BMP文件转换为YUV文件
实验要求
-
将RGB文件转换为YUV文件
-
将BMP文件(加入自己的水印)转换为YUV文件,并且最终的YUV文件包含200帧,能使用YUV播放器观看
实验流程分析
1.程序初始化(打开两个文件、定义变量和缓冲区等)
2.读取BMP文件,抽取或生成RGB数据写入缓冲区
- 读位图文件头:判断是否可读出 / 判断是否是BMP文件
- 读位图信息头(判断是否读出)
- 判断像素的实际点阵数
- 开辟缓冲区,读数据,倒序存放
- 根据每像素位数的不同,执行不同的操作
8bit以下:构造调色板,位与移位取像素数据查调色板写RGB缓冲区
16bit:位与移位取像素数据转换为8bit/彩色分量写RGB缓冲区
24/32bit:直接取像素数据写RGB缓冲区
3.调用RGB2YUV的函数实现RGB到YUV数据的转换
4.写YUV文件
5.程序收尾工作(关闭文件,释放缓冲区)
实验原理
BMP文件格式
位图文件(Bitmap-File,BMP)格式是Windows采用的图像文件存储格式,在Windows环境下运行的所有图像处理软件都支持这种格式。BMP位图文件默认的文件扩展名是bmp或者dib。
| 位图文件头BITMAPFILEHEADER |
| 位图信息头BITMAPINFOHEADER |
| 调色板Palette |
| 实际的位图数据ImageData |
位图文件头BITMAPFILEHEADER
包含BMP图像文件的类型、显示内容等信息 。
typedef struct tagBITMAPFILEHEADER {
WORD bfType; /* 说明文件的类型*/
DWORD bfSize; /* 说明文件的大小,用字节为单位*//*注意此处的字节序问题
WORD bfReserved1; /* 保留,设置为0 */
WORD bfReserved2; /* 保留,设置为0 */
DWORD bfOffBits; /* 说明从BITMAPFILEHEADER结构开始到实际的图像数据之间的字节偏移量*/
} BITMAPFILEHEADER;
位图信息头BITMAPINFOHEADER
它包含有BMP图像的宽、高、压缩方法,以及定义颜色等信息。
typedef struct tagBITMAPINFOHEADER {
DWORD biSize; /* 说明结构体所需字节数*/
LONG biWidth; /* 以像素为单位说明图像的宽度*/
LONG biHeight; /* 以像素为单位说明图像的高速*/
WORD biPlanes; /* 说明位面数,必须为1 */
WORD biBitCount; /* 说明位数/像素,1、2、4、8、24 */
DWORD biCompression; /* 说明图像是否压缩及压缩类型BI_RGB,BI_RLE8,BI_RLE4,BI_BITFIELDS */
DWORD biSizeImage; /* 以字节为单位说明图像大小,必须是4的整数倍*/
LONG biXPelsPerMeter; /*目标设备的水平分辨率,像素/米*/
LONG biYPelsPerMeter; /*目标设备的垂直分辨率,像素/米*/
DWORD biClrUsed; /* 说明图像实际用到的颜色数,如果为0,则颜色数为2的biBitCount次方*/
DWORD biClrImportant; /*说明对图像显示有重要影响的颜色索引的数目,如果是0,表示都重要。*/
} BITMAPINFOHEADER;调色板Palette
实际上是一个数组,它所包含的元素与位图所具有的颜色数相同,决定于biClrUsed和biBitCount字段。数组中每个元素的类型是一个RGBQUAD结构。真彩色无调色板部分。
这个部分是可选的,有些位图需要调色板,有些位图,比如真彩色图(24位的BMP)就不需要调色板。
typedef struct tagRGBQUAD {
BYTE rgbBlue; /*指定蓝色分量*/
BYTE rgbGreen; /*指定绿色分量*/
BYTE rgbRed; /*指定红色分量*/
BYTE rgbReserved; /*保留,指定为0*/
} RGBQUAD;位图数据
这部分的内容根据BMP位图使用的位数不同而不同,在24位图中直接使用RGB,而其他的小于24 位的使用调色板中颜色索引值。
紧跟在调色板之后的是图像数据字节阵列。对于用到调色板的位图,图像数据就是该像素颜色在调色板中的索引值(逻辑色)。对于真彩色图,图像数据就是实际的R、G、B值。图像的每一扫描行由表示图像像素的连续的字节组成,每一行的字节数取决于图像的颜色数目和用像素表示的图像宽度。规定每一扫描行的字节数必须是4的整倍数,也就是DWORD对齐的。扫描行是由底向上存储的,这就是说,阵列中的第一个字节表示位图左下角的像素,而最后一个字节表示位图右上角的像素。
字节序
不同的计算机系统采用不同的字节序存储数据,同样一个4字节的32位整数,在内存中存储的方式不同。字节序分为小尾字节序(Little Endian)和大尾字节序(Big Endian)。Intel处理器大多数使用小尾字节序,Motorola处理器大多数使用大尾(Big Endian)字节序。
小尾就是低位字节排放在内存的低端,高位字节排放在内存的高端,即所谓的“低位在前,高位在后”。大尾就是高位字节排放在内存的低端,低位字节排放在内存的高端,即所谓的“高位在前,低位在后”。TCP/IP各层协议将字节序定义为大尾,因此TCP/IP协议中使用的字节序通常称之为网络字节序。
