《剑指offer》题解——week6(持续更新)
❤ 作者主页:Java技术一点通的博客
❀ 个人介绍:大家好,我是Java技术一点通!( ̄▽ ̄)~*
❀ 微信公众号:Java技术一点通
记得点赞、收藏、评论⭐️⭐️⭐️
认真学习!!!
文章目录
- 一、剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 代码实现
- 二、剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 代码实现
- 三、剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 代码实现
- 四、剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 代码实现
- 五、剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 代码实现
- 六、剑指 Offer 56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 代码实现
- 七、剑指 Offer 57. 和为s的两个数字
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 代码实现
- 八、剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 代码实现
- 九、剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 代码实现
- 十、剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 代码实现
一、剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
排序数组中的搜索问题,首先想到 二分法 解决。
假设我们缺失的元素数值为 x x x,那么对于 x x x 左边的元素(若有)必然是完整且连续的,也就是其必然满足 n u m s [ i ] = i nums[i] = i nums[i]=i,而其右边的元素(若有)必然由于 x 的缺失,导致必然不满足 n u m s [ i ] = i nums[i] = i nums[i]=i,因此在以缺失元素为分割点的数轴上,具有二段性,我们可以使用 「二分」 来找该分割点。
同时由于缺失元素可能是 [ 0 , n − 1 ] [0, n - 1] [0,n−1] 范围内的最大值,因此我们需要 二分结束后 再 c h e c k check check 一次,若不满足,说明缺失的元素值为 n − 1 n - 1 n−1。
3. 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector& nums) {
int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r + 1) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == mid) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
if (nums[r] == r) r ++;
return r;
}
};
二、剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
基于此性质: 二叉搜索树的中序遍历为 递增序列 。
- 根据以上性质,易得二叉搜索树 中序遍历倒序 为 递减序列。
- 因此,求 “二叉搜索树第 k k k 大的节点” 可转化为求 “此树的中序遍历倒序的第 k k k 个节点”。
算法流程:
- 终止条件: 当节点 r o o t root root 为空(越过叶节点),则直接返回;
- 递归右子树: 即
dfs(root->right); - 为求第 k k k 个节点,需要实现以下 三个步骤 :
- 提前返回: 若 k = 0 k = 0 k=0 ,代表已找到目标节点,无需继续遍历,因此直接返回;
- 统计序号: 执行 k = k − 1 k = k - 1 k=k−1 (即从 k k k 减至 0 );
- 记录结果: 若 k = 0 k = 0 k=0 ,代表当前节点为第 k k k 大的节点,因此记录 r e s = r o o t . v a l u e res = root.value res=root.value ;
- 递归左子树: 即
dfs(root->left)。
3. 代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int res;
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
dfs(root, k);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int &k) {
if (root == NULL) return;
dfs(root->right, k);
if (--k == 0) {
res = root->val;
return;
}
dfs(root->left, k);
}
};
三、剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
关键点: 此树的深度和其左(右)子树的深度之间的关系。显然,此树的深度 等于 左子树的深度 与 右子树的深度 中的 最大值 +1 。
算法流程:
