天池竞赛——工业蒸汽量预测(完整代码分享)
@[By 爱吃肉的小吃货]
给自己定个小目标,榜上有名。从刚开始的1263到目前的395,小目标达成。
目录
一、赛题描述
赛事链接:https://tianchi.aliyun.com/competition/entrance/231693/information
1.1 赛题背景
- 火力发电的基本原理是:燃料在燃烧时加热水生成蒸汽,蒸汽压力推动汽轮机旋转,然后汽轮机带动发电机旋转,产生电能。在这一系列的能量转化中,影响发电效率的核心是锅炉的燃烧效率,即燃料燃烧加热水产生高温高压蒸汽。锅炉的燃烧效率的影响因素很多,包括锅炉的可调参数,如燃烧给量,一二次风,引风,返料风,给水水量;以及锅炉的工况,比如锅炉床温、床压,炉膛温度、压力,过热器的温度等。
1.2 赛题描述
- 经脱敏后的锅炉传感器采集的数据(采集频率是分钟级别),根据锅炉的工况,预测产生的蒸汽量。
1.3 数据说明
- 数据分成训练数据(train.txt)和测试数据(test.txt),其中字段”V0”-“V37”,这38个字段是作为特征变量,”target”作为目标变量。选手利用训练数据训练出模型,预测测试数据的目标变量,排名结果依据预测结果的MSE(mean
square error)。
1.4 结果提交
- 选手需要提交测试数据的预测结果(txt格式,只有1列预测结果)。
1.5 结果评估
- 预测结果以mean square error作为评判标准。
二、数据导入
2.1 导库
# 导库
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split,learning_curve
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVR
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
2.2 数据读取
# 数据读取
train_data = pd.read_table('dataset/zhengqi_train.txt')
test_data = pd.read_table('dataset/zhengqi_test.txt')
print(train_data.describe())
三、数据预处理
3.1 检查有无NULL
print(train_data.isnull().sum())
- 无空值,不需要填充,继续下一步划分操作。
3.2 数据划分
train_data_X = train_data.drop(['target'], axis = 1)
train_data_y = train_data['target']
- 根据target值进行初步数据的划分
3.3 比较特征变量
- 对train和test中的38个变量特征分布进行比较,通过分布图对特征进行去除无关变量
plt.figure(figsize=(30,30))
i = 1
for col in test_data.columns:
plt.subplot(5,8,i)
sns.distplot(train_data_X[col], color = 'red')
sns.distplot(test_data[col], color = 'blue')
plt.legend(['Train', 'Test'])
i += 1
3.4 删除差异较大变量
- 根据上述对比图可知:V2,V5,V9,V11,v13,V14,V17,V19,V20,V21,V22,V27,这12个训练集和测试集的特征差异较大,予以删除
train_data_X_new = train_data_X.drop(['V2','V5','V9','V11','V13','V14','V17','V19','V20','V21','V22','V27'], axis = 1)
test_data_new = test_data.drop(['V2','V5','V9','V11','V13','V14','V17','V19','V20','V21','V22','V27'], axis = 1)
all_data_X = pd.concat([train_data_X_new,test_data_new])
3.5 数据集的切割
- 从去掉差异较大变量之后的数据,进行train_test_split
# train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(train_data_X_new, train_data_y, test_size = 0.3, random_state = 827)
四、模型训练
本文选择如下模型进行训练和融合:
-
Linear Regression
-
Linear SVR
-
RandomForest Regression
-
XGB Regression
4.1 Linear Regression
# 线性回归
def Linear_Regression(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test):
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test,model.predict(X_test))
print('Linear_Regression的训练集得分:{}'.format(model.score(X_train,y_train)))
print('Linear_Regression的测试集得分:{}'.format(model.score(X_test,y_test)))
print('Linear_Regression的测试集的MSE得分为:{}'.format(mse))
print('--------------------------------')
4.2 Linear SVR
# SVM
def Linear_SVR(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test):
model = LinearSVR()
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test,model.predict(X_test))
print('Linear_SVR的训练集得分:{}'.format(model.score(X_train,y_train)))
print('Linear_SVR的测试集得分:{}'.format(model.score(X_test,y_test)))
