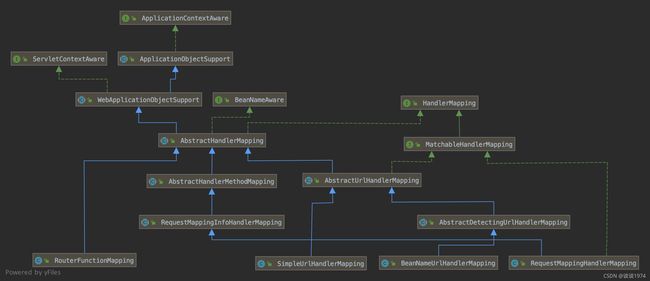
Spring WebMVC 源码分析(5)-注解@RequestMapping的实现原理
文章目录
- 1. 注解 @RequestMapping 的作用
- 2. 源码分析
-
-
- 2.1 关键组件的配置
- 2.2 路由映射保存
- 2.3 路由分发
-
1. 注解 @RequestMapping 的作用
@RequestMapping 用在方法或者 Controller 上面,其作用是将请求路径 Path 与实际的请求处理方法进行映射,从而完成当请求来临时将其路由到目标处理方法的功能。在 Spring WebMVC 框架的实际处理中,@RequestMapping注解实现功能主要分为以下几步:
RequestMappingHandlerMapping组件的配置- 路径
Path与实际处理请求的方法的映射保存- 请求到来时,根据请求的路由将其分发到对应处理方法
2. 源码分析
2.1 关键组件的配置
-
在 SpringBoot 自动配置原理源码分析 中笔者分析了自动配置的实现原理,而
Spring WebMVC的自动配置类WebMvcAutoConfiguration也会在容器准备阶段被解析,从而将其内部@Configuration修饰的配置类EnableWebMvcConfiguration引入容器。框架在解析配置类的过程中,会将@Bean修饰的方法封装为BeanDefinition注册到 Bean 工厂,本文主要关注EnableWebMvcConfiguration#requestMappingHandlerMapping(),可以看到其定义如下@Bean @Primary @Override public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping( @Qualifier("mvcContentNegotiationManager") ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager, @Qualifier("mvcConversionService") FormattingConversionService conversionService, @Qualifier("mvcResourceUrlProvider") ResourceUrlProvider resourceUrlProvider) { // Must be @Primary for MvcUriComponentsBuilder to work return super.requestMappingHandlerMapping(contentNegotiationManager, conversionService, resourceUrlProvider); } -
RequestMappingHandlerMapping组件注册到了容器中,其实际的实例化其实是在DispatcherServlet#initStrategies()初始化时完成的,读者如不了解 Servlet 初始化的触发流程,可参考 Spring WebMVC 源码分析(1)-请求处理主流程此处可看到会调用
DispatcherServlet#initHandlerMappings()方法进行HandlerMapping的初始化动作protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); initHandlerMappings(context); initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); } -
DispatcherServlet#initHandlerMappings()方法会从容器中获取HandlerMapping的实例并保存起来,这里实际是使用容器中注册的BeanDefinition通过反射完成对象的创建,也就是会调用到本节步骤1 配置类对象的方法EnableWebMvcConfiguration#requestMappingHandlerMapping()private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerMappings = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { // Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts. Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values()); // We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order. AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings); } } else { try { HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later. } } // Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering // a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found. if (this.handlerMappings == null) { this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties"); } } } -
EnableWebMvcConfiguration#requestMappingHandlerMapping()核心逻辑其实是调用父类方法WebMvcConfigurationSupport#requestMappingHandlerMapping(),可以看到此处的核心逻辑如下,至此组件的配置告一段落- 调用
WebMvcConfigurationSupport#createRequestMappingHandlerMapping()方法创建RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象 - 配置
RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象各项属性,包括Interceptor拦截器等
@Bean public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping( @Qualifier("mvcContentNegotiationManager") ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager, @Qualifier("mvcConversionService") FormattingConversionService conversionService, @Qualifier("mvcResourceUrlProvider") ResourceUrlProvider resourceUrlProvider) { RequestMappingHandlerMapping mapping = createRequestMappingHandlerMapping(); mapping.setOrder(0); mapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors(conversionService, resourceUrlProvider)); mapping.setContentNegotiationManager(contentNegotiationManager); mapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations()); PathMatchConfigurer configurer = getPathMatchConfigurer(); Boolean useSuffixPatternMatch = configurer.isUseSuffixPatternMatch(); if (useSuffixPatternMatch != null) { mapping.setUseSuffixPatternMatch(useSuffixPatternMatch); } Boolean useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch = configurer.isUseRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(); if (useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch != null) { mapping.setUseRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch); } Boolean useTrailingSlashMatch = configurer.isUseTrailingSlashMatch(); if (useTrailingSlashMatch != null) { mapping.setUseTrailingSlashMatch(useTrailingSlashMatch); } UrlPathHelper pathHelper = configurer.getUrlPathHelper(); if (pathHelper != null) { mapping.setUrlPathHelper(pathHelper); } PathMatcher pathMatcher = configurer.getPathMatcher(); if (pathMatcher != null) { mapping.setPathMatcher(pathMatcher); } Map<String, Predicate<Class<?>>> pathPrefixes = configurer.getPathPrefixes(); if (pathPrefixes != null) { mapping.setPathPrefixes(pathPrefixes); } return mapping; } protected RequestMappingHandlerMapping createRequestMappingHandlerMapping() { return new RequestMappingHandlerMapping(); } - 调用
2.2 路由映射保存
-
RequestMappingHandlerMapping的父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping实现了InitializingBean接口,则当其对象被创建出来后,容器会触发其父类实现的接口方法AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#afterPropertiesSet()开始进行请求路径与对应处理方法的映射注册,核心处理如下:- 调用
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getCandidateBeanNames()从容器中获取所有候选的可能包含路由处理方法的对象 - 调用
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#processCandidateBean()实际处理路由注册
@Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { initHandlerMethods(); } protected void initHandlerMethods() { for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) { if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) { processCandidateBean(beanName); } } handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); } - 调用
-
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#processCandidateBean()方法重要的逻辑分为两步:- 调用子类
RequestMappingHandlerMapping#isHandler()方法判断当前处理的对象是否是处理路由请求的对象 - 调用
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#detectHandlerMethods()方法将处理请求的Controller中的方法与路由进行映射注册
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) { Class<?> beanType = null; try { beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { // An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it. if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex); } } if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) { detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } - 调用子类
