匈牙利算法与python实现
匈牙利算法
0 引出
最近看DETR论文,发现其通过匈牙利算法来进行预测和ground truth匹配,从而实现set prediction。这个思路很有意思,并且该匹配算法能适用多种问题,因此,对其进行详细记录,便于后续回顾。
首先来看,匈牙利算法能够解决什么问题。不妨以宝可梦作为例子引入。
现在有五个工作(搬砖、送快递、洗衣服、打扫、做饭)需要安排给有5个宝可梦(皮卡丘、杰尼龟、喷火龙、小拳石、妙蛙草)。每个宝可梦对每一项工作收费标准不同。如何安排工作使得成本最低。
(注:①每个宝可梦只能做一项工作;②每项工作只能分配给一个宝可梦做;③所有工作都要安排完。
| 搬砖 | 送快递 | 洗衣服 | 打扫 | 做饭 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 皮卡丘 | 12 | 7 | 9 | 7 | 9 |
| 杰尼龟 | 8 | 9 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 喷火龙 | 7 | 17 | 12 | 14 | 9 |
| 小拳石 | 15 | 14 | 6 | 6 | 10 |
| 妙蛙草 | 4 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 9 |
下面来看,匈牙利算法如何解决这种指派问题。
1 模型建立与求解
1.1 符号规定
对上述问题进行抽象,首先进行如下符号定义
| 符号 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| C C C | 宝可梦的成本矩阵 |
| c i j c_{ij} cij | 宝可梦 i i i对 j j j工作的收费. |
| w i j w_{ij} wij | 是否将工作 j j j配给宝可梦 i i i,若是则为 1 1 1,若否则为 0 0 0 |
| m m m | 宝可梦的数量 |
| n n n | 工作的数量 |
1.2 模型建立
通过上述符号定义,宝可梦的指派问题可进行如下抽象。
-
目标函数:
设计合适的指派策略使得用最低的成本完成工作。
min ∑ i = 1 m ∑ j = 1 n w i j c i j \min \sum_{i=1}^{m} \sum_{j=1}^{n} w_{i j} c_{i j} mini=1∑mj=1∑nwijcij
-
约束条件
-
每个宝可梦只能做一件工作
∑ j = 1 n w i j = 1 , i = 1 , 2 , 3 , … , m \sum_{j=1}^{n} w_{i j}=1, i=1,2,3, \ldots, \mathrm{m} j=1∑nwij=1,i=1,2,3,…,m -
每项工作只能分配给一个宝可梦
∑ i = 1 m w i j = 1 , j = 1 , 2 , 3 , … , n \sum_{i=1}^{m} w_{i j}=1, j=1,2,3, \ldots, \mathrm{n} i=1∑mwij=1,j=1,2,3,…,n -
所有工作都要被分配
∑ i = 1 m ∑ j = 1 n w i j = n \sum_{i=1}^{m} \sum_{j=1}^{n} w_{i j}=n i=1∑mj=1∑nwij=n
-
综上所述,上述对宝可梦指派问题的模型可以表述为:
目标函数 min ∑ i = 1 m ∑ j = 1 n w i j c i j 约束条件 { ∑ j = 1 n w i j = 1 , i = 1 , 2 , 3 , … , m ∑ i = 1 m w i j = 1 , j = 1 , 2 , 3 , … , n ∑ i = 1 m ∑ j = 1 n w i j = n \begin{array}{l} \text { 目标函数 } \min \sum_{i=1}^{m} \sum_{j=1}^{n} w_{i j} c_{i j}\\ \text { 约束条件 }\left\{\begin{array}{c} \sum_{j=1}^{n} w_{i j}=1, i=1,2,3, \ldots, \mathrm{m} \\ \sum_{i=1}^{m} w_{i j}=1, j=1,2,3, \ldots, \mathrm{n} \\ \sum_{i=1}^{m} \sum_{j=1}^{n} w_{i j}=n \end{array}\right. \end{array} 目标函数 min∑i=1m∑j=1nwijcij 约束条件 ⎩⎨⎧∑j=1nwij=1,i=1,2,3,…,m∑i=1mwij=1,j=1,2,3,…,n∑i=1m∑j=1nwij=n
1.3 模型求解
为了求解上述模型,最直接的方法是穷举法。不难得出共有 C m n C n 1 C n − 1 1 … C 1 1 = C m n n ! C_{m}^{n} C_{n}^{1} C_{n-1}^{1} \ldots C_{1}^{1}=C_{m}^{n} n ! CmnCn1Cn−11…C11=Cmnn!种可能的组合, 为 O ( n ! ) O(n!) O(n!)的时间复杂度。匈牙利算法可以将上述的时间复杂度从 O ( n ! ) O(n!) O(n!)降低到多项式的时间复杂度。下面来看匈牙利算法是如何进行的。
