage the use of this
dataset unless the purpose of the code is to study and educate about
ethical issues in data science and machine learning.
In this special case, you can fetch the dataset from the original
source::
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data_url = "http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/datasets/boston"
raw_df = pd.read_csv(data_url, sep="\s+", skiprows=22, header=None)
data = np.hstack([raw_df.values[::2, :], raw_df.values[1::2, :2]])
target = raw_df.values[1::2, 2]
Alternative datasets include the California housing dataset (i.e.
:func:`~sklearn.datasets.fetch_california_housing`) and the Ames housing
dataset. You can load the datasets as follows::
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
housing = fetch_california_housing()
for the California housing dataset and::
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
housing = fetch_openml(name="house_prices", as_frame=True)
for the Ames housing dataset.
warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning)
[4]
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
lin_reg = LinearRegression()
lin_reg.fit(X,y)
LinearRegression()
[5]
lin_reg.coef_
array([-1.06715912e-01, 3.53133180e-02, -4.38830943e-02, 4.52209315e-01,
-1.23981083e+01, 3.75945346e+00, -2.36790549e-02, -1.21096549e+00,
2.51301879e-01, -1.37774382e-02, -8.38180086e-01, 7.85316354e-03,
-3.50107918e-01])
[6]
np.argsort(lin_reg.coef_)
array([ 4, 7, 10, 12, 0, 2, 6, 9, 11, 1, 8, 3, 5], dtype=int64)
[7]
boston.feature_names
array(['CRIM', 'ZN', 'INDUS', 'CHAS', 'NOX', 'RM', 'AGE', 'DIS', 'RAD',
'TAX', 'PTRATIO', 'B', 'LSTAT'], dtype='