pytorch1.7教程实验——DCGAN生成对抗网络
教程原网址:https://pytorch.apachecn.org/#/docs/1.7/22
DCGAN 是上述 GAN 的直接扩展,不同之处在于,DCGAN 分别在判别器和生成器中分别使用卷积和卷积转置层。 它最早由 Radford 等人,在论文《使用深度卷积生成对抗网络的无监督表示学习》中描述。 判别器由分层的卷积层,批量规范层和 LeakyReLU 激活组成。 输入是3x64x64的输入图像,输出是输入来自真实数据分布的标量概率。 生成器由转置卷积层,批量规范层和 ReLU 激活组成。 输入是从标准正态分布中提取的潜向量z,输出是3x64x64 RGB 图像。 跨步的转置层使潜向量可以转换为具有与图像相同形状的体积。 在本文中,作者还提供了一些有关如何设置优化器,如何计算损失函数以及如何初始化模型权重的提示,所有这些都将在接下来的部分中进行解释。
先贴上我跑通了的代码(如果中间有什么报错,这里不做解决方法说明):
其中需要用到的celeba数据集的下载地址:http://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/CelebA.html
数据集网址打开后如下
这里有谷歌云盘和百度网盘两种方式下载,其中谷歌云盘不需登录,下载速度快,前提是可以,不然就用百度网盘,提取密码已给出。
from __future__ import print_function
#%matplotlib inline
import argparse
import os
import random
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.parallel
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.utils.data
import torchvision.datasets as dset
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision.utils as vutils
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
from IPython.display import HTML
# os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"]="TRUE" #注意会不会报libiomp5.dll的错误,会的话取消注释
# Set random seed for reproducibility
manualSeed = 999
#manualSeed = random.randint(1, 10000) # use if you want new results
print("Random Seed: ", manualSeed)
random.seed(manualSeed)
torch.manual_seed(manualSeed)
# Root directory for dataset
dataroot = "../data/celeba"
# Number of workers for dataloader
workers = 0
# Batch size during training
batch_size = 4
# Spatial size of training images. All images will be resized to this
# size using a transformer.
image_size = 64
# Number of channels in the training images. For color images this is 3
nc = 3
# Size of z latent vector (i.e. size of generator input)
nz = 100
# Size of feature maps in generator
ngf = 64
# Size of feature maps in discriminator
ndf = 64
# Number of training epochs
num_epochs = 2
# Learning rate for optimizers
lr = 0.0002
# Beta1 hyperparam for Adam optimizers
beta1 = 0.5
# Number of GPUs available. Use 0 for CPU mode.
ngpu = 1
# We can use an image folder dataset the way we have it setup.
# Create the dataset
dataset = dset.ImageFolder(root=dataroot,
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(image_size),
transforms.CenterCrop(image_size),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)),
]))
# Create the dataloader
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True, num_workers=workers)
# Decide which device we want to run on
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if (torch.cuda.is_available() and ngpu > 0) else "cpu")
# Plot some training images
real_batch = next(iter(dataloader))
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Training Images")
plt.imshow(np.transpose(vutils.make_grid(real_batch[0].to(device)[:64], padding=2, normalize=True).cpu(),(1,2,0)))
# custom weights initialization called on netG and netD
def weights_init(m):
classname = m.__class__.__name__
if classname.find('Conv') != -1:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 0.0, 0.02)
elif classname.find('BatchNorm') != -1:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, 0.02)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0)
# Generator Code
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ngpu):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.ngpu = ngpu
self.main = nn.Sequential(
# input is Z, going into a convolution
nn.ConvTranspose2d( nz, ngf * 8, 4, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 8),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf*8) x 4 x 4
nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 8, ngf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 4),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf*4) x 8 x 8
nn.ConvTranspose2d( ngf * 4, ngf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 2),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf*2) x 16 x 16
nn.ConvTranspose2d( ngf * 2, ngf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf) x 32 x 32
nn.ConvTranspose2d( ngf, nc, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.Tanh()
# state size. (nc) x 64 x 64
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.main(input)
# Create the generator
netG = Generator(ngpu).to(device)
# Handle multi-gpu if desired
if (device.type == 'cuda') and (ngpu > 1):
netG = nn.DataParallel(netG, list(range(ngpu)))