在实现BMP文件头信息的写入和读出时,需要注意整数保存时的字节序。例如:文件大小是以Intel序保存的。在编程前先用二进制打开方式观察BMP文件各个部分的数据存储格式。
RGB和YUV的转换
RGB图像存储:444格式,按照BGRBGR存储
YUV图像存储:420格式,这种取样格式表示色差信号U和V的取样点数在水平和垂直方向上均为Y的1/2,存储时先存储Y分量,再存储U、V分量
转换公式:
![]()
![]()
![]()
实验过程
本次实验选取5个BMP文件,各重复40次,共200帧。
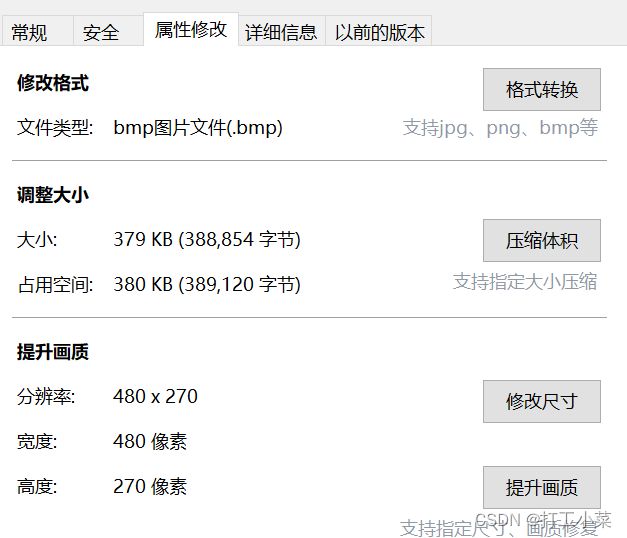
查看图像属性格式
程序
命令行参数
头文件
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int rgb2yuv(int width, int heigth, unsigned char* rgb, unsigned char* y, unsigned char* u, unsigned char* v);
void InitLookupTable(); 主函数
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include"head.h"
using namespace std;
int main(char argc, char* argv[])
{
BITMAPFILEHEADER File_header;
BITMAPINFOHEADER Info_header;
FILE* bmpFile = NULL;
FILE* yuvFile = NULL;
yuvFile = fopen(argv[6], "wb");
for (int n = 1; n < 6; n++)
{
bmpFile = fopen(argv[n], "rb");
if (bmpFile == NULL)
{
cout <<< "bmp文件打开失败" << endl;
return 0;
}
fread(&File_header, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), 1, bmpFile);
fread(&Info_header, sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER), 1, bmpFile);
if (File_header.bfType != 0x4D42) {
cout << n << "文件不是bmp格式" << endl;
return 0;
}
int width, height, w, h;
if (((Info_header.biWidth / 8 * Info_header.biBitCount) % 4) == 0)
w = Info_header.biWidth;
else
w = (Info_header.biWidth * Info_header.biBitCount + 31) / 32 * 4;
if ((Info_header.biHeight % 2) == 0)
h = Info_header.biHeight;
else
h = Info_header.biHeight + 1;
width = w / 8 * Info_header.biBitCount;
height = h;
unsigned char* bmp_rgb = (unsigned char*)malloc(width * height);
unsigned char* rgb = (unsigned char*)malloc(width * height);
fseek(bmpFile, File_header.bfOffBits, 0);
if (fread(bmp_rgb, width * height, 1, bmpFile) == 0)
{
printf("read file error!\n\n");
return 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
rgb[i * width + j] = bmp_rgb[(height - i - 1) * width + j];
}
}
free(bmp_rgb);
unsigned char* y = new unsigned char[height * width];
unsigned char* u = new unsigned char[height * width / 4];
unsigned char* v = new unsigned char[height * width / 4];
rgb2yuv(w, h, rgb, y, u, v);
int time = atoi(argv[n + 6]);
for (int count = 0; count < time; count++)
{
fwrite(y, 1, w * h, yuvFile);
fwrite(u, 1, w * h / 4, yuvFile);
fwrite(v, 1, w * h / 4, yuvFile);
}
free(rgb);
fclose(bmpFile);
}
fclose(yuvFile);
}
rgb2yuv
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "head.h"
static float RGBYUV02990[256], RGBYUV05870[256], RGBYUV01140[256];