- 终止条件: 当 r o o t root root 为空,说明已越过叶节点,因此返回 深度 0 。
- 递推工作: 本质上是对树做后序遍历。
- 计算节点 r o o t root root 的 左子树的深度 ,即调用
maxDepth(root->left); - 计算节点 r o o t root root 的 右子树的深度 ,即调用
maxDepth(root->right);
- 计算节点 r o o t root root 的 左子树的深度 ,即调用
- 返回值: 返回 此树的深度 ,即
max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1。
3. 代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
四、剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
平衡二叉树的定义是:二叉树的每个节点的左右子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1,则二叉树是平衡二叉树。
根据定义,一棵二叉树是平衡二叉树,当且仅当其所有子树也都是平衡二叉树,因此可以使用递归的方式判断二叉树是不是平衡二叉树。
定义函数 h e i g h t height height, 用于计算二叉树中的任意一个节点 p p p 的高度:
h e i g h t ( p ) = { 0 , p 是空节点 m a x ( h e i g h t ( p − > l e f t ) , h e i g h t ( p − > r i g h t ) ) + 1 , p 是非空节点 height(p)= \begin{cases} 0, p是空节点\\ max(height(p->left),height(p->right))+1, p是非空节点 \end{cases} height(p)={0,p是空节点max(height(p−>left),height(p−>right))+1,p是非空节点
有了计算节点高度的函数,即可判断二叉树是否平衡。具体做法类似于二叉树的前序遍历,即对于当前遍历到的节点,首先计算左右子树的高度,如果左右子树的高度差是否不超过 1,再分别递归地遍历左右子节点,并判断左子树和右子树是否平衡。
3. 代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return true;
else return abs(height(root->left) - height(root->right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);
}
int height(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
else return max(height(root->left), height(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
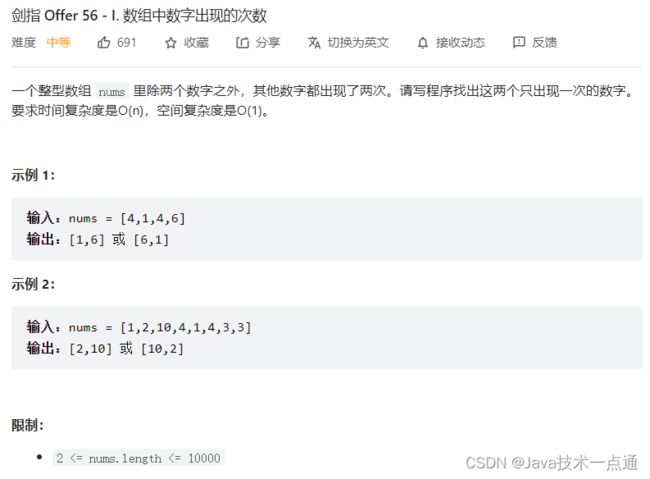
五、剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
设整型数组 n u m s nums nums 中出现一次的数字为 x x x ,出现两次的数字为 a , a , b , b , . . . a, a, b, b, ... a,a,b,b,... ,即: n u m s = [ a , a , b , b , . . . , x ] nums=[a,a,b,b,...,x] nums=[a,a,b,b,...,x]
异或运算有个重要的性质,两个相同数字异或为 0 ,即对于任意整数 a a a 有 a ⊕ a = 0 a \oplus a = 0 a⊕a=0 。因此,若将 n u m s nums nums 中所有数字执行异或运算,留下的结果则为 出现一次的数字 x x x ,即:
a ⊕ a ⊕ b ⊕ b . . . ⊕ x a \oplus a \oplus b \oplus b ... \oplus x a⊕a⊕b⊕b...⊕x
= 0 ⊕ 0 ⊕ . . . ⊕ x 0 \oplus 0 \oplus ... \oplus x 0⊕0⊕...⊕x
= x x x
本题难点:数组 n u m s nums nums 有 两个 只出现一次的数字,因此无法通过异或直接得到这两个数字。
设两个只出现一次的数字为 x , y x , y x,y ,由于 x ≠ y x \ne y x=y ,则 x x x 和 y y y 二进制至少有一位不同(即分别为 0 和 1 ),根据此位可以将 n u m s nums nums 拆分为分别包含 x x x 和 y y y 的两个子数组。
易知两子数组都满足 「除一个数字之外,其他数字都出现了两次」。因此,仿照以上简化问题的思路,分别对两子数组遍历执行异或操作,即可得到两个只出现一次的数字 x x x, y y y 。
算法流程:
-
遍历 n u m s nums nums 执行异或:
- 设整型数组 n u m s = [ a , a , b , b , . . . , x , y ] nums = [a, a, b, b, ..., x, y] nums=[a,a,b,b,...,x,y] ,对 n u m s nums nums 中所有数字执行异或,得到的结果为 x ⊕ y x \oplus y x⊕y ,即:
a ⊕ a ⊕ b ⊕ b . . . ⊕ x ⊕ y a \oplus a \oplus b \oplus b ... \oplus x \oplus y a⊕a⊕b⊕b...⊕x⊕y