-
RequestMappingHandlerMapping#isHandler()方法逻辑简练,可以看到主要是判断类对象上是否有@RequestMapping注解和@Controller注解,如果存在这两个注解则这个类属于请求处理器,需要进行下一步的路由映射操作@Override protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) { return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) || AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class)); } -
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#detectHandlerMethods()方法实际进行的动作如下:- 调用
MethodIntrospector.selectMethods()方法解析处理器类中的处理器方法,将处理方法和其上@RequestMapping注解中的路由信息形成映射 - 遍历映射列表,调用
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#registerHandlerMethod()方法将路由映射信息保存起来
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) { Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ? obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass()); if (handlerType != null) { Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType, (MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> { try { return getMappingForMethod(method, userType); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" + userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex); } }); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods)); } methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> { Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType); registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping); }); } } - 调用
-
MethodIntrospector.selectMethods()方法逻辑清晰,关键处理如下:- 通过反射遍历处理器类的方法列表,通过
metadataLookup.inspect()调用函数式接口方法组装处理器方法的路由信息,此处关键点在于本节步骤4 中调用的AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getMappingForMethod()方法 - 使用 Map 收集处理器方法及其路由映射信息
public static <T> Map<Method, T> selectMethods(Class<?> targetType, final MetadataLookup<T> metadataLookup) { final Map<Method, T> methodMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); Set<Class<?>> handlerTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>(); Class<?> specificHandlerType = null; if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetType)) { specificHandlerType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetType); handlerTypes.add(specificHandlerType); } handlerTypes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetType)); for (Class<?> currentHandlerType : handlerTypes) { final Class<?> targetClass = (specificHandlerType != null ? specificHandlerType : currentHandlerType); ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(currentHandlerType, method -> { Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass); T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod); if (result != null) { Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod); if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) { methodMap.put(specificMethod, result); } } }, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS); } return methodMap; } - 通过反射遍历处理器类的方法列表,通过
-
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getMappingForMethod()方法实际由其子类RequestMappingHandlerMapping#getMappingForMethod()方法实现,此处的重要逻辑如下:- 首先调用
RequestMappingHandlerMapping#createRequestMappingInfo()方法创建处理器类方法上@RequestMapping注解的路由信息 - 其次同样调用
RequestMappingHandlerMapping#createRequestMappingInfo()方法创建处理器类本身@RequestMapping注解的路由信息,最终将两部分路由信息拼接起来形成一个处理器方法的完整路由映射
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) { RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method); if (info != null) { RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType); if (typeInfo != null) { info = typeInfo.combine(info); } String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType); if (prefix != null) { info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info); } } return info; } - 首先调用
-
RequestMappingHandlerMapping#createRequestMappingInfo()方法负责解析@RequestMapping注解中的路由信息,将其封装到RequestMappingInfo对象中@Nullable private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) { RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class); RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ? getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element)); return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null); } protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo( RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) { RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo .paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path())) .methods(requestMapping.method()) .params(requestMapping.params()) .headers(requestMapping.headers()) .consumes(requestMapping.consumes()) .produces(requestMapping.produces()) .mappingName(requestMapping.name()); if (customCondition != null) { builder.customCondition(customCondition); } return builder.options(this.config).build(); } -
此时回到本节步骤4第2步,
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#registerHandlerMethod()方法如下,可以看到核心其实是调用MappingRegister#register()方法完成路由信息和处理器方法的映射注册protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) { this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method); } -
MappingRegister#register()方法的注册逻辑如下,其实就是使用 Map 保存路由信息与处理器方法,至此路由映射的保存流程结束public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) { // Assert that the handler method is not a suspending one. if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(method.getDeclaringClass()) && KotlinDelegate.isSuspend(method)) { throw new IllegalStateException("Unsupported suspending handler method detected: " + method); } this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock(); try { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method); validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping); this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod); List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping); for (String url : directUrls) { this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping); } String name = null; if (getNamingStrategy() != null) { name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping); addMappingName(name, handlerMethod); } CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping); if (corsConfig != null) { this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig); } this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name)); } finally { this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock(); } }
