字符图像
字符图像
——《C++沉思录》第9章 一个课堂练习的分析(上)
设计一个字符图像,用字符代替像素,实现的基本操作有加边框、将两个图像横排、竖排等。然后再对其进行一些扩展:横排下边对齐、竖排右边对齐、将重载运算符封装、去边框处理等。
具体细节详见代码和注释。
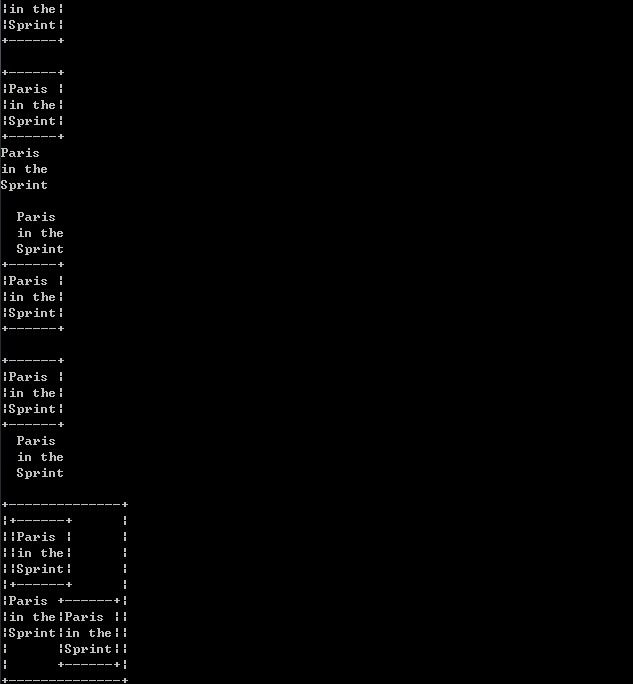
// 字符图像 #include <iostream> #include <assert.h> using namespace std; // 图像类 class Picture { private: int height; // 高 int width; // 宽 char* data; // 可用string代替 int isframe; // 标示是否有边框,其值表示边框数 private: void copyblock(int, int, const Picture&); // 块拷贝 void copyblock2(int, int, const Picture&, int, int, int, int); // 块拷贝第二版 char& position(int, int); char position(int, int) const; void clear(int, int, int, int); // 将矩形内的字符清空为空格 void init(int, int); // 初始化 static int max(int, int); public: Picture(); Picture(const char* const*, int); Picture(const Picture&); ~Picture(); Picture& operator = (const Picture&); // 友元 friend ostream& operator << (ostream&, const Picture&); // 添加边框 friend Picture frame(const Picture&); // 去边框 friend Picture removeframe(const Picture&); // 竖排,左边并齐 friend Picture operator & (const Picture&, const Picture&); // 竖排,右边并齐 friend Picture operator + (const Picture&, const Picture&); // 横排,上边并齐 friend Picture operator | (const Picture&, const Picture&); // 横排,下边并齐 friend Picture operator * (const Picture&, const Picture&); }; int Picture::max(int m, int n) { return m > n ? m : n; } char& Picture::position(int row, int col) { return data[row * width + col]; } char Picture::position(int row, int col) const { return data[row * width + col]; } void Picture::init(int h, int w) { height = h; width = w; data = new char[height * width]; isframe = 0; } // 可以用memset函数填充空格,避免clear以及补充空格操作 void Picture::clear(int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2) { for (int r = r1; r < r2; ++r) { for (int c = c1; c < c2; ++c) { position(r, c) = ' '; } } } // 将图像p从(0,0)拷贝到(row,col)起始的区域 void Picture::copyblock(int row, int col, const Picture& p) { for (int i = 0; i < p.height; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < p.width; ++j) { position(i + row, j + col) = p.position(i, j); } } } // copyblock实现的功能是将p拷贝到自身,p是从第一个字符开始拷贝的 // 这里我们实现一个可以指定p的起始字符位置 void Picture::copyblock2(int row, int col, const Picture& p, int prow, int pcol, int h, int w) { for (int i = 0; i < h; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < w; ++j) { position(row + i, col + j) = p.position(prow + i, pcol + j); } } } Picture::Picture() : height(0), width(0), data(0), isframe(0) {} Picture::Picture(const char* const* array, int n) { int w = 0; int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { w = Picture::max(w, strlen(array[i])); } init(n, w); for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { const char* src = array[i]; int len = strlen(src); int j = 0; while (j < len) { position(i, j) = src[j]; ++j; } while (j < width) { position(i, j) = ' '; ++j; } } } Picture::Picture(const Picture& p) : height(p.height), width(p.width), data(new char[p.height * p.width]), isframe(p.isframe) { copyblock(0, 0, p); } Picture::~Picture() { delete [] data; } Picture& Picture::operator = (const Picture& p) { if (this != &p) { delete [] data; init(p.height, p.width); isframe = p.isframe; copyblock(0, 0, p); } return *this; } ostream& operator << (ostream& o, const Picture& p) { for (int i = 0; i < p.height; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < p.width; ++j) { o << p.position(i, j); } o << endl; } return o; } Picture frame(const Picture& p) { Picture r; r.init(p.height + 2, p.width + 2); r.isframe = p.isframe + 1; // 将左右边放上'|'字符 for (int i = 1; i < r.height - 1; ++i) { r.position(i, 0) = '|'; r.position(i, r.width - 1) = '|'; } // 将上下边放上'-'字符 for (int i = 1; i < r.width - 1; ++i) { r.position(0, i) = '-'; r.position(r.height - 1, i) = '-'; } // 将四个角放上'+'字符 r.position(0, 0) = '+'; r.position(0, r.width - 1) = '+'; r.position(r.height - 1, 0) = '+'; r.position(r.height - 1, r.width - 1) = '+'; r.copyblock(1, 1, p); return r; } Picture removeframe(const Picture& p) { if (p.isframe == 0) { return p; } Picture r; assert(p.height >= 2 && p.width >= 2); r.init(p.height - 2, p.width - 2); r.isframe = p.isframe - 1; r.copyblock2(0, 0, p, 1, 1, r.height, r.width); return r; } // 竖排,左边并齐 Picture operator & (const Picture& p, const Picture& q) { Picture r; r.init(p.height + q.height, Picture::max(p.width, q.width)); // 将多余的矩形空间置为空格 r.clear(0, p.width, p.height, r.width); r.clear(p.height, q.width, r.height, r.width); r.copyblock(0, 0, p); r.copyblock(p.height, 0, q); return r; } // 竖排,右边并齐 Picture operator + (const Picture& p, const Picture& q) { Picture r; r.init(p.height + q.height, Picture::max(p.width, q.width)); // 将多余的矩形置为空格 r.clear(0, 0, p.height, r.width - p.width); r.clear(p.height, 0, r.height, r.width - q.width); r.copyblock(0, r.width - p.width, p); r.copyblock(p.height, r.width - q.width, q); return r; } // 对竖排封装 Picture vcatleft(const Picture& p, const Picture& q) { return p & q; } Picture vcatright(const Picture& p, const Picture& q) { return p + q; } // 横排,上边并齐 Picture operator | (const Picture& p, const Picture& q) { Picture r; r.init(Picture::max(p.height, q.height), p.width + q.width); r.clear(p.height, 0, r.height, p.width); r.clear(q.height, p.width, r.height, r.width); r.copyblock(0, 0, p); r.copyblock(0, p.width, q); return r; } // 横排,下边并齐 Picture operator * (const Picture& p, const Picture& q) { Picture r; r.init(Picture::max(p.height, q.height), p.width + q.width); r.clear(0, 0, r.height - p.height, p.width); r.clear(0, p.width, r.height - q.height, r.width); r.copyblock(r.height - p.height, 0, p); r.copyblock(r.height - q.height, p.width, q); return r; } // 对横排封装 Picture hcatabove(const Picture& p, const Picture& q) { return p | q; } Picture hcatbelow(const Picture& p, const Picture& q) { return p * q; } // 测试 int main() { char* init[] = {"Paris", "in the", "Sprint"}; // 新建图像 Picture p(init, 3); cout << p << endl; // 加边框 Picture q = frame(p); cout << q << endl; // 去边框 Picture r = removeframe(q); cout << r << endl; // 再去边框 Picture s = removeframe(r); cout << s << endl; // 再加边框 Picture t = frame(q); cout << t << endl; // 去边框1 Picture u1 = removeframe(t); cout << u1 << endl; // 去边框2 Picture u2 = removeframe(u1); cout << u2 << endl; // 去边框3 Picture u3 = removeframe(u2); cout << u3 << endl; // 横排,上边并齐 Picture v1 = p | q; cout << v1 << endl; Picture v3 = q | p; cout << v3 << endl; // 横排,下边并齐 Picture v2 = p * q; cout << v2 << endl; Picture v4 = q * p; cout << v4 << endl; // 竖排,左边并齐 Picture w1 = p & q; cout << w1 << endl; Picture w3 = q & p; cout << w3 << endl; // 竖排,下边并齐 Picture w2 = p + q; cout << w2 << endl; Picture w4 = q + p; cout << w4 << endl; // 组合 Picture x = frame(q & v1); cout << x << endl; return 0; }
以上是对图像的表象进行的处理,没涉及图像深层结构。图像处理是一门很有意思的学科。