# Apply the weights_init function to randomly initialize all weights
# to mean=0, stdev=0.2.
netG.apply(weights_init)
# Print the model
print(netG)
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ngpu):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.ngpu = ngpu
self.main = nn.Sequential(
# input is (nc) x 64 x 64
nn.Conv2d(nc, ndf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf) x 32 x 32
nn.Conv2d(ndf, ndf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf*2) x 16 x 16
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 2, ndf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 4),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf*4) x 8 x 8
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 4, ndf * 8, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf*8) x 4 x 4
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 8, 1, 4, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.main(input)
# Create the Discriminator
netD = Discriminator(ngpu).to(device)
# Handle multi-gpu if desired
if (device.type == 'cuda') and (ngpu > 1):
netD = nn.DataParallel(netD, list(range(ngpu)))
# Apply the weights_init function to randomly initialize all weights
# to mean=0, stdev=0.2.
netD.apply(weights_init)
# Print the model
print(netD)
# Initialize BCELoss function
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
# Create batch of latent vectors that we will use to visualize
# the progression of the generator
fixed_noise = torch.randn(64, nz, 1, 1, device=device)
# Establish convention for real and fake labels during training
real_label = 1.
fake_label = 0.
# Setup Adam optimizers for both G and D
optimizerD = optim.Adam(netD.parameters(), lr=lr, betas=(beta1, 0.999))
optimizerG = optim.Adam(netG.parameters(), lr=lr, betas=(beta1, 0.999))
# Training Loop
# Lists to keep track of progress
img_list = []
G_losses = []
D_losses = []
iters = 0
print("Starting Training Loop...")
# For each epoch
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# For each batch in the dataloader
for i, data in enumerate(dataloader, 0):
############################
# (1) Update D network: maximize log(D(x)) + log(1 - D(G(z)))
###########################
## Train with all-real batch
netD.zero_grad()
# Format batch
real_cpu = data[0].to(device)
b_size = real_cpu.size(0)
label = torch.full((b_size,), real_label, dtype=torch.float, device=device)
# Forward pass real batch through D
output = netD(real_cpu).view(-1)
# Calculate loss on all-real batch
errD_real = criterion(output, label)
# Calculate gradients for D in backward pass
errD_real.backward()
D_x = output.mean().item()
## Train with all-fake batch
# Generate batch of latent vectors
noise = torch.randn(b_size, nz, 1, 1, device=device)
# Generate fake image batch with G
fake = netG(noise)
label.fill_(fake_label)
# Classify all fake batch with D
output = netD(fake.detach()).view(-1)
# Calculate D's loss on the all-fake batch
errD_fake = criterion(output, label)
# Calculate the gradients for this batch
errD_fake.backward()
D_G_z1 = output.mean().item()
# Add the gradients from the all-real and all-fake batches
errD = errD_real + errD_fake
# Update D
optimizerD.step()
############################
# (2) Update G network: maximize log(D(G(z)))
###########################
netG.zero_grad()
label.fill_(real_label) # fake labels are real for generator cost
# Since we just updated D, perform another forward pass of all-fake batch through D
output = netD(fake).view(-1)
