Java字符串(String类)
目录
一.认识String类
二.String类的使用
2.1构造字符串
2.2字符串长度
2.3String对象的比较
2.4字符串查找
charAt方法
indexOf方法
lastIndexOf方法
2.5字符串的转化
数值和字符串转化
大小写转换
字符串转数组
格式化
2.6字符串的替换
2.7字符串拆分
2.8字符串截取
三.StringBuilder和StringBuffffer
3.1StringBuilder和StringBuffffer的使用
3.2StringBuilder和StringBuffffer的好处
四.总结
前面小编给大家分享了Java语法的知识,今天和大家一起学习关于Java字符串的相关知识,字符串在校招笔试中也是常考的一类题目,也是非常的重要,希望看完这篇文章,能对你们有所帮助,fighting冲冲冲~~~
一.认识String类
字符串广泛应用 在 Java 编程中,在 Java 中字符串属于对象,Java 提供了 String 类来创建和操作字符串。
二.String类的使用
2.1构造字符串
构造字符串有不同的方式,接下来给大家介绍常见的几种:
1)定义字符串变量并赋值
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str="abcd"; System.out.println(str); } }2)通过引用构造字符串
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str=new String("abcd"); System.out.println(str); } }3)通过字符数组构造字符串
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { char[] arr={'a','b','c','d'}; String str=new String(arr); System.out.println(str); } }
2.2字符串长度
String 类的一个访问器方法是 length() 方法,它返回字符串对象包含的字符数。
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "hello"; char[] str2 = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'}; String str3 = ""; System.out.println(str1.length()); System.out.println(str2.length); System.out.println(str3.isEmpty());//判断字符串是否为空,为空返回true,否则返回false } }
2.3String对象的比较
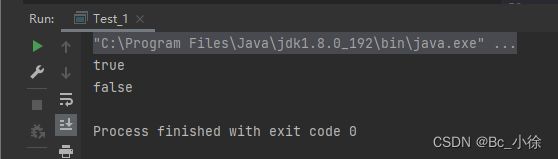
字符串的比较是常见操作之一,举个例子:public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1="abcd"; String str2="abcd"; String str3=new String("abcd"); String str4=new String("abcd"); System.out.println(str1 == str2);//比较变量的值 System.out.println(str3 == str4);//比较的是地址 } }我们可以看到,str3和str4这两个引用的地址是不同的,所以输出结果为false,如果要比较两个引用里面的值,我们可以用equal方法来比较:
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { /*String str1="abcd"; String str2="abcd";*/ String str3 = new String("abcd"); String str4 = new String("abcd"); /*System.out.println(str1 == str2); System.out.println(str3 == str4);*/ System.out.println(str3.equals(str4)); } }
那么如何比较两个字符串的大小呢,在Java中,提供了compareTo这样的方法:
- 先按照字典次序大小比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值
- 如果前k个字符相等(k为两个字符长度最小值),返回值两个字符串长度差值
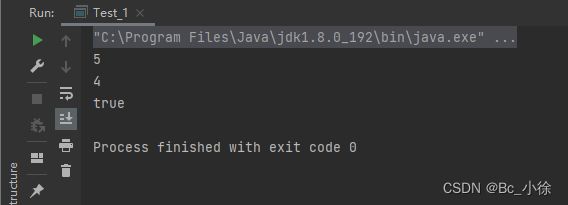
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = new String("abc"); String s2 = new String("ac"); String s3 = new String("abc"); String s4 = new String("abcdef"); System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1 System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); // 相同输出 0 System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3 } }Java中还要一种方法时忽略大小写的比较是compareToIgnoreCase的方法,举个例子:
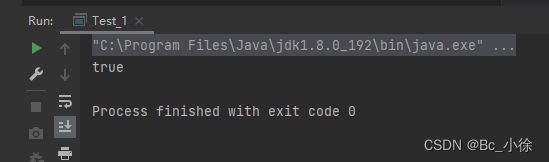
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = new String("Abc"); String s2 = new String("abc"); System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2));//输出0 } }
2.4字符串查找
字符串查找也是字符串中非常常见的操作, String 类提供的常用查找的方法:charAt方法
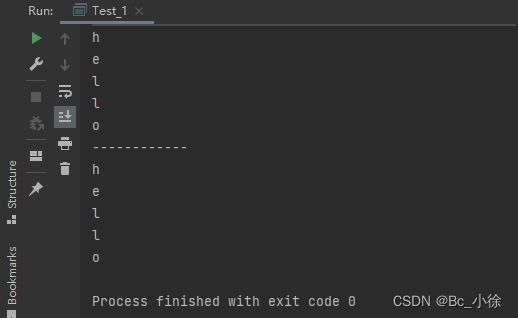
