Integer源码详解
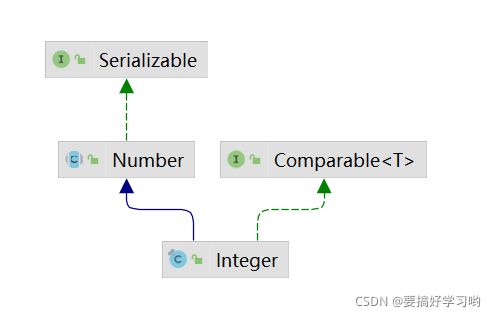
一、结构图
二、Integer类介绍
1、静态属性方法介绍
@Native public static final int MIN_VALUE = 0x80000000;
@Native public static final int MAX_VALUE = 0x7fffffff;
public static final Class<Integer> TYPE = (Class<Integer>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("int");
// 将数字表示为字符串的所有可能字符
final static char[] digits = {
'0' , '1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' ,
'6' , '7' , '8' , '9' , 'a' , 'b' ,
'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' , 'g' , 'h' ,
'i' , 'j' , 'k' , 'l' , 'm' , 'n' ,
'o' , 'p' , 'q' , 'r' , 's' , 't' ,
'u' , 'v' , 'w' , 'x' , 'y' , 'z'
};
Native注解表示定义常量值的字段可以从本机代码中引用。可以被生成本机头文件的工具用作提示,以确定是否需要头文件,如果需要,它应该包含哪些声明。
public static String toString(int i, int radix) {
// 当基数小于2或大于36时没有字母可以表示,将radix默认为10进制
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX || radix > Character.MAX_RADIX)
radix = 10;
/* Use the faster version */
// 当基数为10,调用toString方法
if (radix == 10) {
return toString(i);
}
// 因为int最大32位(2进制的时候),所以我们只需要33位就可以存储int加符号
char buf[] = new char[33];
boolean negative = (i < 0);
int charPos = 32;
// 将正数转换为负数
if (!negative) {
i = -i;
}
// 当i不能用radix进制中一个字符表示的时候,就取余赋值
while (i <= -radix) {
buf[charPos--] = digits[-(i % radix)];
i = i / radix;
}
// 将剩余的一个字符赋值
buf[charPos] = digits[-i];
// 加上符号
if (negative) {
buf[--charPos] = '-';
}
// 取数组的低位赋值部分
return new String(buf, charPos, (33 - charPos));
}
public static String toString(int i) {
// 因为要取反,所以最小整数要分开处理
if (i == Integer.MIN_VALUE)
return "-2147483648";
// 获取i的位数,负数加一
int size = (i < 0) ? stringSize(-i) + 1 : stringSize(i);
char[] buf = new char[size];
// 调用getChars方法将i和符号赋值给buf
getChars(i, size, buf);
return new String(buf, true);
}
static void getChars(int i, int index, char[] buf) {
int q, r;
int charPos = index;
char sign = 0;
if (i < 0) {
sign = '-';
i = -i;
}
// Generate two digits per iteration
// 我们在String源码中看过,这里是两位两位赋值,会快一些
while (i >= 65536) {
q = i / 100;
// really: r = i - (q * 100);
r = i - ((q << 6) + (q << 5) + (q << 2));
i = q;
buf [--charPos] = DigitOnes[r];
buf [--charPos] = DigitTens[r];
}
// Fall thru to fast mode for smaller numbers
// assert(i <= 65536, i);
// 当i<65536时,一位一位赋值
for (;;) {
q = (i * 52429) >>> (16+3);
r = i - ((q << 3) + (q << 1)); // r = i-(q*10) ...