print('Linear_SVR的测试集的MSE得分为:{}'.format(mse))
print('--------------------------------')
4.3 RandomForest Regression
# 随机森林
def RandomForest_Regressor(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test,n_estimators = 70):
model = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators= n_estimators)
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test,model.predict(X_test))
print('RandomForest_Regressor的训练集得分:{}'.format(model.score(X_train,y_train)))
print('RandomForest_Regressor的测试集得分:{}'.format(model.score(X_test,y_test)))
print('RandomForest_Regressor的测试集的MSE得分为:{}'.format(mse))
print('--------------------------------')
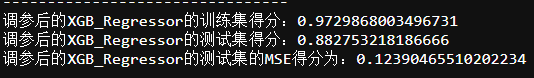
4.4 XGB Regression
# XGBRegression
def XGB_Regressor(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test):
model = XGBRegressor(objective ='reg:squarederror')
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test,model.predict(X_test))
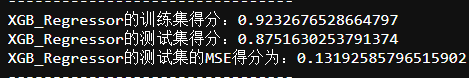
print('XGB_Regressor的训练集得分:{}'.format(model.score(X_train,y_train)))
print('XGB_Regressor的测试集得分:{}'.format(model.score(X_test,y_test)))
print('XGB_Regressor的测试集的MSE得分为:{}'.format(mse))
print('--------------------------------')
4.5 结果显示
if __name__ == '__main__':
Linear_Regression(X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test)
Linear_SVR(X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test)
RandomForest_Regressor(X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, n_estimators = 70)
XGB_Regressor(X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test)
4.6 得到每个模型的predict
# 得出每个模型的predict
lr=LinearRegression()
lr.fit(X_train,y_train)
linear_predict = lr.predict(X_test)
svr=LinearSVR()
svr.fit(X_train,y_train)
svr_predict = svr.predict(X_test)
rf=RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators = 200, max_features = 'sqrt')
rf.fit(X_train,y_train)
rf_predict = rf.predict(X_test)
xgb=XGBRegressor(learning_rate = 0.1,
n_estimators = 200,
max_depth = 6,
min_child_weight =9,
seed = 0,
subsample = 0.8,
colsample_bytree = 0.8,
gamma = 0.3,
reg_alpha = 0,
reg_lambda = 1,
objective ='reg:squarederror')
xgb.fit(X_train,y_train)
xgb_predict = xgb.predict(X_test)
对比四个模型的得分和MSE可知:
- LinearSVR < LinearRegression < RandomForestRegression < XGBRegression,故选择XGBRegression和RandomForestRegression进行测试,然后得到结果。将结果传入官网进行对比
可知,线上RandomForestRegression的MSE更低,为0.1263。
得到的结果会在下面的结果展示中具体表述。
但是,仔细一想,如果调参会不会有更好的结果呢???不妨一试。
五、调参
5.1 RandomForest Regression 调参
5.1.1 未调参之前
5.1.2 参数调整
%%time
# 随机森林 网格搜索,参数调优
param_grid= {'n_estimators':[1,5,10,15,20,25,30,35,40,45,50,55,60,65,70,75,80,85,90,95,100,125,150,200],
'max_features':('auto','sqrt','log2')}
m = GridSearchCV(RandomForestRegressor(random_state=827),param_grid)
m = m.fit(X_train,y_train)mse = mean_squared_error(y_test,m.predict(X_test))
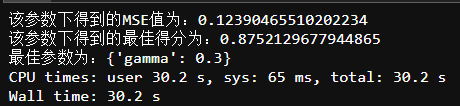
print("该参数下得到的MSE值为:{}".format(mse))
print("该参数下得到的最佳得分为:{}".format(m.best_score_))