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str="hello"; System.out.println(str.charAt(0)); System.out.println(str.charAt(1)); System.out.println(str.charAt(2)); System.out.println(str.charAt(3)); System.out.println(str.charAt(4)); System.out.println("------------"); for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { System.out.println(str.charAt(i)); } } }上图代码中,我们可以给charAt()传参,传的是字符串的下标,我们也可以通过数组的遍历来访问到每个下标所对应的元素。
indexOf方法
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str="onehelloworldmorninghello"; //在字符串中查找第一个出现的字母,并返回字母的下标,输出2 System.out.println(str.indexOf('e')); //从指定位置(fromIndex)开始查找字母,并返回字母的下标,输出7 System.out.println(str.indexOf('o', 6)); //在字符串中寻找第一次出现的子串,并返回子串的首元素的下标,输出8 System.out.println(str.indexOf("world")); //从指定位置(fromIndex)开始查找子串,并返回子串的首元素的下标,输出20 System.out.println(str.indexOf("hello", 5)); } }
lastIndexOf方法
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str="onehelloworldmorninghello"; //从后往前的顺序在字符串中查找第一个出现的字母,并返回字母的下标,输出21 System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf('e')); //从后往前的顺序在指定位置(fromIndex)开始查找字母,并返回字母的下标,输出0 System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf('o', 6)); //从后往前的顺序在字符串中寻找第一次出现的子串,并返回子串的首元素的下标,输出8 System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("world")); //从后往前的顺序在指定位置(fromIndex)开始查找子串,并返回子串的首元素的下标,输出3 System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("hello", 5)); } }
2.5字符串的转化
数值和字符串转化
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1=String.valueOf(100); String str2=String.valueOf(99.99); System.out.println(str1);//输出100 System.out.println(str2);//输出99.99 } }
大小写转换
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "helloworld"; String s2 = "HELLOWORLD"; // 小写转大写,输出HELLOWORLD System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase()); // 大写转小写,输出helloworld System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase()); } }
字符串转数组
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1="hello"; System.out.println(s1.toCharArray()); } }
格式化
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = String.format("%d-%d-%d", 2019, 9,14); System.out.println(s);//输出2019-9-14 } }
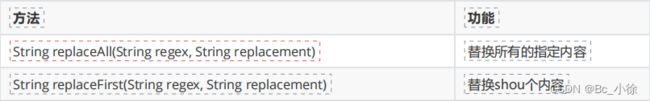
2.6字符串的替换
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "abcabcabcabcabc"; //将字符串中的b转换为a,输出aacaacaacaacaac System.out.println(str.replace('b', 'a')); //将字符串中的ab转换为dd,输出ddcddcddcddcddc System.out.println(str.replaceAll("ab", "dd")); //将字符串中首个ab转换为ff,输出ffcabcabcabcabc System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("ab", "ff")); } }
2.7字符串拆分
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "hello world hello bit"; String[] result = str.split(" ");// 按照空格拆分 String[] result1 = str.split(" ", 2);// 按照空格拆分,分2次分割 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result)); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result1)); } }输出如下:
这里有几种特殊情况,举个例子:
这里就用到了转义字符:
- 1. 字符"|","*","+"都得加上转义字符,前面加上 "\\" .
- 2. 而如果是 "\" ,那么就得写成 "\\\\" .
- 3. 如果一个字符串中有多个分隔符,可以用"|"作为连字符.