= 0 ⊕ 0 ⊕ . . . ⊕ x ⊕ y 0 \oplus 0 \oplus ... \oplus x \oplus y 0⊕0⊕...⊕x⊕y
= x ⊕ y x \oplus y x⊕y
- 设整型数组 n u m s = [ a , a , b , b , . . . , x , y ] nums = [a, a, b, b, ..., x, y] nums=[a,a,b,b,...,x,y] ,对 n u m s nums nums 中所有数字执行异或,得到的结果为 x ⊕ y x \oplus y x⊕y ,即:
-
循环左移计算 m m m :
-
根据异或运算定义,若整数 x ⊕ y x \oplus y x⊕y 某二进制位为 1 ,则 x x x 和 y y y 的此二进制位一定不同。换言之,找到 x ⊕ y x \oplus y x⊕y 某为 1 的二进制位,即可将数组 n u m s nums nums 拆分为上述的两个子数组。根据与运算特点,可知对于任意整数 a a a 有:
- 若 a & 0001 = 1 a \& 0001 = 1 a&0001=1 ,则 a a a 的第一位为1 ;
- 若 a & 0010 = 1 a \& 0010 = 1 a&0010=1 ,则 a a a 的第二位为1 ;
- 依次类推…
-
因此,初始化一个辅助变量 m = 1 m = 1 m=1 ,通过与运算从右向左循环判断,可 获取整数 x ⊕ y x \oplus y x⊕y 首位 1 ,记录于 m m m 中;
-
-
拆分 n u m s nums nums 为两个子数组:
-
分别遍历两个子数组执行异或:
- 通过遍历判断 n u m s nums nums 中各数字和 m m m 做与运算的结果,可将数组拆分为两个子数组,并分别对两个子数组遍历求异或,则可得到两个只出现一次的数字。
-
返回值: 返回只出现一次的数字 x , y x, y x,y 即可。
3. 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
vector singleNumbers(vector& nums) {
int x = 0, y = 0, n = 0, m = 1;
for (int num : nums) n ^= num;
while ((n & m) == 0) m <<= 1;
for (int num : nums) {
if (num & m) x ^= num;
else y ^= num;
}
return vector {x, y};
}
};
六、剑指 Offer 56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
状态转移:
本题与前一题思路类似,前一题中,其他数都出现了两次,因此需要的状态转移方式是,如果出现两个 1 就抵消为 0 ,用一个变量和异或运算即可实现,而本题是需要 1 出现三次时才会抵消,因此有三种状态,即 1 出现的次数为 3 k , 3 k + 1 , 3 k + 2 3k, 3k + 1, 3k + 2 3k,3k+1,3k+2 次。
逐个位来看,要设计一个两位的状态转移,出现三个 1 时,循环抵消,出现 0 时不变,一个变量只能记录两种状态,因此要用两个变量来记录状态,用 o n e one one 和 t w o two two 两个变量来记录1出现次数。
00 表示 1 出现 3 k 3k 3k 次,01表示 1 出现 3 k + 1 3k + 1 3k+1 次,10 表示 1 出现 3 k + 2 3k + 2 3k+2 次。
真值表
two one x two one
0 0 1 0 1
0 1 1 1 0
1 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 1
1 0 0 1 0
先看 o n e one one 的状态转移方程:
one = (~one & ~two & x) | (one & ~two & ~x)
= ~two & ((~one & x) | (one & ~x))
= ~two & (one ^ x)
同理,再用转移后的 o n e one one 来求 t w o two two 的状态转移方程。
这里, o n e one one 为当且仅当 1 出现次数为 3 k + 1 3k + 1 3k+1, t o w tow tow 为当且仅当 1 出现次数为 3 k + 2 3k + 2 3k+2。
因此如果题目改为,有一个数出现了两次,则返回 t w o two two即可。
3. 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
int findNumberAppearingOnce(vector& nums) {
int one=0,two=0;
for(auto x:nums)
{
one=(one^x)&~two;
two=(two^x)&~one;
}
return one;
}
};
七、剑指 Offer 57. 和为s的两个数字
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
创建一个哈希表,对于每一个 x x x,我们首先查询哈希表中是否存在 t a r g e t − x target - x target−x,如果有返回 [ x , t a r g e t − x ] [x, target - x] [x,target−x]。如果没有,将 x x x 插入到哈希表中。