print("最佳参数为:{}".format(m.best_params_))
RandomForest_Regressor_params = {'n_estimators':200, 'max_features':'sqrt'}
def RandomForest_Regressor_Then(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test):
model = RandomForestRegressor(** RandomForest_Regressor_params)
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test,model.predict(X_test))
print('调参后的RandomForest_Regressor的训练集得分:{}'.format(model.score(X_train,y_train)))
print('调参后的RandomForest_Regressor的测试集得分:{}'.format(model.score(X_test,y_test)))
print('调参后的RandomForest_Regressor的测试集的MSE得分为:{}'.format(mse))
print('--------------------------------')
5.1.3 最优参数结果
5.1.4 调参之后
由上述截图可知,经过调参的RandomForest Regression 结果有了一定的变化 ,由此可以看出,调参对于RandomForest Regression会产生很好的MSE。
5.2 XGB Regression 调参
5.2.1 未调参之前
5.2.2 参数调整:
参数说明:
| 最佳迭代次数 | n_estimators |
| 最小样本权重的和 | min_child_weight |
| 最大深度 | max_depth |
| 后剪枝参数 | gamma |
| 样本采样 | subsample |
| 列采样 | colsample_bytree |
| L1正则项参数 | reg_alpha |
| L2正则项参数 | reg_lambda |
| 学习率 | learning_rate |
初始参数:
# 初始参数
params = {'learning_rate': 0.1,
'n_estimators': 500,
'max_depth': 5,
'min_child_weight': 1,
'seed': 0,
'subsample': 0.8,
'colsample_bytree': 0.8,
'gamma': 0,
'reg_alpha': 0,
'reg_lambda': 1}
1.最佳迭代次数:n_estimators
param_grid= {'n_estimators':[50,100,150,200,250,300,350,400,450,500,550,600,650,700,750,800,850,900,950,1000,1250,1500,1750,2000],}

2. min_child_weight 以及 max_depth
param_grid= {'max_depth': [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10],
'min_child_weight': [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10],}
param_grid= {'gamma':
[0,0.01,0.05,0.1,0.15,0.2,0.25,0.3,0.35,0.4,0.45,0.5,0.55,0.6],}
4.样本采样subsample 和 列采样colsample_bytree
param_grid= {
'subsample': [0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9],
'colsample_bytree': [0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9],}
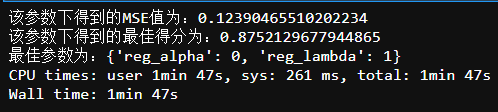
5. L1正则项参数reg_alpha 和 L2正则项参数reg_lambda
param_grid= {
'reg_alpha': [0,0.02,0.05,0.1,1,2,3],
'reg_lambda': [0,0.02,0.05,0.1,1,2,3],}
param_grid= {'learning_rate':
[0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06, 0.07, 0.08, 0.09, 0.1, 0.12, 0.14, 0.16, 0.18, 0.2,]}
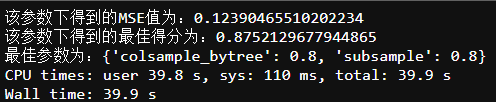
%%time
# xgb 网格搜索,参数调优
# c初始参数
# params = {'learning_rate': 0.1, 'n_estimators': 500, 'max_depth': 5, 'min_child_weight': 1, 'seed': 0,
# 'subsample': 0.8, 'colsample_bytree': 0.8, 'gamma': 0, 'reg_alpha': 0, 'reg_lambda': 1}
XGB_Regressor_Then_params = {
'learning_rate': 0.1, 'n_estimators': 200, 'max_depth': 6, 'min_child_weight': 9, 'seed': 0,
'subsample': 0.8, 'colsample_bytree': 0.8, 'gamma': 0.3, 'reg_alpha': 0, 'reg_lambda': 1}