buf [--charPos] = digits [r];
i = q;
if (i == 0) break;
}
if (sign != 0) {
buf [--charPos] = sign;
}
}
将int类型转换为radix进制的String格式。
public static String toUnsignedString(int i, int radix) {
return Long.toUnsignedString(toUnsignedLong(i), radix);
}
public static long toUnsignedLong(int x) {
return ((long) x) & 0xffffffffL;
}
转换为无符号整数。
public static String toHexString(int i) {
return toUnsignedString0(i, 4);
}
public static String toOctalString(int i) {
return toUnsignedString0(i, 3);
}
public static String toBinaryString(int i) {
return toUnsignedString0(i, 1);
}
private static String toUnsignedString0(int val, int shift) {
// assert shift > 0 && shift <=5 : "Illegal shift value";
// numberOfLeadingZerosf方法找到从最高位开始数,连续为0的个数,负数为0,0为32
int mag = Integer.SIZE - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(val);
// chars存储要用多少位存储返回的字符串
// 这里用mag + (shift - 1) 作为被除数是因为怕剩余的余数被舍去,我们想要向上取整。
int chars = Math.max(((mag + (shift - 1)) / shift), 1);
char[] buf = new char[chars];
formatUnsignedInt(val, shift, buf, 0, chars);
// Use special constructor which takes over "buf".
return new String(buf, true);
}
public static int numberOfLeadingZeros(int i) {
// HD, Figure 5-6
if (i == 0)
return 32;
int n = 1;
if (i >>> 16 == 0) { n += 16; i <<= 16; }
if (i >>> 24 == 0) { n += 8; i <<= 8; }
if (i >>> 28 == 0) { n += 4; i <<= 4; }
if (i >>> 30 == 0) { n += 2; i <<= 2; }
n -= i >>> 31;
return n;
}
// 将val转换为radix进制后长度为len的val存入buf数组中(从offset开始)
static int formatUnsignedInt(int val, int shift, char[] buf, int offset, int len) {
int charPos = len;
// 要转换的进制radix
int radix = 1 << shift;
// 掩码
int mask = radix - 1;
// 一次转换shift位
do {
buf[offset + --charPos] = Integer.digits[val & mask];
val >>>= shift;
} while (val != 0 && charPos > 0);
return charPos;
}
将数组转为16进制、8进制、二进制的字符串表示形式。
final static char [] DigitTens = {
'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0',
'1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1',
'2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2',
'3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3',
'4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4',
'5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5',
'6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6',
'7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7',
'8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8',
'9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9',
} ;
final static char [] DigitOnes = {
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
} ;
final static int [] sizeTable = { 9, 99, 999, 9999, 99999, 999999, 9999999,
99999999, 999999999, Integer.MAX_VALUE };
static int stringSize(int x) {
for (int i=0; ; i++)
if (x <= sizeTable[i])
return i+1;
}
返回x的位数
public static int parseInt(String s, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException
{
/*
* WARNING: This method may be invoked early during VM initialization
* before IntegerCache is initialized. Care must be taken to not use
* the valueOf method.
