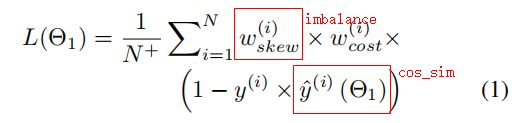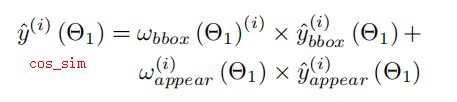FANTrack代码阅读笔记
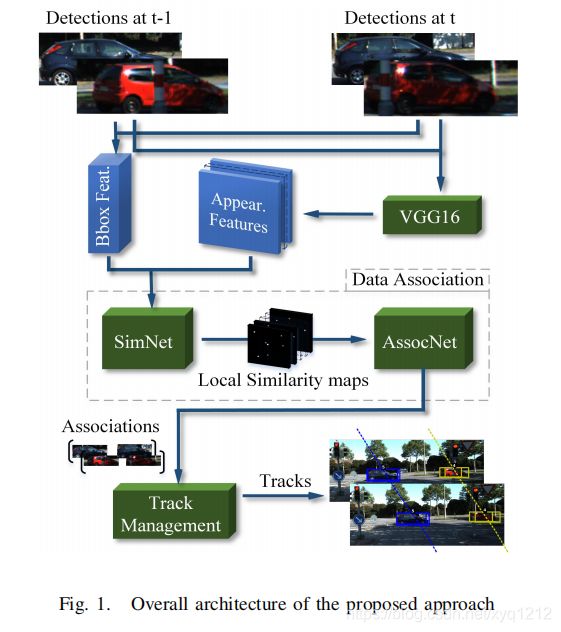
1.FANTrack系统结构图
用于相似性学习的Siamese网络:
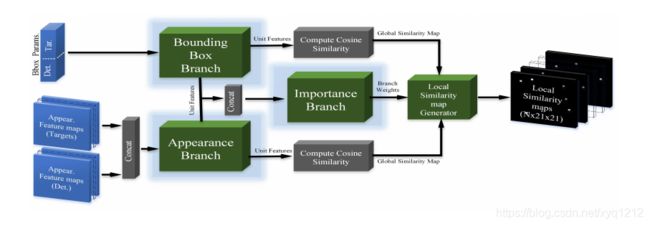
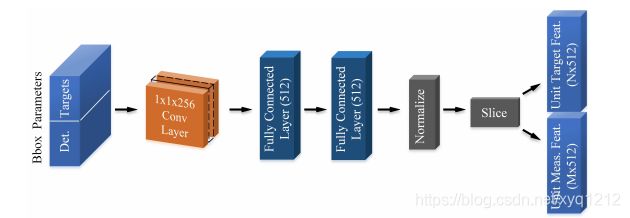
bounding box分支:
appear 分支
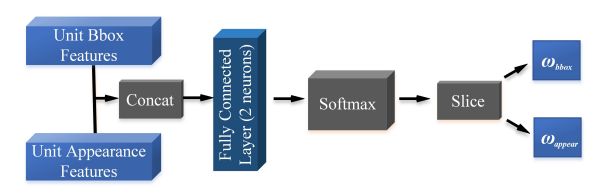
关联网络
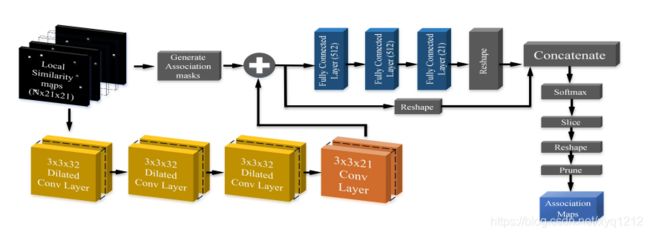
相似图的计算(用于得到最后的追踪结果,训练过程种不需要这一步)
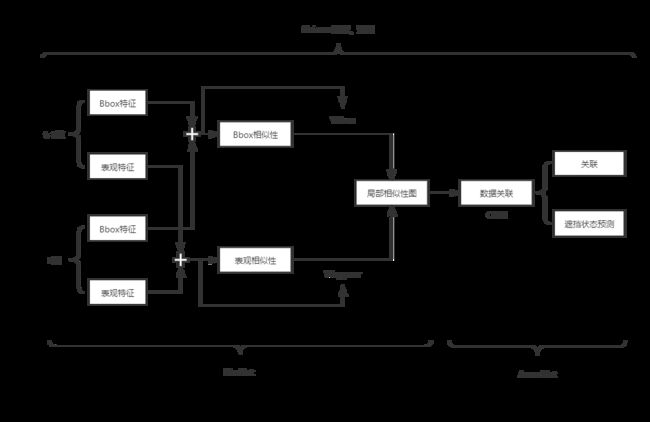
2.FANTrack我理解的框架图
与mmMOT不同的是,FANTrack先分别得到Bbox相似性矩阵和表观相似性矩阵,并基于Bbox和appear特征分别计算它们的权重,再进行加权融合得到最终的相似度矩阵。而在mmMOT中,是先融合特征,再使用融合后的特征计算相似性矩阵。
FANTrack中也加入了对遮挡状态的预测,其实就是加进来了一个网络模型,由几个全连接层组成,用来预测遮挡状态,按文中的意思是可以提高性能的,我也可以尝试加入这个小的预测模型试一下。
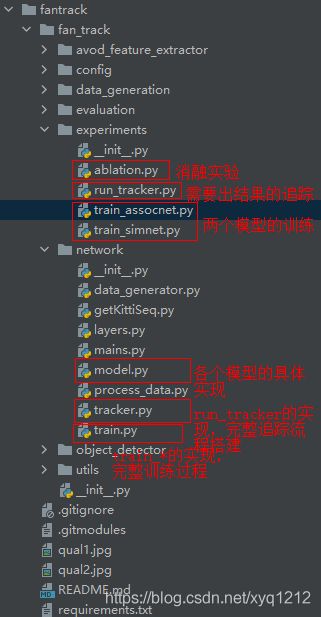
3.FANTrack代码结构
这个代码没有像mmMOT一样模块化做得很好,把相同类型的全部放在了一个文件中,简单的对实现和框架构建做了分离,感觉添加模块可能会比较困难
4.代码解读
Tracker.py
完整的追踪流程,包括Kalman过滤器的预测、数据关联(特征计算、相似度计算、轨迹关联)、轨迹管理(新增、更新、删除)
追踪算法如下:
有三个类,Track、TrackedObject、Tracker,分别代表轨迹、以追踪的目标、追踪器
- class Track:Kalman过滤器相关、轨迹相关
- init:初始化,track_id、current_target、age、type等轨迹相关参数,F/H/P/Q/R等Kalman过滤器相关参数
- 矩阵获取函数:get_P_matrix、get_R_matrix、get_Q_matrix
- 轨迹更新:update()
- 轨迹预测:predict()
- class TrackedObject:已追踪成功的目标相关
- init:初始化,track_id、occluded、truncated等
- 写文件函数
- 标签更新函数
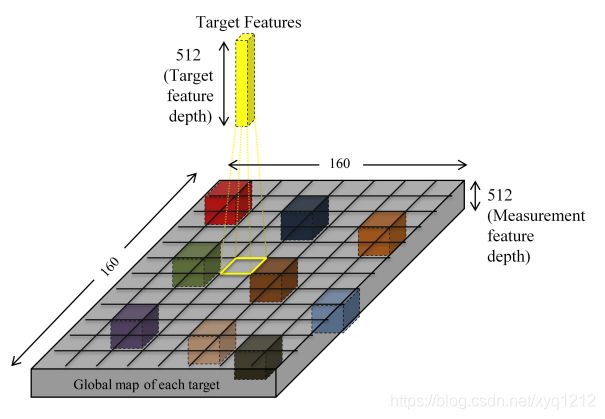
- def build_global_maps():根据simNet的输出结果构建全局/局部相似图
- 在train.py和run simnet中调用了
- class Tracker:追踪过程
- init
- 数据准备
- 目标检测模型初始化:支持AVOD或RPN
- 构建SimNet模型
- 构建AssocNet模型
- begin_tracking():主体的追踪流程
- 计算start_frame和end_frame用于逐帧计算
- 逐帧计算
- 第1帧:为每个detection初始化新的轨迹,create_new_track()
- 非第1帧
- 预测:self.predict_tracks() (其实没有太明白predict是用来做什么的)
- 关联:associations=self.get_associations(tragets,measurements)
- 更新:self.update_tracks(tragets,measurements,associations)
- 后处理:track.age+=1、结果写文档、可视化等
- get_associations():计算关联关系,包括目标识别、计算相似度、数据关联三个大的过程
- 坐标系转换
- 相似图计算
- 计算measurement_locations、target_centers等,用于构建全局、局部相似图
- target和detections的Bbox向量和表观特征特征的获取
- run simNet,根据原始表观特征和Bbox特征得到计算相似性的feature和weights;在这里也有用于消融实验的代码,包括使用马氏距离、不使用AVOD特征、不使用Bbox特征三种消融
- 构建全局/局部相似图
- 关联关系计算
- run assocNet,得到m_pred_x,m_pred_y
- 得到关联结果:associations、corr_scores
- remap得到最终结果
- 轨迹相关函数
- create_new_track()
- destory_track()
- predict_tracks()
- update_track(),根据关联结果完成轨迹的更新、创建和删除
- 数据准备相关函数
- get_meaurements()
- get_gt_detections()
- get_object_attribute()