# Calculate G's loss based on this output
errG = criterion(output, label)
# Calculate gradients for G
errG.backward()
D_G_z2 = output.mean().item()
# Update G
optimizerG.step()
# Output training stats
if i % 50 == 0:
print('[%d/%d][%d/%d]\tLoss_D: %.4f\tLoss_G: %.4f\tD(x): %.4f\tD(G(z)): %.4f / %.4f'
% (epoch, num_epochs, i, len(dataloader),
errD.item(), errG.item(), D_x, D_G_z1, D_G_z2))
# Save Losses for plotting later
G_losses.append(errG.item())
D_losses.append(errD.item())
# Check how the generator is doing by saving G's output on fixed_noise
if (iters % 500 == 0) or ((epoch == num_epochs-1) and (i == len(dataloader)-1)):
with torch.no_grad():
fake = netG(fixed_noise).detach().cpu()
img_list.append(vutils.make_grid(fake, padding=2, normalize=True))
iters += 1
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
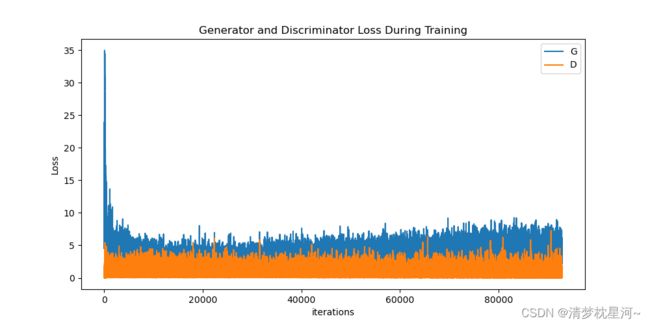
plt.title("Generator and Discriminator Loss During Training")
plt.plot(G_losses,label="G")
plt.plot(D_losses,label="D")
plt.xlabel("iterations")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
#%%capture
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
plt.axis("off")
ims = [[plt.imshow(np.transpose(i,(1,2,0)), animated=True)] for i in img_list]
ani = animation.ArtistAnimation(fig, ims, interval=1000, repeat_delay=1000, blit=True)
HTML(ani.to_jshtml())
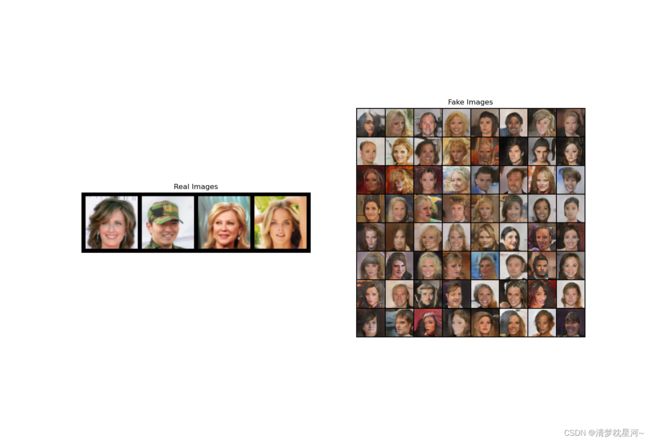
# Grab a batch of real images from the dataloader
real_batch = next(iter(dataloader))
# Plot the real images
plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Real Images")
plt.imshow(np.transpose(vutils.make_grid(real_batch[0].to(device)[:64], padding=5, normalize=True).cpu(),(1,2,0)))
# Plot the fake images from the last epoch
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Fake Images")
plt.imshow(np.transpose(img_list[-1],(1,2,0)))
plt.show()
顺利执行时的效果如下:
mation, please see http://www.intel.com/software/products/support/.
D:\code\pytorch\dcgan
(pytorch) λ python dcgan.py
Random Seed: 999
Generator(
(main): Sequential(
(0): ConvTranspose2d(100, 512, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): ConvTranspose2d(512, 256, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(4): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(5): ReLU(inplace=True)
(6): ConvTranspose2d(256, 128, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(7): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(8): ReLU(inplace=True)
(9): ConvTranspose2d(128, 64, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(10): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(11): ReLU(inplace=True)
(12): ConvTranspose2d(64, 3, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(13): Tanh()
)
)
Discriminator(
(main): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(1): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
(2): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(3): BatchNorm2d(128, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(4): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
(5): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(6): BatchNorm2d(256, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(7): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
(8): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(9): BatchNorm2d(512, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(10): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)
(11): Conv2d(512, 1, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(12): Sigmoid()
)
)
Starting Training Loop...