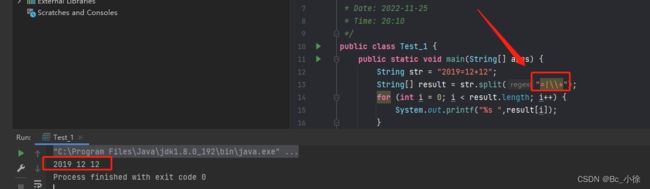
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "2019.12.12"; String[] result = str.split("\\."); for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) { System.out.printf("%s ",result[i]); } } }我们还可以进行多次分割:
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "2019=12+12"; String[] result = str.split("=|\\+");//第一次以=作为分割,第二次以+作为分割 for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) { System.out.printf("%s ",result[i]); } } }
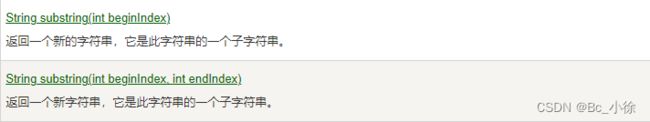
2.8字符串截取
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "helloworld"; System.out.println(str.substring(5));//从下标为5的字符开始截取,输出world System.out.println(str.substring(2, 4));//从下标为2截取到下标为4,但是不包括4,输出ll } }注意事项:
- 索引从0开始
- 注意前闭后开区间的写法, substring(0, 5) 表示包含 0 号下标的字符, 不包含 5 号下标
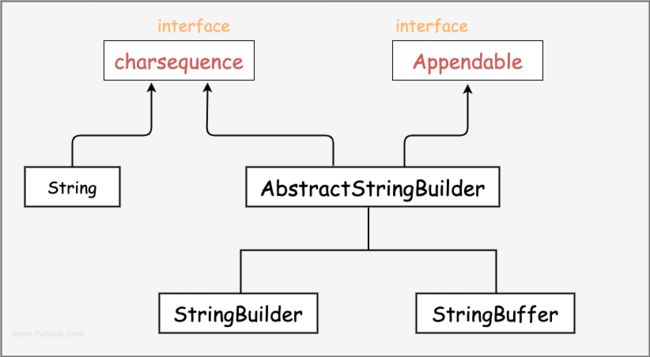
三.StringBuilder和StringBuffffer
3.1StringBuilder和StringBuffffer的使用
当对字符串进行修改的时候,需要使用 StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 类。
和 String 类不同的是,StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 类的对象能够被多次的修改,并且不产生新的未使用对象。
在使用 StringBuffer 类时,每次都会对 StringBuffer 对象本身进行操作,而不是生成新的对象,所以如果需要对字符串进行修改推荐使用 StringBuffer。
public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("abc"); StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer("abc"); System.out.println(stringBuilder);//输出abc System.out.println(stringBuffer);//输出abc } }public class Test_1 { public static void main(String[] args) { StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer("百度网站:"); stringBuffer.append("www."); stringBuffer.append("baidu."); stringBuffer.append("com"); System.out.println(stringBuffer); stringBuffer.delete(0, 5);//删除下班索引0-5,但是不包括下标5的字符 System.out.println(stringBuffer); stringBuffer.reverse(); System.out.println(stringBuffer);//逆序字符串 } }关于StringBuilder和StringBuffer的操作的方法有如下:
序号 方法描述 1 public StringBuffer append(String s)
将指定的字符串追加到此字符序列。2 public StringBuffer reverse()
将此字符序列用其反转形式取代。3 public delete(int start, int end)
移除此序列的子字符串中的字符。4 public insert(int offset, int i)
将int参数的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。5 insert(int offset, String str)
将str参数的字符串插入此序列中。6 replace(int start, int end, String str)
使用给定String中的字符替换此序列的子字符串中的字符。
3.2StringBuilder和StringBuffffer的好处
- StringBuilder 类在 Java 5 中被提出,它和 StringBuffer 之间的最大不同在于 StringBuilder 的方法不是线程安全的(不能同步访问)。
- 由于 StringBuilder 相较于 StringBuffer 有速度优势,所以多数情况下建议使用 StringBuilder 类。
- 然而在应用程序要求线程安全的情况下,则必须使用 StringBuffer 类。
四.总结
String在Java开发也是必不可少的角色,如对上文有意见或者有错误,还请大佬们斧正,觉得有帮助的童鞋们,创作不易,蟹蟹三连!