前置知识:指派问题的最优解有这样一个性质,若从系数矩阵的一行(列)各元素中分别减去该行(列)的最小元素,得到新矩阵,那么以新矩阵为系数矩阵求得的最优解和用原矩阵求得的最优解相同.利用这个性质,可使原系数矩阵变换为含有很多0元素的新矩阵,而最优解保持不变。
-
归约
step1: 行归约(使得每行至少有一个零)
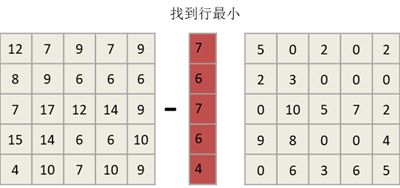
step2 列归约(使得每列至少有一个零) 此处由于每列恰好最小值已为零,故列规约后结果不变。
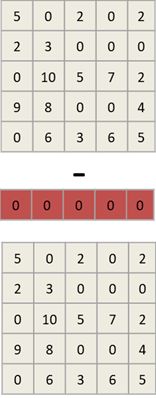
-
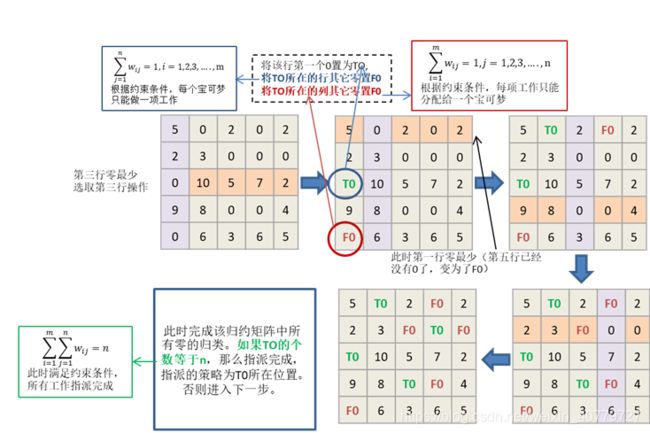
试指派(找到归约后的成本矩阵中独立的零)
step1: 找到含0数目最少的行或列(不妨取行) 随后将该行第一个零置为“T0”,随后将“T0”所在行和列中其他的零置“F0”。依次类推,完成归约矩阵所有行的操作。
以上述的归约矩阵为例:
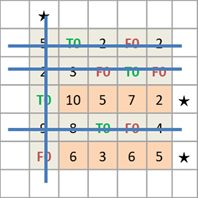
step2: 用最少的直线来覆盖矩阵中所有的零。
具体方法:
① 对没有T0的行用★进行标
② 对★所标记的行中存在的F0所在的列索引进行标记(同样标记★)
③ 对★所标记的列中,对T0所在的行索引进行标记(同样标记★)
④ 重复2、3步骤,直至找不到可以标记的行和列
①~④步骤以上述试指派为例
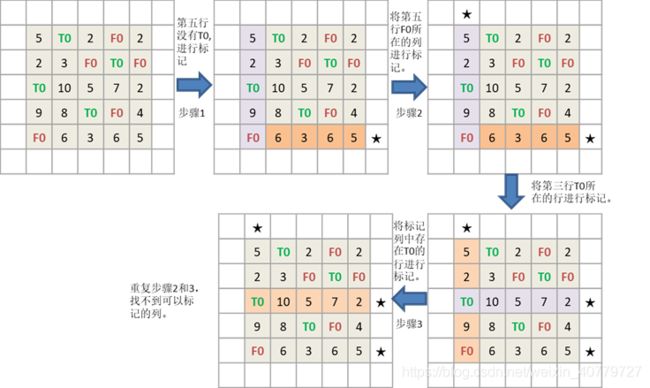
⑤ 对没有标记的行画横线表示去掉这一行,对标记的列画横线表示去掉这一列,这样就得到能覆盖所有0 的最小横线。
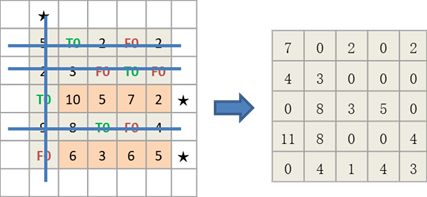
step3 变换试指派矩阵,增加其中的0元素
具体方法:
① 在未被直线覆盖的所有元素中找到min
② 在被★标记的所有行中减去这个元素;
③ 在被★标记的所有列中加上这个元素(保证原来的零不变);
④ 得到新的归约矩阵。返回step1。直至满足约束条件
2 python程序实现
s c i p y scipy scipy中已实现匈牙利算法,可直接调用
from scipy.optimize import linear_sum_assignment
import numpy as np
cost_mat = np.array([[12, 7, 9, 7, 9],
[8, 9, 6, 6, 6],
[7, 17, 12, 14, 9],
[15, 14, 6, 6, 10],
[4, 10, 7, 10, 9]])
work_idx_ls, pokeman_idx_ls = linear_sum_assignment(cost_mat)
cost = 0
work = ["搬砖", "送快递", "洗衣服", "打扫", "做饭"]
pokeman = ["皮卡丘", "杰尼龟", "喷火龙", "小拳石", "妙蛙草"]
for work_idx, poken_idx in zip(work_idx_ls, pokeman_idx_ls):
print(f"work {work[work_idx]} 指派给 pokeman {pokeman[poken_idx]}")
cost += cost_mat[work_idx][poken_idx]
print(f"total cost is {cost}!")
为了深入理解计算过程,使用python进行实现
# encoding: utf-8
# @author wwjiang
# date: 2021/3/4
from typing import List
import numpy as np
class HungarianAssign:
def hungarian_assign(self, cost_mat: np.ndarray, debug: bool = False, epoch=10):
cost_mat_ori = cost_mat[:]
reduce_mat = self.reduce_func(cost_mat)
for i in range(epoch):
out_mat_ls = self.convert_cost_matrix(reduce_mat, debug=debug)
assign_mask = self.gen_assign_mask(out_mat_ls)
if debug:
print(f"epoch: {i} assign: {np.sum(assign_mask)}")
self.show_mat_ls(out_mat_ls)
print(assign_mask)
if np.sum(assign_mask) != cost_mat.shape[1]:
mark_row, mark_col = self.mark_convert_ls(out_mat_ls)
reduce_mat = self.reconstruct_matrix_by_minima(out_mat_ls, mark_row, mark_col)
else:
break