[0/2][0/18579] Loss_D: 1.3820 Loss_G: 12.0391 D(x): 0.8107 D(G(z)): 0.6061 / 0.0002
[0/2][50/18579] Loss_D: 0.0779 Loss_G: 7.6247 D(x): 0.9360 D(G(z)): 0.0039 / 0.0014
[0/2][100/18579] Loss_D: 0.0260 Loss_G: 16.1513 D(x): 0.9753 D(G(z)): 0.0001 / 0.0000
[0/2][150/18579] Loss_D: 0.0388 Loss_G: 13.1409 D(x): 0.9981 D(G(z)): 0.0346 / 0.0000
[0/2][200/18579] Loss_D: 0.0162 Loss_G: 7.8809 D(x): 0.9849 D(G(z)): 0.0006 / 0.0025
[0/2][250/18579] Loss_D: 0.0181 Loss_G: 9.7725 D(x): 0.9868 D(G(z)): 0.0047 / 0.0003
[0/2][300/18579] Loss_D: 0.5012 Loss_G: 12.1612 D(x): 0.9483 D(G(z)): 0.3145 / 0.0000
[0/2][350/18579] Loss_D: 1.1834 Loss_G: 4.7526 D(x): 0.6206 D(G(z)): 0.1919 / 0.0150
[0/2][400/18579] Loss_D: 1.4490 Loss_G: 9.0369 D(x): 0.7937 D(G(z)): 0.3664 / 0.0001
[0/2][450/18579] Loss_D: 1.0938 Loss_G: 9.3627 D(x): 0.9919 D(G(z)): 0.2552 / 0.0001
[0/2][500/18579] Loss_D: 0.1821 Loss_G: 5.1612 D(x): 0.8762 D(G(z)): 0.0313 / 0.0122
[0/2][550/18579] Loss_D: 0.9535 Loss_G: 4.7503 D(x): 0.5773 D(G(z)): 0.1484 / 0.0232
[0/2][600/18579] Loss_D: 0.2484 Loss_G: 3.4991 D(x): 0.8649 D(G(z)): 0.0878 / 0.0408
[0/2][650/18579] Loss_D: 3.4329 Loss_G: 8.1064 D(x): 0.8574 D(G(z)): 0.8436 / 0.0004
[0/2][700/18579] Loss_D: 0.1063 Loss_G: 3.9823 D(x): 0.9932 D(G(z)): 0.0919 / 0.0203
[0/2][750/18579] Loss_D: 0.3126 Loss_G: 3.1015 D(x): 0.8560 D(G(z)): 0.1302 / 0.0480
[0/2][800/18579] Loss_D: 0.1231 Loss_G: 6.9449 D(x): 0.9156 D(G(z)): 0.0318 / 0.0028
[0/2][850/18579] Loss_D: 0.4055 Loss_G: 2.5964 D(x): 0.7798 D(G(z)): 0.0892 / 0.0835
[0/2][900/18579] Loss_D: 0.8483 Loss_G: 4.5182 D(x): 0.5921 D(G(z)): 0.0260 / 0.0207
[0/2][950/18579] Loss_D: 1.5340 Loss_G: 1.5336 D(x): 0.3850 D(G(z)): 0.0217 / 0.2542
[0/2][1000/18579] Loss_D: 1.8439 Loss_G: 6.5032 D(x): 0.4649 D(G(z)): 0.0024 / 0.0041
[0/2][1050/18579] Loss_D: 0.4488 Loss_G: 4.1966 D(x): 0.8664 D(G(z)): 0.2313 / 0.0205
[0/2][1100/18579] Loss_D: 0.3662 Loss_G: 3.8391 D(x): 0.8769 D(G(z)): 0.1729 / 0.0323
[0/2][1150/18579] Loss_D: 0.9625 Loss_G: 4.0377 D(x): 0.6261 D(G(z)): 0.1720 / 0.0251
[0/2][1200/18579] Loss_D: 0.6242 Loss_G: 2.7605 D(x): 0.7379 D(G(z)): 0.1765 / 0.0958
[0/2][1250/18579] Loss_D: 2.9154 Loss_G: 7.8489 D(x): 0.9978 D(G(z)): 0.9003 / 0.0015
[0/2][1300/18579] Loss_D: 0.6282 Loss_G: 5.1438 D(x): 0.8800 D(G(z)): 0.2477 / 0.0209
[0/2][1350/18579] Loss_D: 2.0330 Loss_G: 2.2330 D(x): 0.2520 D(G(z)): 0.2362 / 0.1620