3. 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
vector twoSum(vector& nums, int target) {
unordered_set hash;
for (auto x : nums)
{
if (hash.count(target - x)) return {target - x, x};
hash.insert(x);
}
return {};
}
};
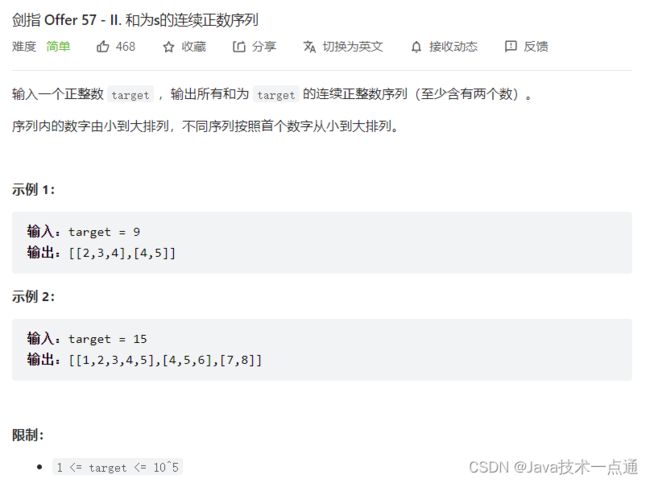
八、剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
滑动窗口(双指针):
设连续正整数序列的左边界 i i i 和右边界 j j j ,则可构建滑动窗口从左向右滑动。循环中,每轮判断滑动窗口内元素和与目标值 t a r g e t target target 的大小关系,若相等则记录结果,若大于 t a r g e t target target 则移动左边界 i i i (以减小窗口内的元素和),若小于 t a r g e t target target 则移动右边界 j j j (以增大窗口内的元素和)。
算法流程:
-
初始化: 左边界 i = 1 i = 1 i=1,有边界 j = 2 j = 2 j=2,元素和 s = 3 s = 3 s=3,结果列表 r e s res res;
-
循环:当 i ≥ j i \geq j i≥j时跳出;
- 当 s > t a r g e t s > target s>target 时:向右移动左边界 i = i + 1 i = i + 1 i=i+1,并更新元素和 s s s;
- 当 s < t a r g e t s < target s<target 时:向右移动右边界 j = j + 1 j = j + 1 j=j+1,并更新元素和 s s s;
- 当 s = t a r g e t s = target s=target 时:记录连续整数序列,并向右移动左边界 i = i + 1 i = i + 1 i=i+1;
-
返回值: 返回结果列表 r e s res res。
3. 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
vector> findContinuousSequence(int target) {
int i = 1, j = 2, s = 3;
vector> res;
while (i < j) {
if (s == target) {
vector ans;
for (int k = i; k <= j; k ++ )
ans.push_back(k);
res.push_back(ans);
}
if (s >= target) {
s -= i;
i ++;
} else {
j ++;
s += j;
}
}
return res;
}
};
九、剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
解题方法:双指针
算法流程:
- 倒序遍历字符串 s s s,记录单词左右索引边界 l e f t , r i g h t left, right left,right;
- 每确定一个单词的边界,则将其添加至单词列表 r e s res res;
- 最后,将单词列表返回即可。
3. 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
string reverseWords(string s) {
string res;
int n = s.size();
if (!n) return res;
int right = n - 1;
while (right >= 0) {
//从后往前寻找第一个字符
while (right >= 0 && s[right] == ' ') right --;
if (right < 0) break;
// 从后往前寻找第一个空格
int left = right;
while (left >= 0 && s[left] != ' ') left --;
// 添加单词到结果集
res += s.substr(left + 1, right - left);
res += ' ';
right = left;
}
// 去除最后一个字符空格
if (!res.empty()) res.pop_back();
return res;
}
};
十、剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
算法流程:
- 定义一个字符串结果集 r e s res res;
- 先向 r e s res res 中添加“第 n + 1 n + 1 n+1 位至末位的字符”;
- 再向 r e s res res 中添加“首位至第 n n n 位的字符”;
- 直接将 r e s res res 返回即可。
3. 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
string reverseLeftWords(string s, int n) {
string res;
for (int i = n; i < s.size(); i ++ ) {
res += s[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
res += s[i];
}
return res;
}
};
创作不易,如果有帮助到你,请给文章点个赞和收藏,让更多的人看到!!!
关注博主不迷路,内容持续更新中。