- get_predictions_from_avod()
- 其它函数
- check_none_associations() 处理measurements或targets为空的情况
- get_associations() 根据AssocNet的预测结果得到关联结果
- prepare_simnet_inputs() 根据measurements和tragets准备simNet的输入
- init
Train.py
有一个类Trainer,用于训练不同模型
- train_simnet()
- 初始化:设置保存、变量初始化
- 逐epoch训练
- 训练
- checkpoint保存
- 验证:validation,损失
- train_assocnet()
- 初始化:设置保存、变量初始化
- 逐epoch训练
- 训练
- checkpoint保存
- 验证:validation,损失
- run_simnet():运行simnet并保存输出(局部相似度图),作为AssocNet的输入
- 调用create_similarity_maps()
- create_similarity_maps()
- 运行simnet得到特征、权重,target_center等
- 构建local_corr_map(tracker.py->build_global_maps)
- 得到输出
- associations_results():根据预测值m_pred_x、m_pred_y得到最终关联结果
- 涉及到全局坐标和局部坐标的转换
- train_combine_network():两个网络联合训练
- 初始化:设置保存、变量初始化
- 逐epoch训练
- 训练
- checkpoint保存
- 验证:validation,损失
model.py
关联模型,有一个类AssocModel
-
init():初始化,包括Bbox shape、appearance shape、center shape、correlation shape、locations等
-
build_simnet():simnet网络的搭建
-
一些变量的初始化,包括t-1 targets的Bbox和表观向量、t目标的Bbox和表观向量、labels、tragets numbers等
self.in_bbox_tar_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, self.pos_shp_shape, 'in_bbox_tar') self.in_bbox_meas_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, self.pos_shp_shape, 'in_bbox_meas') self.in_appear_tar_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, self.appear_shape, 'in_appear_tar') self.in_appear_meas_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, self.appear_shape, 'in_appear_meas') self.simnet_labels_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, self.lab_shape, 'labels') self.training_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.bool, name = 'training') self.num_target_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,shape=[1], name = 'num_targets') self.global_step = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, name = 'global_step') self.in_bbox_ph = tf.concat([self.in_bbox_tar_ph,self.in_bbox_meas_ph], axis=0) self.in_appear_ph = tf.concat([self.in_appear_tar_ph,self.in_appear_meas_ph], axis=0) self.num_targets = self.num_target_ph[0]
-
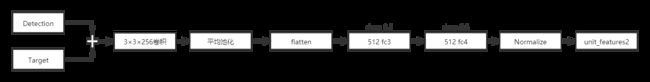
'''bbox branch'''
# cross channel pooling of 3d bbox params
self.conv1_0_act = slim.conv2d(self.in_bbox_ph, 256, 1, scope = 'conv1_0')
# flattens the bbox maps into 1D for each batch
net1 = slim.flatten(self.conv1_0_act, scope = 'feat_1d_1')