# 最佳迭代次数:n_estimators、min_child_weight 、最大深度 max_depth、后剪枝参数 gamma、样本采样subsample 、 列采样colsample_bytree
# L1正则项参数reg_alpha 、 L2正则项参数reg_lambda、学习率learning_rate
# param_grid= {
# 'n_estimators':[50,100,150,200,250,300,350,400,450,500,550,600,650,700,750,800,850,900,950,1000,1250,1500,1750,2000],
# 'max_depth': [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10],
# 'min_child_weight': [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10],
# 'gamma': [0,0.01,0.05,0.1,0.15,0.2,0.25,0.3,0.35,0.4,0.45,0.5,0.55,0.6],
# 'subsample': [0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9],
# 'colsample_bytree': [0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9],
# 'reg_alpha': [0,0.02,0.05,0.1,1,2,3],
# 'reg_lambda': [0,0.02,0.05,0.1,1,2,3],
# 'learning_rate': [0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06, 0.07, 0.08, 0.09, 0.1, 0.12, 0.14, 0.16, 0.18, 0.2,]}
# m = GridSearchCV(XGBRegressor(objective ='reg:squarederror',**params),param_grid)
# m = m.fit(X_train,y_train)
# mse = mean_squared_error(y_test,m.predict(X_test))
# print("该参数下得到的MSE值为:{}".format(mse))
# print("该参数下得到的最佳得分为:{}".format(m.best_score_))
# print("最佳参数为:{}".format(m.best_params_))
每一步做的时候,把其他#即可。然后算出每一步的最佳参数时候,对XGB_Regressor_Then_params进行实时参数更新。
5.2.3 调参之后
六、模型融合
由于调参之后,结果也未能让那自己的小目标达成。
然后仔细思考了一下,是否可以进行模型融合。
于是,就趁热打铁,进行了模型融合——>模型取舍——>模型融合——>模型调优
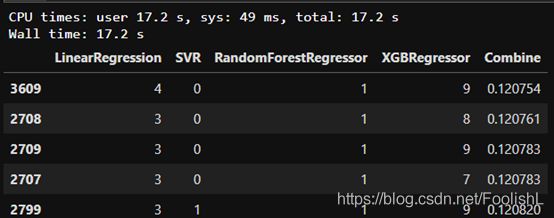
6.1 模型融合
对每个模型进行设置权重:a,b,c,d
a,b,c,d取值较小时:
# 4个模型融合
def model_mix(pred_1, pred_2, pred_3, pred_4):
result = pd.DataFrame(columns=['LinearRegression','SVR','RandomForestRegressor','XGBRegressor','Combine'])
for a in range (10):
for b in range(10):
for c in range(10):
for d in range(1,10):
y_pred = (a*pred_1 + b*pred_2 + c*pred_3 + d*pred_4) / (a+b+c+d)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred)
result = result.append([{'LinearRegression':a,
'SVR':b,
'RandomForestRegressor':c,
'XGBRegressor':d,
'Combine':mse}],
ignore_index=True)
return result
model_combine = model_mix(linear_predict, svr_predict, rf_predict, xgb_predict)
model_combine.sort_values(by='Combine', inplace=True)
model_combine.head()
a,b,c,d逐渐增大时:
%%time
# 4个模型融合
def model_mix(pred_1, pred_2, pred_3, pred_4):
result = pd.DataFrame(columns=['LinearRegression','SVR','RandomForestRegressor','XGBRegressor','Combine'])
for a in range (20):
for b in range(20):
for c in range(20):
for d in range(1,20):
y_pred = (a*pred_1 + b*pred_2 + c*pred_3 + d*pred_4) / (a+b+c+d)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred)
result = result.append([{'LinearRegression':a,
'SVR':b,
'RandomForestRegressor':c,
'XGBRegressor':d,
'Combine':mse}],
ignore_index=True)
return result
model_combine = model_mix(linear_predict, svr_predict, rf_predict, xgb_predict)
model_combine.sort_values(by='Combine', inplace=True)
model_combine.head()
模型加权融合
# 对四种模型进行加权融合
pre_lr = lr.predict(test_data_new)
pre_svr = svr.predict(test_data_new)
pre_rf = rf.predict(test_data_new)
pre_xgb = xgb.predict(test_data_new)
mix_predict = (7*pre_lr + 0*pre_svr + 1*pre_rf + 18*pre_xgb) /26
np.savetxt('download/four_mix_predict.txt',mix_predict)
print('Finished!')