[0/2][1400/18579] Loss_D: 0.1549 Loss_G: 5.1178 D(x): 0.9453 D(G(z)): 0.0848 / 0.0167
[0/2][1450/18579] Loss_D: 0.1487 Loss_G: 4.1128 D(x): 0.9134 D(G(z)): 0.0419 / 0.0385
[0/2][1500/18579] Loss_D: 0.1799 Loss_G: 6.6777 D(x): 0.8656 D(G(z)): 0.0030 / 0.0013
[0/2][1550/18579] Loss_D: 0.3534 Loss_G: 3.4015 D(x): 0.8459 D(G(z)): 0.1279 / 0.0386
[0/2][1600/18579] Loss_D: 0.5875 Loss_G: 4.9939 D(x): 0.7353 D(G(z)): 0.0743 / 0.0196
[0/2][1650/18579] Loss_D: 0.3142 Loss_G: 5.3559 D(x): 0.7500 D(G(z)): 0.0065 / 0.0090
[0/2][1700/18579] Loss_D: 0.6114 Loss_G: 3.8932 D(x): 0.8574 D(G(z)): 0.3115 / 0.0213
[0/2][1750/18579] Loss_D: 0.6434 Loss_G: 6.0262 D(x): 0.6605 D(G(z)): 0.0581 / 0.0277
[0/2][1800/18579] Loss_D: 0.4345 Loss_G: 4.2774 D(x): 0.8217 D(G(z)): 0.1581 / 0.0334
[0/2][1850/18579] Loss_D: 0.1958 Loss_G: 4.5753 D(x): 0.8834 D(G(z)): 0.0593 / 0.0198
[0/2][1900/18579] Loss_D: 0.9996 Loss_G: 5.7754 D(x): 0.8214 D(G(z)): 0.4628 / 0.0032
[0/2][1950/18579] Loss_D: 0.7947 Loss_G: 4.2188 D(x): 0.7518 D(G(z)): 0.3216 / 0.0157
[0/2][2000/18579] Loss_D: 0.2939 Loss_G: 3.2757 D(x): 0.9000 D(G(z)): 0.1616 / 0.0421
[0/2][2050/18579] Loss_D: 0.5883 Loss_G: 4.5314 D(x): 0.7336 D(G(z)): 0.0686 / 0.0136
[0/2][2100/18579] Loss_D: 0.6695 Loss_G: 2.0829 D(x): 0.6109 D(G(z)): 0.1248 / 0.2239
[0/2][2150/18579] Loss_D: 2.0007 Loss_G: 2.0684 D(x): 0.1938 D(G(z)): 0.0221 / 0.2185
[0/2][2200/18579] Loss_D: 1.1943 Loss_G: 2.6751 D(x): 0.3835 D(G(z)): 0.0441 / 0.0746
[0/2][2250/18579] Loss_D: 0.9207 Loss_G: 4.7640 D(x): 0.7008 D(G(z)): 0.0192 / 0.0155
[0/2][2300/18579] Loss_D: 0.1813 Loss_G: 3.1062 D(x): 0.9910 D(G(z)): 0.1548 / 0.0528
[0/2][2350/18579] Loss_D: 0.5774 Loss_G: 2.8078 D(x): 0.7397 D(G(z)): 0.1623 / 0.0789
[0/2][2400/18579] Loss_D: 0.6620 Loss_G: 3.4095 D(x): 0.9961 D(G(z)): 0.3208 / 0.0375
[0/2][2450/18579] Loss_D: 0.2893 Loss_G: 3.8130 D(x): 0.9506 D(G(z)): 0.1999 / 0.0270
[0/2][2500/18579] Loss_D: 1.6749 Loss_G: 3.2526 D(x): 0.4009 D(G(z)): 0.3853 / 0.0411
[0/2][2550/18579] Loss_D: 0.5661 Loss_G: 4.9590 D(x): 0.9844 D(G(z)): 0.3471 / 0.0081
[0/2][2600/18579] Loss_D: 0.4371 Loss_G: 3.0584 D(x): 0.7488 D(G(z)): 0.0928 / 0.0496
[0/2][2650/18579] Loss_D: 0.9468 Loss_G: 3.0954 D(x): 0.6227 D(G(z)): 0.1914 / 0.0644
[0/2][2700/18579] Loss_D: 1.2500 Loss_G: 5.9707 D(x): 0.9393 D(G(z)): 0.6179 / 0.0030