# fc layers with dropout for bbox features
net1 = slim.dropout(net1, keep_prob=0.5, scope = 'dropout1')
self.fc1_act = slim.fully_connected(net1, 512, scope='fc1')
net1 = slim.dropout(self.fc1_act, keep_prob=0.5, scope = 'dropout2')
self.fc2_act = slim.fully_connected(net1, 512, scope='fc2')
# remove the feature distribution change before normalization
features1 = slim.batch_norm(self.fc2_act,scope='ball1')
# project thself.training_phe features to unit hypersphere
self.unit_features1 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(features1, axis=1)
- appearance分支(用的自己写的网络,没有用现成的网络)
# fc layer implemented by a conv layer for avod's features
self.conv2_0_act = slim.conv2d(self.in_appear_ph, 256, 3, scope = 'conv2_0')
''' To do: The fc layer is implemented using 7x7 kernel and valid padding'''
# Global Average Pooling
# self.conv2_1_act = tf.layers.average_pooling2d(inputs=self.conv2_0_act, pool_size=7, strides=7)
self.conv2_1_act = tf.nn.avg_pool(self.conv2_0_act,ksize=[1, 7, 7, 1], strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='VALID')
# fc layer implemented by a conv layer for avod's features
# self.conv2_1_act = slim.conv2d(self.conv2_0_act, 256, 1, scope = 'conv2_1')
# flattens the bbox maps into 1D for each batch
net2 = slim.flatten(self.conv2_1_act, scope = 'feat_1d_2')
# fc layers with dropout for bbox features
net2 = slim.dropout(net2, keep_prob=0.5, scope = 'dropout3')
self.fc3_act = slim.fully_connected(net2, 512, scope='fc3')
net2 = slim.dropout(self.fc3_act, keep_prob=0.5, scope = 'dropout4')
self.fc4_act = slim.fully_connected(net2, 512, scope='fc4')
# remove the feature distribution change before normalization
features2 = slim.batch_norm(self.fc4_act,scope='ball2')
# project the features to unit hypersphere
self.unit_features2 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(features2, axis=1)
-
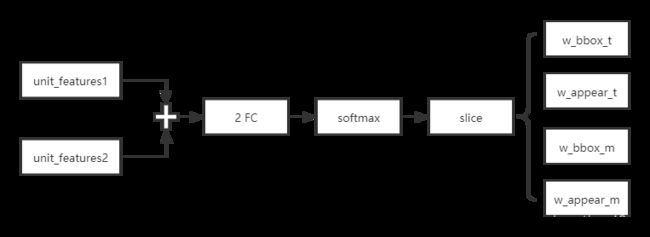
特征分离,将target和measurement拼接在一起的Bbox特征和表观特征分离,便于之后计算相似性
# slice bbox feature tensor into targets and measurements self.t_feat1 = tf.slice(self.unit_features1,[0,0],[self.num_targets,-1], 't_feat1') self.m_feat1 = tf.slice(self.unit_features1,[self.num_targets,0],[-1,-1], 'm_feat1') # slice appearance feature tensor into targets and measurements self.t_feat2 = tf.slice(self.unit_features2,[0,0],[self.num_targets,-1], 't_feat2') self.m_feat2 = tf.slice(self.unit_features2,[self.num_targets,0],[-1,-1], 'm_feat2') -
Bbox相似性和表观相似性权重的计算
