java 类内存分配计算
因为跟同事大哥一起看一个社区的jira,不得不恶补了一下java的类内存分配与使用计算方法。原文请参照http://www.codeinstructions.com/2008/12/java-objects-memory-structure.html 。不得不说,一件事情做进去真的越来越复杂。
在c和c++中,程序员可以自由的操纵内存数据,包括内存分配,内存释放等等,在java中这些繁琐(或者也可以说其实不错)的特性完全由虚拟机搞定,不用再管内存分配回收,看起来相当爽,但是到底类占用了多少空间,如何计算,对于大内存应用的程序,如hadoop hbase等有十分现实的意义。
首先描述一下内存使用情况的分类,一种是shallow size,一种是是deep size。这里主要说明一下shallow size的计算方法。
1、没有实力属性的类内存占用情况
每个java类(除了数组)都占用2个字(word)的头信息(header),header的第一个字(word)内容包括有类的hash值,锁信息以及一些存活时间信息等。header的第二个字(word)包含有类的引用。
规则(1):每个对象都要占用8字节对齐。 every object is aligned to an 8 bytes granularity
2、类内部内存使用情况
类头部8字节后面是属性情况,基本数据类型内存的使用情况按照我们从课本上解释的,如图:
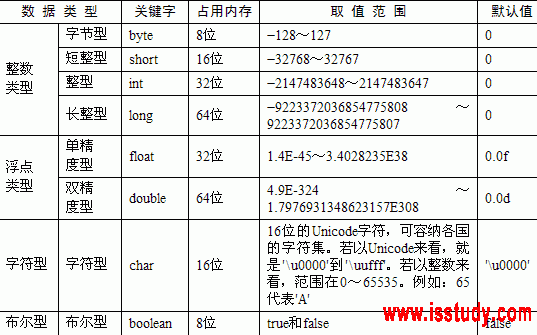
但是注意,这些类型在内存的分配是需要对齐的!对齐的原因可以参看这篇文章,http://www.devx.com/tips/Tip/13265 简单的说就是为了性能方面的考虑,int是4bytes对齐,double是8个bytes对齐。在对齐的方式上,jvm是做了优化的,即在一个类中,数据是按照以下顺序进行存储的。
- doubles and longs
- ints and floats
- shorts and chars
- booleans and bytes
- references
这样能够最小限度的减少padding,节约内存。如对一个类
class MyClass {
byte a;
int c;
boolean d;
long e;
Object f;
}
如果按照顺序存储在内存中,则总共需要40bytes
[HEADER: 8 bytes] 8
[a: 1 byte ] 9
[padding: 3 bytes] 12
[c: 4 bytes] 16
[d: 1 byte ] 17
[padding: 7 bytes] 24
[e: 8 bytes] 32
[f: 4 bytes] 36
[padding: 4 bytes] 40
按照jvm的规则存取,则只需要32bytes
[HEADER: 8 bytes] 8
[e: 8 bytes] 16
[c: 4 bytes] 20
[a: 1 byte ] 21
[d: 1 byte ] 22
[padding: 2 bytes] 24
[f: 4 bytes] 28
[padding: 4 bytes] 32
规则(2)jvm内部存储属性是按照先保存long,double;然后int,float;然后char,short;然后byte,boolean,最后是类的引用(reference)。
3、子类内存分布
规则(3)子类和父类的属性不会混合在一起重排保存,父类先保存,子类后保存
class A {
long a;
int b;
int c;
}
class B extends A {
long d;
}
[HEADER: 8 bytes] 8
[a: 8 bytes] 16
[b: 4 bytes] 20
[c: 4 bytes] 24
[d: 8 bytes] 32
Rule 4: Between the last field of the superclass and the first field of the subclass there must be padding to align to a 4 bytes boundary.
Rule 5: When the first field of a subclass is a double or long and the superclass doesn't align to an 8 bytes boundary, JVM will break rule 2 and try to put an int, then shorts, then bytes, and then references at the beginning of the space reserved to the subclass until it fills the gap.
rule4,rule5参照原文。
对于数组加了4个字节的length信息,所以数组的header是12个bytes。