Non-maximum Suppression (NMS) 流程回顾
前言
NMS全称Non-maximum Suppression,非极大值抑制。通常用于检测任务中的bbox去冗余。
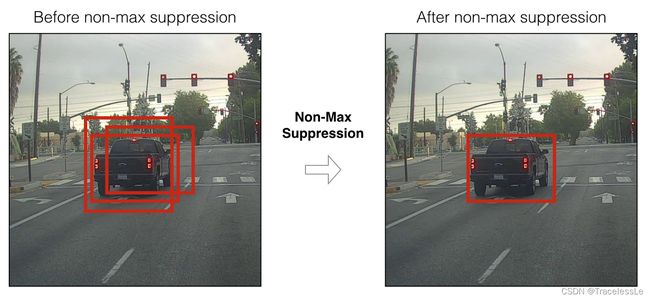
流程分析
procedure NMS(dets, thresh): # dets->bboxes, thresh->filter iou thresh
keep = [] # a list to put final picked bbox indexes
x1, y1, x2, y2, scores = dets[:, idx] # parse bboxes
order = scores.argsort()[::-1] # sort reverse by scores
while order.size > 0: # need compare bboxes not empty
i = order[0] # largest score bbox
keep.append(i) # add this bbox to list
inter_area = bbox_i ∩ bbox_others # cal inter
iou = inter_area/union_area # cal iou
inds = bbox(iou<=thresh) # choose rest bboxes by iou (drop bboxes which iou>thresh)
order = order[inds+1] # update compare list
return keep # return remained bbox indexes
代码实现
Python版本
来源:https://github.com/rbgirshick/py-faster-rcnn/blob/master/lib/nms/py_cpu_nms.py#L10
# --------------------------------------------------------
# Fast R-CNN
# Copyright (c) 2015 Microsoft
# Licensed under The MIT License [see LICENSE for details]
# Written by Ross Girshick
# --------------------------------------------------------
import numpy as np
def py_cpu_nms(dets, thresh):
"""Pure Python NMS baseline."""
x1 = dets[:, 0] # bbox左上角点x坐标
y1 = dets[:, 1] # bbox左上角点y坐标
x2 = dets[:, 2] # bbox右下角点x坐标
y2 = dets[:, 3] # bbox右下角点y坐标
scores = dets[:, 4] # 检测得分
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1) # 每一个bbox自身面积
order = scores.argsort()[::-1] # 按得分逆序排序得到新的bbox的顺序
keep = [] # 用于存放保留的bboxes的list
while order.size > 0: # 一直处理直至需要比较的bbox为空
i = order[0] # 当前需要比较的bboxes中得分最大的那个
keep.append(i) # 加入存放list
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]]) # 以下四行是用于求
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]]) # 其他bbox与该bbox
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]]) # 的交集部分的坐标点:
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]]) # 左上点和右下点
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1) # 交集部分的宽
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1) # 交集部分的高
inter = w * h # 交集面积
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter) # iou
inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0] # 去除iou大于thresh的bbox,保留剩下的用于下一轮比较
order = order[inds + 1] # 由于ovr数组长度比原order小1,所以index需要加1,这样取得的才是剩下的下一轮比较的bboxes
return keep # 返回过滤后得到的bbox在原dets中的索引
if __name__ == "__main__":
bbox = np.array([[1,2,3,5,0.7], [1,3,2,5,0.9], [2,3,3,4,0.5]])
thresh=0.4
keep = py_cpu_nms(bbox, thresh)
print(keep)
输出:
[1, 2]
PyTorch版本
来源:https://github.com/biubug6/Pytorch_Retinaface/blob/b984b4b775/utils/box_utils.py#L264
def nms(boxes, scores, overlap=0.5, top_k=200):
"""Apply non-maximum suppression at test time to avoid detecting too many
overlapping bounding boxes for a given object.
Args:
boxes: (tensor) The location preds for the img, Shape: [num_priors,4].
scores: (tensor) The class predscores for the img, Shape:[num_priors].
overlap: (float) The overlap thresh for suppressing unnecessary boxes.
top_k: (int) The Maximum number of box preds to consider.
Return:
The indices of the kept boxes with respect to num_priors.
"""
keep = torch.Tensor(scores.size(0)).fill_(0).long()
if boxes.numel() == 0:
return keep
x1 = boxes[:, 0]
y1 = boxes[:, 1]
x2 = boxes[:, 2]
y2 = boxes[:, 3]
area = torch.mul(x2 - x1, y2 - y1)
v, idx = scores.sort(0) # sort in ascending order
# I = I[v >= 0.01]
idx = idx[-top_k:] # indices of the top-k largest vals
xx1 = boxes.new()
yy1 = boxes.new()
xx2 = boxes.new()
yy2 = boxes.new()
w = boxes.new()
h = boxes.new()
# keep = torch.Tensor()
count = 0
while idx.numel() > 0:
i = idx[-1] # index of current largest val
# keep.append(i)
keep[count] = i
count += 1
if idx.size(0) == 1:
break
idx = idx[:-1] # remove kept element from view
# load bboxes of next highest vals
torch.index_select(x1, 0, idx, out=xx1)
torch.index_select(y1, 0, idx, out=yy1)
torch.index_select(x2, 0, idx, out=xx2)
torch.index_select(y2, 0, idx, out=yy2)
# store element-wise max with next highest score
xx1 = torch.clamp(xx1, min=x1[i])
yy1 = torch.clamp(yy1, min=y1[i])
xx2 = torch.clamp(xx2, max=x2[i])
yy2 = torch.clamp(yy2, max=y2[i])
w.resize_as_(xx2)
h.resize_as_(yy2)
w = xx2 - xx1
h = yy2 - yy1
# check sizes of xx1 and xx2.. after each iteration
w = torch.clamp(w, min=0.0)
h = torch.clamp(h, min=0.0)
inter = w*h
# IoU = i / (area(a) + area(b) - i)
rem_areas = torch.index_select(area, 0, idx) # load remaining areas)
union = (rem_areas - inter) + area[i]
IoU = inter/union # store result in iou
# keep only elements with an IoU <= overlap
idx = idx[IoU.le(overlap)]
return keep, count
版权说明
本文为原创文章,独家发布在blog.csdn.net/TracelessLe。未经个人允许不得转载。如需帮助请email至[email protected]。
![]()
参考资料
[1] py-faster-rcnn/py_cpu_nms.py at master · rbgirshick/py-faster-rcnn
[2] Pytorch_Retinaface/box_utils.py at b984b4b775b2c4dced95c1eadd195a5c7d32a60b · biubug6/Pytorch_Retinaface
[3] 非极大值抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression,NMS) - 康行天下 - 博客园
[4] Non-maximum Suppression (NMS). A Technique to remove duplicates and… | by Sambasivarao. K | Towards Data Science
[5] Non Maximum Suppression: Theory and Implementation in PyTorch
[6] Non Max Suppression (NMS). What is Non Max Suppression, and why is… | by Vineeth S Subramanyam | Analytics Vidhya | Medium
[7] Non-max Suppression - Object Detection | Coursera
[8] 吴恩达deep learning ai 笔记总结(4-3) 目标检测_keke_Memory的博客-CSDN博客