return np.sum(cost_mat_ori[assign_mask]), assign_mask
def convert_cost_matrix(self, reduce_mat: np.ndarray, debug: bool = False) -> bool:
row, col = reduce_mat.shape[:2]
mat_ls = reduce_mat.tolist() # 每一各元素代表一行
zeros_count = [ls.count(0) for ls in mat_ls]
zeros_loc = self._find_each_line_zeros_loc(reduce_mat)
max_count = max(zeros_count) + 1
zeros_count = [i if i != 0 else max_count for i in zeros_count]
if debug:
print(f"ori zeros count: {zeros_count}")
print(f"ori zeros_loc {zeros_loc}")
print("ori mat_ls")
for temp in mat_ls:
print(temp)
print("--------------------------------------------------")
while set(zeros_count) != {max_count}:
tgt_row_idx = np.argmin(zeros_count)
# 置零
# 将第一个元素记为 “T0”
tgt_line_idx = zeros_loc[tgt_row_idx].pop(0) # 注意该操作会修改zeros_loc的值
mat_ls[tgt_row_idx][tgt_line_idx] = "T0"
# 将同行的零和同列的零置为 “F0”
while zeros_loc[tgt_row_idx]: # 同行置为0
other_line_idx = zeros_loc[tgt_row_idx].pop(0)
mat_ls[tgt_row_idx][other_line_idx] = "F0"
zeros_count[tgt_row_idx] = max_count
for row_idx, ls in enumerate(mat_ls): # 同列置零
if row_idx == tgt_row_idx:
continue
if ls[tgt_line_idx] == 0:
ls[tgt_line_idx] = "F0"
zeros_count[row_idx] -= 1
temp_idx = zeros_loc[row_idx].index(tgt_line_idx)
zeros_loc[row_idx].pop(temp_idx)
if zeros_count[row_idx] == 0:
zeros_count[row_idx] = max_count
if debug:
print(f"tgt_row_idx: {tgt_row_idx}")
print("mat_ls")
print(f"zeros_count: {zeros_count}")
print(f"zeros_loc {zeros_loc}")
for temp in mat_ls:
print(temp)
print("-----------------------------------------")
if debug:
print("output mat_ls")
for temp in mat_ls:
print(temp)
return mat_ls
def reduce_func(self, mat: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
col_reduce = mat - np.min(mat, axis=1, keepdims=True)
row_reduce = col_reduce - np.min(col_reduce, axis=0, keepdims=True)
return row_reduce
def mark_convert_ls(self, mat_ls: List[List[int]]):
"""获得覆盖所有0的最小横线"""
mark_row = []
mark_col = []
row_mask_queue = []
# step1 标记 没有 TO的行
mark_row.extend([row_idx for row_idx, ls in enumerate(mat_ls)
if "T0" not in ls])
# step2 标记mark_row_idx中,存在列为 F0, 对该列标记
row_mask_queue = mark_row[:] # 浅拷贝
while row_mask_queue:
row_idx = row_mask_queue.pop(0) # 注意这个row idx是所有不包含TO的行
# 找到该行的F0,将列序号存入 mark_col
col_idx_ls = [col_idx for col_idx, i in enumerate(mat_ls[row_idx])
if i == "F0"]