2.3 路由分发
-
当请求到来时,将触发
DispatcherServlet#doDispatch()进行请求的处理流程,此时首先要做的就是根据请求的 URL 找到处理该请求的处理器方法,也就是调用DispatcherServlet#getHandler()方法protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } } -
DispatcherServlet#getHandler()方法会遍历其在初始化时保存的映射器列表,映射器子类实现的HandlerMapping#getHandler()方法去获取处理器,此处实际完成了路由分发protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { if (this.handlerMappings != null) { for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) { HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } } return null; } -
RequestMappingHandlerMapping#getHandler()实际由其父类AbstractHandlerMapping#getHandler()实现,可以看到其处理逻辑分以下几步:- 调用子类
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerInternal()方法去路由注册中获取真正的处理器方法 - 调用
AbstractHandlerMapping#getHandlerExecutionChain()方法将处理器方法及相关拦截器HandlerInterceptor封装到HandlerExecutionChain对象中返回
@Override @Nullable public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); if (handler == null) { handler = getDefaultHandler(); } if (handler == null) { return null; } // Bean name or resolved handler? if (handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler); } else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) { logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler()); } if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) { CorsConfiguration config = (this.corsConfigurationSource != null ? this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request) : null); CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request); config = (config != null ? config.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig); executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config); } return executionChain; } - 调用子类
-
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerInternal()方法如下,关键处理显而易见:- 通过
getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request)解析获取请求中携带的 URI 字符串 - 调用
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#lookupHandlerMethod()方法根据请求中的 URI 去路由注册中获取对应的处理器方法,获取到后调用子类实现的AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#handleMatch()方法进行下一步处理,此处将调用到RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping#handleMatch()
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); request.setAttribute(LOOKUP_PATH, lookupPath); this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock(); try { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null); } finally { this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock(); } } protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>(); List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath); if (directPathMatches != null) { addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request); } if (matches.isEmpty()) { // No choice but to go through all mappings... addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request); } if (!matches.isEmpty()) { Match bestMatch = matches.get(0); if (matches.size() > 1) { Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request)); matches.sort(comparator); bestMatch = matches.get(0); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches); } if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) { return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH; } Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1); if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) { Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); String uri = request.getRequestURI(); throw new IllegalStateException( "Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}"); } } request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod); handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request); return bestMatch.handlerMethod; } else { return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request); } } - 通过
-
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping#handleMatch()方法的处理比较简单,可以看到主要是对 URI 的进一步处理,比如将@RequestMapping配置的路径上的{}模版包裹的参数从请求的 URI 上解析出来保存protected void handleMatch(RequestMappingInfo info, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) { super.handleMatch(info, lookupPath, request); String bestPattern; Map<String, String> uriVariables; Set<String> patterns = info.getPatternsCondition().getPatterns(); if (patterns.isEmpty()) { bestPattern = lookupPath; uriVariables = Collections.emptyMap(); } else { bestPattern = patterns.iterator().next(); uriVariables = getPathMatcher().extractUriTemplateVariables(bestPattern, lookupPath); } request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE, bestPattern); if (isMatrixVariableContentAvailable()) { Map<String, MultiValueMap<String, String>> matrixVars = extractMatrixVariables(request, uriVariables); request.setAttribute(HandlerMapping.MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE, matrixVars); } Map<String, String> decodedUriVariables = getUrlPathHelper().decodePathVariables(request, uriVariables); request.setAttribute(HandlerMapping.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE, decodedUriVariables); if (!info.getProducesCondition().getProducibleMediaTypes().isEmpty()) { Set<MediaType> mediaTypes = info.getProducesCondition().getProducibleMediaTypes(); request.setAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE, mediaTypes); } } -
此时回到本节步骤3第2步,
AbstractHandlerMapping#getHandlerExecutionChain()方法完成请求处理需要用到的组件的聚合,主要处理如下,至此路由映射分发结束,后续的处理器方法调用可参考 Spring WebMVC 源码分析(2)-从注解@RequestBody开始- 新建
HandlerExecutionChain对象封装以上步骤中查找到的处理器方法 - 根据请求的 URI 查找需要在本次请求处理中应用的
HandlerInterceptor拦截器,将其封装到HandlerExecutionChain对象
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) { HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ? (HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler)); String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request, LOOKUP_PATH); for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) { if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) { MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor; if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) { chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor()); } } else { chain.addInterceptor(interceptor); } } return chain; } - 新建