# compute the weights of bbox and appearance similarities concat_feat = tf.concat((self.unit_features1,self.unit_features2), axis=1) logits = slim.fully_connected(concat_feat, 2, scope='logits') branch_weights = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=1, name='branch_weights') # slice normalized weights into bbox and appearance weights for targets and measurements self.w_bbox_t = tf.slice(branch_weights,[0,0],[self.num_targets,1], 'w_bbox_t') self.w_appear_t = tf.slice(branch_weights,[0,1],[self.num_targets,1], 'w_appear_t') self.w_bbox_m = tf.slice(branch_weights,[self.num_targets,0],[-1,1], 'w_bbox_m') self.w_appear_m = tf.slice(branch_weights,[self.num_targets,1],[-1,1], 'w_appear_m') -
定义loss、optimizer、predictor
if self.training_type == TrainingType.Simnet or self.training_type == TrainingType.Both: self.build_simnet_loss_function() -
build_simnet_loss_function()
-
分别计算表观特征和Bbox特征的cosine相似性,得到相似性矩阵之后就可以计算simNet的损失,之后进行反向传播。全局/局部相似图只需要在真正追踪的时候计算,不需要参与到模型训练的过程当中
# compute the cosine similarities self.cosine_sim1 = tf.reduce_sum( tf.multiply(self.t_feat1, self.m_feat1), 1, keepdims=True) self.cosine_sim2 = tf.reduce_sum( tf.multiply(self.t_feat2, self.m_feat2), 1, keepdims=True) -
计算Bbox和appear相似性权重,w_bbox=w_bbox_t*w_bbox_m、w_appear=w_appear_t*w_appear_m,再归一化得到对应权重
# compute weights for cosine similarities self.w_bbox = tf.multiply(self.w_bbox_t, self.w_bbox_m, 'weight_bbox') self.w_appear = tf.multiply(self.w_appear_t, self.w_appear_m, 'weight_appear') # normalize weights for each target-measurement pair w_norm_const = self.w_bbox + self.w_appear self.w_bbox = self.w_bbox / w_norm_const self.w_appear = self.w_appear / w_norm_const -
决策融合,最终相似性的计算,权重*相似性
# decision fusion self.cosine_sim = tf.add(self.w_bbox*self.cosine_sim1,self.w_appear*self.cosine_sim2,'cosine_sim') # clipcosine_sim to a value in [-1,1] self.cosine_sim = tf.clip_by_value(self.cosine_sim, -1.0, 1.0) -
计算precision和recall,计算loss并优化,损失函数是weighted cosine distance
-
-
build_assoc_model()
-
变量:局部关联图、目标数量、label、平均损失、平均准确率、epoch no
-
框架
-
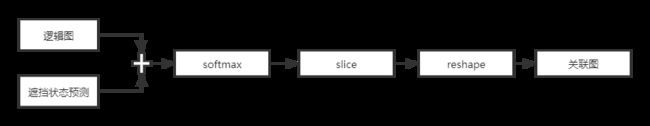
