实验四 | DPCM 压缩系统的实现和分析
DPCM压缩系统的实现和分析
一、实验目的
掌握DPCM编解码系统的基本原理。初步掌握实验用C/C++/Python等语言编程实现DPCM编码器,并分析其压缩效率。
二、实验原理
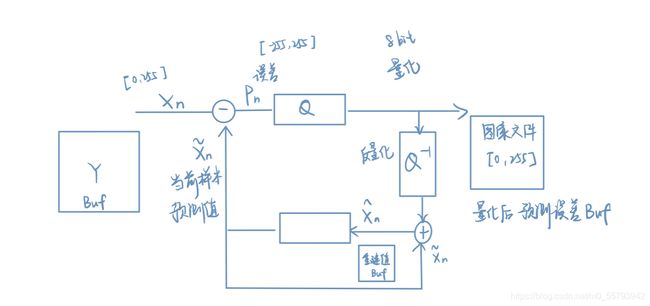
1、DPCM编解码原理
差分预测编码是预测器的输入是已经解码以后的样本。之所以不用原始样本来做预测,因为在解码端无法得到原始样本,只能得到存在误差的样本。因此,在DPCM编码器中实际内嵌了一个解码器。

2、DPCM编码系统的设计
在本次实验中,我们采用固定预测器和均匀量化器。预测器采用左侧、上方预测均可。量化器采用8比特均匀量化。


三、实验步骤
- 输入一个256*256的图像,在DPCM编码器实现的过程中可输出预测误差图像和重建图像。
- 将预测误差图像写入文件并将该文件输入Huffman编码器,得到输出码流、给出概率分布图并计算压缩比。
- 将原始图像文件输入Huffman编码器,得到输出码流、给出概率分布图并计算压缩比。
- 比较两种系统(1.DPCM+熵编码和2.仅进行熵编码)之间的编码效率(压缩比和图像质量),压缩质量以PSNR进行计算。
四、代码实现
main.cpp
#include DPCM.h
void DPCMLeft(int Width,int Height,void *yBuff,void *recBuff,void *errBuff);
int simplest_yuv420_psnr(void *yBuff1,void *yBuff2, int w, int h, int num);
DPCM.cpp
#include 五、实验结果
此处的概率分布使用作业一的yuv文件概率分布程序得出:
| 熵编码 | DPCM+熵编码 | |
|---|---|---|
| 原文件大小 | 98304字节 | 98304字节 |
| 文件大小 | 69885字节 | 45410 字节 |
| 编码效率(压缩比) | 0.71 | 0.46 |
| 压缩质量(PSNR) | 51.177 |
| YUV文件 | 概率分布 |
|---|---|
原图 |
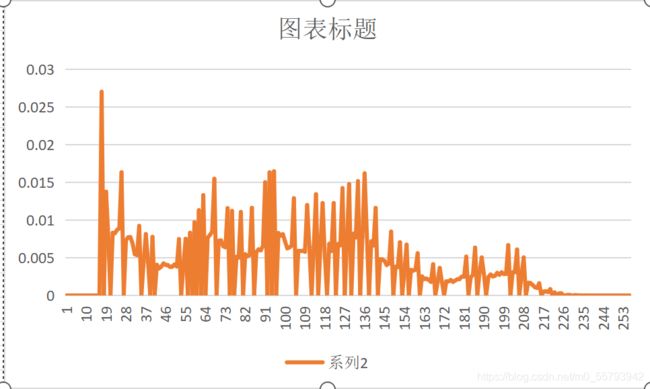 |
误差图片 |
 |
结论:
- 熵编码之后使图像压缩。DPCM+熵编码的编码效率比直接熵编码更高。
- DPCM+熵编码的PSNR值比直接熵编码的PSNR值小,经过DPCM预测编码后重建图像的压缩质量比原图的差。