深度学习(3)--ResNet&ResNext
目录
一、ResNet概述
二、BN层(BatchNormalization)
1、BN层原理
2、注意事项
三、ResNet网络的实现
四、ResNext网络概述
五、ResNext网络实现
一、ResNet概述
ResNet网络由Kaiming He等人于2015年提出,论文名为《Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition》,论文见:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf
ResNet又称残差网络,通过每个残差块中的恒等映射(identity mapping)和残差映射(residual mapping)构建,并输出两者的和,如下图所示。
残差块的设计方式有两种,上述左图针对ResNet18,ResNet34网络,右图针对ResNet50,Res101,ResNet151网络,通过这一方式目的是降低参数数目。
ResNet网络结构如下图:
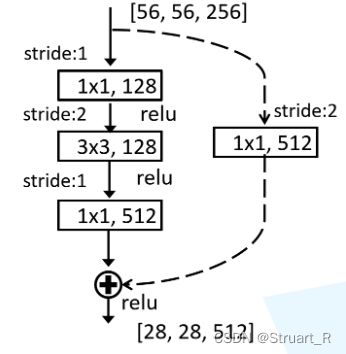
由于在conv2,conv3,conv4,conv5中任意一个残差块循环体的第一个残差块的恒等映射的输出与残差映射输出不相等,所以在支路添加一个conv用来转换输出,如下图所示。
注:conv2,conv3,conv4,conv5中的循环要在每一个中括号进行之后再循环,而不是每一步循环多次
二、BN层(BatchNormalization)
BN层结构是由谷歌团队在2015年提出的,通过该方法可以加速网络收敛并提升准确率。
1、BN层原理
由于图像预处理中通常会进行标准化处理,来加速网络收敛,这样对于conv1来说输入的特征矩阵是满足一定分布的,但是对于conv2所输入的特征矩阵就不一定遵循这一分布规律了,而BN层的目的就是使我们的特征矩阵满足均值为0,方差为1的高斯分布。
2、注意事项
(1)在使用BN层时要注意conv层中bias要置为False,在数学运算后bias=True和False输出的效果相同,但增加了参数与计算量
(2)BN层要放在conv层和Relu层之间
三、ResNet网络的实现
BasicBlock类用于resnet18和resnet34网络,Bottleneck类用于更深层的网络
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
class BasicBlock(nn.Module): #仅限于resnet-18和resnet-34
expansion = 1
def __init__(self,in_channel,out_channel,stride=1,downsample=None):
super(BasicBlock,self).__init__()
self.conv1=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel,out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3,stride=stride,padding=1,bias=False) #bias为什么去False?由于BN层存在的缘故
self.bn1=nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel) #BN层
self.relu=nn.ReLU()
self.conv2=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel,out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False)
self.bn2=nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.downsample=downsample
def forward(self,x):
identity=x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity=self.downsample(x) #虚线部分的捷径
out=self.conv1(x) #实线部分
out=self.bn1(out)
out=self.relu(out)
out=self.conv2(out)
out=self.bn2(out)
out+=identity
out=self.relu(out) #在实线和虚线相加之后再进入激活函数
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module): #仅限于resnet-50,resnet-101和resnet-151
expansion=4
def __init__(self,in_channel,out_channel,stride=1,downsample=None):
super(Bottleneck,self).__init__()
self.conv1=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel,out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=1,stride=1,bias=False)
self.bn1=nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.conv2=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel,out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3,stride=stride,bias=False,padding=1)
self.bn2=nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.conv3=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel,out_channels=out_channel*self.expansion, #注意这里输出为4倍关系
kernel_size=1,stride=1,bias=False)
self.bn3=nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel*self.expansion)
self.relu=nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample=downsample
def forward(self,x):
identity=x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity=self.downsample(x)
out=self.conv1(x)
out=self.bn1(out)
out=self.relu(out)
out=self.conv2(out)
out=self.bn2(out)
out=self.relu(out)
out=self.conv3(out)
out=self.bn3(out)
out+=identity
out=self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
block, #block为BasicBlock(resnet18,resnet34)或Bottleneck(resnet50,resnet101,resnet151)
blocks_num, #conv2,conv3,conv4,conv5的倒残差结构具体的个数
num_classes=1000,
include_top=True) : #为进一步增加Resnet结构做铺垫
#groups=1,
#width_per_group=64): #组卷积个数,对于Resnext网络而言
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.include_top = include_top
self.in_channel = 64
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2, #conv1
padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1) #conv2
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, blocks_num[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, blocks_num[1], stride=2) #conv3
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, blocks_num[2], stride=2) #conv4
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, blocks_num[3], stride=2) #conv5
if self.include_top:
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # output size = (1, 1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes) #输出是2048=512*4
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): #对卷积层的初始化操作
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
def _make_layer(self, block, channel, block_num, stride=1): #本质通过循环创建conv的若干层