mark_col.extend(col_idx_ls)
for col_idx in col_idx_ls: # 找到该列元素所有 TO的行索引,并存如mark_row
tgt_col_item = self.get_col_item(mat_ls, col_idx)
row_idx_ls = [row_idx for row_idx, i in enumerate(tgt_col_item)
if i == "T0"]
mark_row.extend(row_idx_ls)
row_mask_queue.extend(row_idx_ls)
return mark_row, mark_col
@staticmethod
def _find_each_line_zeros_loc(reduce_mat: np.ndarray) -> List[List[int]]:
zeros_loc = np.array(np.where(reduce_mat[:] == 0)).T
res = [[] for _ in range(reduce_mat.shape[0])]
for i in range(zeros_loc.shape[0]):
row_idx = zeros_loc[i][0]
line_idx = zeros_loc[i][1]
res[row_idx].append(line_idx)
return res
@staticmethod
def get_col_item(mat_ls: List[List[int]], col_idx: int) -> List[int]:
tgt_col = [ls[col_idx] for ls in mat_ls]
return tgt_col
@staticmethod
def find_minima_uncover(mat_ls, mark_row, mark_col):
# step1 取行
tgt_row = [mat_ls[i] for i in mark_row]
# step2 清除不需要的列
clean = [item for row in tgt_row
for col_idx, item in enumerate(row)
if col_idx not in mark_col]
return min(clean)
def reconstruct_matrix_by_minima(self, mat_ls, mark_row, mark_col):
# minima_value = self.find_minima_uncover(mat_ls, mark_row, mark_col)
mat = self.mat_ls2np(mat_ls)
# print("mat")
# print(mat)
mask_valid = np.zeros_like(mat).astype(np.bool)
mask_valid[mark_row, :] = True
# mask_valid[:, mark_col] = False
valid_col_idx = [i for i in range(mat.shape[1]) if i not in mark_col]
res_item = mat[mark_row, :][:, valid_col_idx]
min_value = np.min(res_item)
# print(f"minvalue {min_value}")
mat[mask_valid] = mat[mask_valid] - min_value
mat[:, mark_col] = mat[:, mark_col] + min_value
return mat
@staticmethod
def mat_ls2np(mat_ls):
mat_ls_new = []
for row in mat_ls:
mat_ls_new.append([i if i not in ["T0", "F0"] else 0 for i in row])
return np.array(mat_ls_new)
@staticmethod
def gen_assign_mask(mat_ls):
mat_ls_new = []
for row in mat_ls:
mat_ls_new.append([True if i == "T0" else False for i in row])
return np.array(mat_ls_new)
@staticmethod
def show_mat_ls(mat_ls):
for temp in mat_ls:
print(temp)
hungar = HungarianAssign()
if __name__ == "__main__":
cost_mat = np.array([[12, 7, 9, 7, 9],
[8, 9, 6, 6, 6],
[7, 17, 12, 14, 9],
[15, 14, 6, 6, 10],
[4, 10, 7, 10, 9]])
cost, assign_mat = hungar.hungarian_assign(cost_mat, debug=False, epoch=10)
print(cost, assign_mat )