*/
if (s == null) {
throw new NumberFormatException("null");
}
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
}
if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");
}
int result = 0;
boolean negative = false;
int i = 0, len = s.length();
int limit = -Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int multmin;
int digit;
if (len > 0) {
char firstChar = s.charAt(0);
// 若firstChar < '0' 说明第一个字符是+或—。
if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-"
if (firstChar == '-') {
negative = true;
limit = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
} else if (firstChar != '+')
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
if (len == 1) // Cannot have lone "+" or "-"
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
i++;
}
// 这个变量是为了防止超过最大整数
multmin = limit / radix;
while (i < len) {
// Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE
// 获取进制为radix的字符i的整数int类型
digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix);
if (digit < 0) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
// 乘以radix之前先判断是否越界
if (result < multmin) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
result *= radix;
if (result < limit + digit) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
// 这里使用负数进行计算,因为最小负数比最大正数多一个,不然可能出现溢出
result -= digit;
}
} else {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
return negative ? result : -result;
}
// 默认十进制
public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return parseInt(s,10);
}
将radix进制的String类型整数转换为int类型。
public static int parseUnsignedInt(String s, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException {
if (s == null) {
throw new NumberFormatException("null");
}
int len = s.length();
if (len > 0) {
char firstChar = s.charAt(0);
if (firstChar == '-') {
throw new
NumberFormatException(String.format("Illegal leading minus sign " +
"on unsigned string %s.", s));
} else {
// 这里先判断String长度是否小于等于5,这是因为最大整数用36进制表示为6位,但是zzzzzz却越界了
if (len <= 5 || // Integer.MAX_VALUE in Character.MAX_RADIX is 6 digits
// 因为10进制比较常用,所以这里它专门判断是不是10进制
(radix == 10 && len <= 9) ) { // Integer.MAX_VALUE in base 10 is 10 digits
return parseInt(s, radix);
} else {
// 如果无法用parseInt来转换就需要使用长整型long
long ell = Long.parseLong(s, radix);
// 若转换后的long高32位有数字说明越界了
if ((ell & 0xffff_ffff_0000_0000L) == 0) {
return (int) ell;
} else {
throw new
NumberFormatException(String.format("String value %s exceeds " +
"range of unsigned int.", s));
}
}
}
} else {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
}
public static int parseUnsignedInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return parseUnsignedInt(s, 10);
}
将String类型的无符号数转换为int类型。
public static Integer valueOf(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException {
return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s,radix));
}
public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s, 10));
}
调用ParseInt方法将String转换为Integer。
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
// 这个是启动虚拟机的时候带的参数,可以自行设置表示缓存的最大整数
// 这时候你是不是想为什么不缓存负数呢?可以缓存,但没必要。
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
// 缓存的最大整数
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}
缓存静态内部类
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
首先判断缓存里有没有,如果有就从缓存里面拿,没有就创建一个。
public static Integer getInteger(String nm, int val) {
Integer result = getInteger(nm, null);
return (result == null) ? Integer.valueOf(val) : result;
}
public static Integer getInteger(String nm, Integer val) {
String v = null;
try {
v = System.getProperty(nm);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException | NullPointerException e) {
}
if (v != null) {
try {
return Integer.decode(v);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
}
}
return val;
}
从系统中找到名为nm所存储的值,如果没有返回默认值val。
public static Integer decode(String nm) throws NumberFormatException {
int radix = 10;
int index = 0;
boolean negative = false;
Integer result;
if (nm.length() == 0)
throw new NumberFormatException("Zero length string");
char firstChar = nm.charAt(0);
// Handle sign, if present
// 首先判断是否有符号
if (firstChar == '-') {
negative = true;
index++;
} else if (firstChar == '+')
index++;
// Handle radix specifier, if present
// 查看字符串表示的整数的进制
// 是否是16进制
if (nm.startsWith("0x", index) || nm.startsWith("0X", index)) {
index += 2;
radix = 16;
}
// 是否是16进制
else if (nm.startsWith("#", index)) {
index ++;
radix = 16;
}
// 是否是8进制
else if (nm.startsWith("0", index) && nm.length() > 1 + index) {
index ++;
radix = 8;
}
// 判断符号是否写错地方了
if (nm.startsWith("-", index) || nm.startsWith("+", index))
throw new NumberFormatException("Sign character in wrong position");
try {
// 将相应进制的字符串转换为对应的Integer类型
// 这里如果是最小负数会出错进入到下面的catch语句中处理
// 这里有点操作麻烦了,如果是我就会在这里将nm的符号一起传入
result = Integer.valueOf(nm.substring(index), radix);
// 将符号赋值给result
result = negative ? Integer.valueOf(-result.intValue()) : result;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
// If number is Integer.MIN_VALUE, we'll end up here. The next line
// handles this case, and causes any genuine format error to be
// rethrown.