逻辑图
#初始输入为simNet计算得到的局部相似图 # input node for the first dilated convolutional layer net = self.in_local_corr_map_ph #空洞卷积 for l in range(0, num_layers): # the dilation rate for convolutional layers if (l < 2): dilation_rate = 2**(l+1) else: dilation_rate = 6 net = slim.conv2d(net,num_kernels,kernel_size,rate=dilation_rate, padding='SAME', normalizer_params={'is_training': self.in_training_assocnet_ph, 'scope': 'bn_{}'.format(str(l)) }, scope='conv_{}'.format(str(l))) # save activations to summarize their histogram hist_activations[l] = net #省略了mask的计算代码 # use this to make logits for irrelevant pixels -inf self.masks = tf.to_float(np.finfo(np.float64).min*self.masks) logits_maps = slim.conv2d(net, self.channels, kernel_size, scope='logits') # make the network predict one of the measurements if available for each targets. logits_maps = tf.add(logits_maps, self.masks, 'masked_logits') -
遮挡状态预测
# compute the logits for undetection probabilities of each targets net= slim.flatten(logits_maps, scope='flat_logit_maps') net = slim.fully_connected(net, 512, scope='fc1') net = slim.fully_connected(net, 512, scope='fc2') logits_undetect = slim.fully_connected(net, self.channels, scope='fc3')-
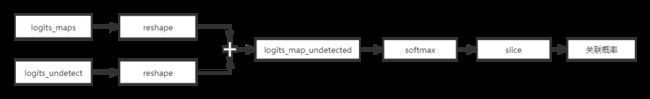
计算关联结果
# flat out maps for each target logits_maps_1d = tf.reshape(logits_maps,[1,GlobalConfig.CROP_SIZE**2,-1]) # flat out undetection logits logits_undetect_1d = tf.reshape(logits_undetect,[1, 1, -1]) # concatenate logits for maps and pixels for undetections logits_map_undetect = tf.concat([logits_maps_1d,logits_undetect_1d], axis=1) # perform softmax op on each map to compute association prob. and 1 - detection probability maps_undetect_1d =tf.nn.softmax(logits_map_undetect, axis=1) # obtain real maps for each targets maps_1d = tf.slice(maps_undetect_1d, [0,0,0], [1, GlobalConfig.CROP_SIZE**2, -1]) # obtain detection probability for each targets self.Pd = 1 - tf.slice(maps_undetect_1d, [0, GlobalConfig.CROP_SIZE**2, 0], [1,-1,-1]) # 2D predicted output maps self.maps = tf.reshape(maps_1d,tf.shape(logits_maps)) -
后处理:直方图统计、无关信息的移除(设置固定数量的轨迹解决轨迹动态变化的问题,在这里把那些dummy轨迹移除)
-
precision和recall
-
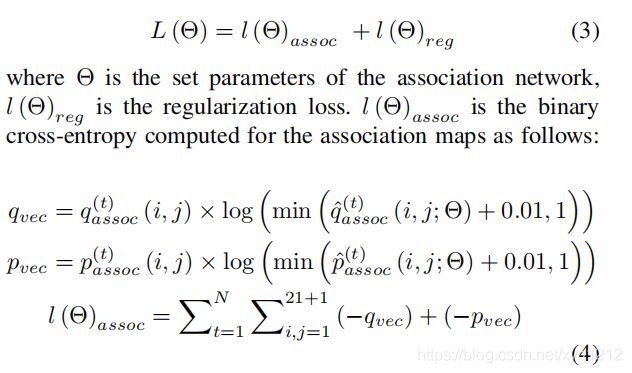
损失函数,assoc损失是交叉熵损失
-
后处理:直方图统计、无关信息的移除(设置固定数量的轨迹解决轨迹动态变化的问题,在这里把那些dummy轨迹移除)
-
precision和recall
-