static float RGBYUV01684[256], RGBYUV03316[256], RGBYUV05000[256];
static float RGBYUV04187[256], RGBYUV00813[256];
int rgb2yuv(int width, int height, unsigned char* rgb, unsigned char* y, unsigned char* u, unsigned char* v)
{
InitLookupTable();
unsigned char* u_temp = (unsigned char*)malloc(width * height * sizeof(unsigned char));
unsigned char* v_temp = (unsigned char*)malloc(width * height * sizeof(unsigned char));
unsigned long b, g, r, count;
count = 0;
for (unsigned long i = 0; i < width * height * 3; i += 3)
{
b = unsigned long(rgb[i]);
g = unsigned long(rgb[i + 1]);
r = unsigned long(rgb[i + 2]);
y[count] = (unsigned char)(RGBYUV02990[r] + RGBYUV05870[g] + RGBYUV01140[b]);
u_temp[count] = (unsigned char)(-RGBYUV01684[r] - RGBYUV03316[g] + RGBYUV05000[b] + 128);
v_temp[count] = (unsigned char)(RGBYUV05000[r] - RGBYUV04187[g] - RGBYUV00813[b] + 128);
count++;
}
int k = 0;
for (unsigned long i = 0; i < height; i += 2)
{
for (unsigned long j = 0; j < width; j += 2)
{
u[k] = (u_temp[i * width + j] + u_temp[(i + 1) * width + j] + u_temp[i * width + j + 1] + u_temp[(i + 1) * width + j + 1]) / 4;
v[k] = (v_temp[i * width + j] + v_temp[(i + 1) * width + j] + v_temp[i * width + j + 1] + v_temp[(i + 1) * width + j + 1]) / 4;
k++;
}
}
free(u_temp);
free(v_temp);
for (unsigned long i = 0; i < width * height; i++)
{
if (y[i] < 16)
y[i] = 16;
if (y[i] > 235)
y[i] = 235;
}
for (unsigned long i = 0; i < width * height / 4; i++)
{
if (u[i] < 16)
u[i] = 16;
if (v[i] < 16)
v[i] = 16;
if (u[i] > 240)
u[i] = 240;
if (v[i] > 240)
v[i] = 240;
}
return 0;
}
void InitLookupTable()
{
unsigned long i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) RGBYUV02990[i] = (double)0.2990 * i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) RGBYUV05870[i] = (double)0.5870 * i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) RGBYUV01140[i] = (double)0.1140 * i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) RGBYUV01684[i] = (double)0.1684 * i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) RGBYUV03316[i] = (double)0.3316 * i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) RGBYUV04187[i] = (double)0.4187 * i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) RGBYUV00813[i] = (double)0.0813 * i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) RGBYUV05000[i] = (double)0.5000 * i;
}实验结果
播放软件参数参考bmp文件格式大小,bmp文件序列的格式大小要一致 。