6.2 模型取舍
将3种模型融合 得到0.1192.
# 将3种模型融合 得到0.1192.
pre_lr = lr.predict(test_data_new)
pre_svr = svr.predict(test_data_new)
pre_rf = rf.predict(test_data_new)
mix_predict = (10*pre_lr+0*pre_svr+12*pre_rf) / 22
np.savetxt('download/mix_predict.txt',mix_predict)
print('Finished!')
通过对上述得到的权重结论,经过对比分析,发现SVR并没有太大影响,故删去不用。
经过分析,发现XGB所占权重很高,但是,权重的提高对实验并无很大影响,故思考是否可以删去。尝试了删除,发现得到结果,反而低于加入XGB的,所以,对于XGB也做删除处理。
6.3 模型融合
%%time
# 2种模型融合
def model_mix(pred_1, pred_2):
result = pd.DataFrame(columns=['LinearRegression','RandomForestRegressor','Combine'])
for a in range (100):
for b in range(1,100):
y_pred = (a*pred_1 + b*pred_2 ) / (a+b)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred)
result = result.append([{'LinearRegression':a,
'RandomForestRegressor':b,
'Combine':mse}],
ignore_index=True)
return result
model_combine = model_mix(linear_predict, rf_predict)
model_combine.sort_values(by='Combine', inplace=True)
model_combine.head()
得到结果0.1188,进入前400
# 对2种模型进行加权融合,多次训练
pre_lr = lr.predict(test_data_new)
# pre_svr = svr.predict(test_data_new)
pre_rf = rf.predict(test_data_new)
# pre_xgb = xgb.predict(test_data_new)
mix_predict = (29*pre_lr + 41*pre_rf) /70
np.savetxt('download/lr+Rf_mix_predict.txt',mix_predict)
print('Finished!')
6.4 模型调优
%%time
# 2种模型融合,继续优化
def model_mix(pred_1, pred_2):
result = pd.DataFrame(columns=['LinearRegression','RandomForestRegressor','Combine'])
for a in range (500):
for b in range(1,500):
y_pred = (a*pred_1 + b*pred_2 ) / (a+b)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred)
result = result.append([{'LinearRegression':a,
'RandomForestRegressor':b,
'Combine':mse}],
ignore_index=True)
return result
model_combine = model_mix(linear_predict, rf_predict)
model_combine.sort_values(by='Combine', inplace=True)
model_combine.head()
得到结果0.1190
# # 对2种模型进行加权融合,多次训练
pre_lr = lr.predict(test_data_new)
# pre_svr = svr.predict(test_data_new)
pre_rf = rf.predict(test_data_new)
# pre_xgb = xgb.predict(test_data_new)
mix_predict = (275*pre_lr + 365*pre_rf) /640
np.savetxt('download/lr+Rf_Then2_mix_predict.txt',mix_predict)
print('Finished!')
七、结果展示
7.1 第一轮结果
RandomForestRegression和XGBRegression的对比之后的最优值:0.1263


7.2 第二轮结果
7.3 第三轮结果
7.4 第四轮结果
回归+SVR+随机森林
将3种模型融合,截图为当时别人成绩的排名。
对应到的成绩,成功进入前500。
完成小目标,继续优化!!
小高兴一下

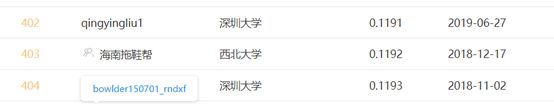
对比,第三轮结果,可以发现,xgb对我这个模型融合,起了反作用,故舍去不用。通过观察取到的数据来看,SVR所占的权重为0,所以,也舍去。故进行最新实验,只有LinearRegression+RandomForestRegression。
7.5 第五轮结果
LinearRegression+RandomForestRegression


7.6 第六轮结果
LinearRegression+RandomForestRegression
加大a,b的取值

故通过以上6轮实验结果可以得出,第五轮结果最优。为最终结果。
八、最终结果
LinearRegression+RandomForestRegression


线上提交分数:MSE = 0.1188
排名 395/7022