String constant = negative ? ("-" + nm.substring(index))
: nm.substring(index);
result = Integer.valueOf(constant, radix);
}
return result;
}
将String类型的nm解码为Integer类型
public static int compareUnsigned(int x, int y) {
return compare(x + MIN_VALUE, y + MIN_VALUE);
}
不考虑符号的比较大小,比如在这个方法上 -1 > 1。
public static long toUnsignedLong(int x) {
return ((long) x) & 0xffffffffL;
}
将x转化为long类型,这里只保留低32位给long类型
public static int divideUnsigned(int dividend, int divisor) {
// In lieu of tricky code, for now just use long arithmetic.
return (int)(toUnsignedLong(dividend) / toUnsignedLong(divisor));
}
无符号除法
public static int remainderUnsigned(int dividend, int divisor) {
// In lieu of tricky code, for now just use long arithmetic.
return (int)(toUnsignedLong(dividend) % toUnsignedLong(divisor));
}
无符号余数
public static int highestOneBit(int i) {
// HD, Figure 3-1
i |= (i >> 1);
i |= (i >> 2);
i |= (i >> 4);
i |= (i >> 8);
i |= (i >> 16);
return i - (i >>> 1);
}
返回int的最高位的值
public static int lowestOneBit(int i) {
// HD, Section 2-1
return i & -i;
}
返回i的最低的不为0位的值。如果i = 0,则返回0。
public static int numberOfTrailingZeros(int i) {
// HD, Figure 5-14
int y;
if (i == 0) return 32;
int n = 31;
y = i <<16; if (y != 0) { n = n -16; i = y; }
y = i << 8; if (y != 0) { n = n - 8; i = y; }
y = i << 4; if (y != 0) { n = n - 4; i = y; }
y = i << 2; if (y != 0) { n = n - 2; i = y; }
return n - ((i << 1) >>> 31);
}
返回指定int值的二进制补码表示中最低位(“最右边”)一位之后的零位数。
public static int bitCount(int i) {
// HD, Figure 5-2
i = i - ((i >>> 1) & 0x55555555);
i = (i & 0x33333333) + ((i >>> 2) & 0x33333333);
i = (i + (i >>> 4)) & 0x0f0f0f0f;
i = i + (i >>> 8);
i = i + (i >>> 16);
return i & 0x3f;
}
public static int rotateLeft(int i, int distance) {
return (i << distance) | (i >>> -distance);
}
public static int rotateRight(int i, int distance) {
return (i >>> distance) | (i << -distance);
}
public static int reverse(int i) {
// HD, Figure 7-1
i = (i & 0x55555555) << 1 | (i >>> 1) & 0x55555555;
i = (i & 0x33333333) << 2 | (i >>> 2) & 0x33333333;
i = (i & 0x0f0f0f0f) << 4 | (i >>> 4) & 0x0f0f0f0f;
i = (i << 24) | ((i & 0xff00) << 8) |
((i >>> 8) & 0xff00) | (i >>> 24);
return i;
}
public static int signum(int i) {
// HD, Section 2-7
return (i >> 31) | (-i >>> 31);
}
2、方法介绍
private final int value;
public Integer(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Integer(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
this.value = parseInt(s, 10);
}
public byte byteValue() {
return (byte)value;
}
public short shortValue() {
return (short)value;
}
public int intValue() {
return value;
}
public long longValue() {
return (long)value;
}
public float floatValue() {
return (float)value;
}
public double doubleValue() {
return (double)value;
}
public String toString() {
return toString(value);
}
public int hashCode() {
return Integer.hashCode(value);
}
public static int hashCode(int value) {
return value;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue();
}
return false;
}
public int compareTo(Integer anotherInteger) {
return compare(this.value, anotherInteger.value);
}
// 比较两个无符号的值的大小
public static int compare(int x, int y) {
return (x < y) ? -1 : ((x == y) ? 0 : 1);
}
// 位数
@Native public static final int SIZE = 32;
public static final int BYTES = SIZE / Byte.SIZE;