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != channel * block.expansion: #如果存在conv2中stride为1或者resnet50,resnet101,resnet151中倒残差结构(64-64-256)
#中后一个64到256则需要升维
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channel, channel * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channel * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
downsample=downsample,
stride=stride))
self.in_channel = channel * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, block_num): #一个conv中的循环的个数,例如resnet50中conv2循环3次
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel
))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def resnet34(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth
return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet50(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet101(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)四、ResNext网络概述
ResNext网络可以看做是VGG,Inception,ResNet网络的组合体,体现了VGG网络的堆叠网络形式,Inception网络的split-transform-merge和ResNet的残差结构,有效避开了Inception网络中对于超参数设定的针对性较强,应用在其他数据集时需要修改若干参数,可扩展性一般的问题。
在2017CVPR上提出了ResNext 网络架构,主要原因是通过不增加参数复杂度的前提下提高准确率,得益于组卷积的拓扑结构,减少超参数的数量。论文中与ResNet的网络架构对比如下:
五、ResNext网络实现
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None, **kwargs):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
"""
注意:原论文中,在虚线残差结构的主分支上,第一个1x1卷积层的步距是2,第二个3x3卷积层步距是1。
但在pytorch官方实现过程中是第一个1x1卷积层的步距是1,第二个3x3卷积层步距是2,
这么做的好处是能够在top1上提升大概0.5%的准确率。
可参考Resnet v1.5 https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/model-scripts/nvidia:resnet_50_v1_5_for_pytorch
"""
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None,
groups=1, width_per_group=64):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
width = int(out_channel * (width_per_group / 64.)) * groups
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=width,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # squeeze channels
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(width)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=width, out_channels=width, groups=groups,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(width)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=width, out_channels=out_channel*self.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # unsqueeze channels
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel*self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
block,
blocks_num,
num_classes=1000,
include_top=True,
groups=1, #初始组卷积数为1,就是ResNet结构
width_per_group=64):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.include_top = include_top
self.in_channel = 64
self.groups = groups
self.width_per_group = width_per_group
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2,
padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, blocks_num[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, blocks_num[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, blocks_num[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, blocks_num[3], stride=2)
if self.include_top:
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # output size = (1, 1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
def _make_layer(self, block, channel, block_num, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != channel * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channel, channel * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channel * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
downsample=downsample,
stride=stride,
groups=self.groups,
width_per_group=self.width_per_group))
self.in_channel = channel * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, block_num):
layers.append(block(self.in_channel,
channel,
groups=self.groups,
width_per_group=self.width_per_group))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def resnet34(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth
return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet50(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet101(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnext50_32x4d(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth
groups = 32
width_per_group = 4
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],
num_classes=num_classes,
include_top=include_top,
groups=groups,
width_per_group=width_per_group)
def resnext101_32x8d(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext101_32x8d-8ba56ff5.pth
groups = 32
width_per_group = 8
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],
num_classes=num_classes,
include_top=include_top,
groups=groups,
width_per_group=width_per_group)参考视频:6.1 ResNet网络结构,BN以及迁移学习详解_哔哩哔哩_bilibili