android bindService()
bindService简介
Service一般用于不用显示,运行在后台的服务。
startService 是我们最常用的启动Service的方法。而如何让service与其他组件通信呢?一般在一个进程内,可以使用广播的方式让Service与本进程其他Actvity/service进行通信,那么还有更好的方法吗?如果要进行进程间通信(IPC)呢?
bindService就是解决这些问题的。
Binder通信机制介绍
在学习bindService之前,有必要对Binder通信机制有个基本的认识。为了提供系统全局服务,让系统中的任何应用程序都能访问这个全局服务,android设计了这个叫做Binder的client/server的通信结构。
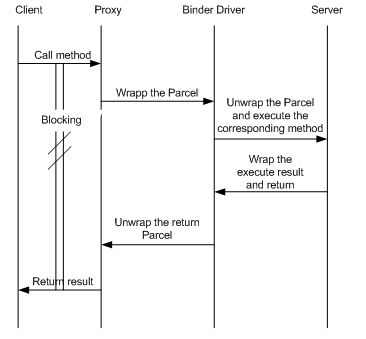
binder通信是一种client-server的通信结构,
1.从表面上来看,是client通过获得一个server的代理接口(Binder),对server进行直接调用;
2.实际上,代理接口中定义的方法与server中定义的方法是一一对应的;
3.client调用某个代理接口中的方法时,代理接口的方法会将client传递的参数打包成为Parcel对象;
4.代理接口将该Parcel发送给内核中的binder driver.
5.server会读取binder driver中的请求数据,如果是发送给自己的,解包Parcel对象,处理并将结果返回;
6.整个的调用过程是一个同步过程,在server处理的时候,client会block住。
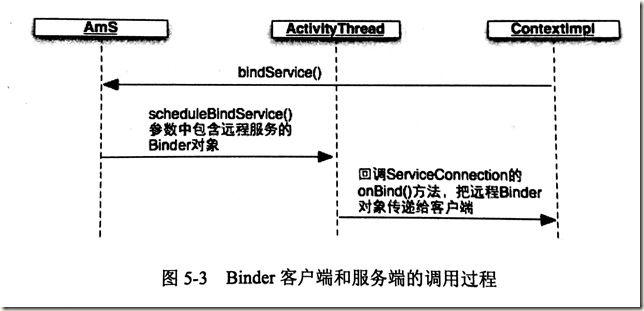
对于开发者而言,Binder通信中有个问题需要解决:客户端如何获得服务端的Binder对象应用
Service类已经解决了这个问题
bindService和Binder机制
public boolean bindService(Intent service , ServiceConnection conn, int flags);
public interface ServiceConnection {
public void onServiceConnected(ComponetName name , IBinder service);
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name);
}
当客户端请求Ams启动某个Service后,该Service如果正常启动,那么Ams就会远程调用ActivityThread类中的ApplicationThread对象,调用的参数包含Service的Binder引用,然后在ApplicationThread中会回调bindService中的conn接口。这样客户端就可以在onServiceConnected()方法中将其参数Service保存为一个全局变量。
这样,客户端(一般是activity)就可以直接访问Service中的public方法和属性了。
BindService Basics
如果要使用BindService,Service必须要实现onBind()回调方法,onBind()返回IBinder对象,这个IBinder对象就是客户端程序中onServiceConnected()方法所需要的参数IBinder。一个客户端可以使用BinderService绑定到一个Service上,此时这个客户端必须提供ServiceConnection的实现,这样才能获得从Service中返回的IBinder。
多个客户端可以绑定到一个Service,但Service只在第一个客户端BindService时才会调用onBind()。后续BindService的客户端获得的IBinder都是从Service第一次调用onBind()中返回的IBinder。
如果Service是bindService启动的(不是startService),那么当最后一个客户端unBindService(),Service将会destroy。
Android官方定义IBinder的几种方式
扩展binder类-Extending the Binder class
如果Service不需要在多个进程间工作,那么你可以实现你自己的Binder类,让客户端(一般是Activity)可以直接调用Service的public方法。(注:在同一个应用程序中,Activity和Service都属于UI线程)
- 注解:这个方法只有在客户端和Service在同一个应用程序和线程中时才可行,这种情况很常见。例如,这个方法对于一个音乐应用程序将会非常有用,它需要绑定一个Activity到它自己的Service用来以后台播放音乐。
以下为如何设定这个binder类:
1.在你的Service中,创建一个Binder类的实例,实现以下功能之一:
-
- 包含客户端可以调用的public方法
- 返回当前Service的实例,其包含了客户端可以访问的public方法
- 或返回这个Service包含的另一个类,并含有客户端可以访问的public方法
3.在客户端,从onServiceConnected()回调方法接收这个Binder,调用bindService()。
- 注解:Service和客户端必须在同一个应用程序中的原因是客户端可以计算返回的对象并恰当的调用其APIs。服务和客户端也必须在同一个线程的原因是这种技术不能执行线程间操作。
例如,以下为一个为客户端提供了通过Binder实现接入服务中方法的服务范例:
1 public class LocalService extends Service { 2 // Binder given to clients 3 private final IBinder mBinder = new LocalBinder(); 4 // Random number generator 5 private final Random mGenerator = new Random(); /** 6 * Class used for the client Binder. Because we know this service always 7 * runs in the same process as its clients, we don't need to deal with IPC. 8 */ 9 public class LocalBinder extends Binder { 10 LocalService getService() { 11 // Return this instance of LocalService so clients can call public methods 12 return LocalService.this; 13 } 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { 18 return mBinder; 19 } /** method for clients */ 20 public int getRandomNumber() { 21 return mGenerator.nextInt(100); 22 } 23 }
LocalBinder为客户端提供了getService()方法来取得当前的LocalService实例。这个允许客户端调用服务中的公共方法。例如,客户端可以从服务中调用getRandomNumber()。
以下为,当一个按钮被点击时,一个绑定到LocalService的活动并调用getRandomNumber()方法:
1 public class BindingActivity extends Activity { 2 LocalService mService; 3 boolean mBound = false; 4 5 @Override 6 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 7 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 8 setContentView(R.layout.main); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 protected void onStart() { 13 super.onStart(); 14 // Bind to LocalService 15 Intent intent = new Intent(this, LocalService.class); 16 bindService(intent, mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); 17 } 18 19 @Override 20 protected void onStop() { 21 super.onStop(); 22 // Unbind from the service 23 if (mBound) { 24 unbindService(mConnection); 25 mBound = false; 26 } 27 } 28 29 /** Called when a button is clicked (the button in the layout file attaches to 30 * this method with the android:onClick attribute) */ 31 public void onButtonClick(View v) { 32 if (mBound) { 33 // Call a method from the LocalService. 34 // However, if this call were something that might hang, then this request should 35 // occur in a separate thread to avoid slowing down the activity performance. 36 int num = mService.getRandomNumber(); 37 Toast.makeText(this, "number: " + num, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); 38 } 39 } 40 41 /** Defines callbacks for service binding, passed to bindService() */ 42 private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() { 43 44 @Override 45 public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, 46 IBinder service) { 47 // We've bound to LocalService, cast the IBinder and get LocalService instance 48 LocalBinder binder = (LocalBinder) service; 49 mService = binder.getService(); 50 mBound = true; 51 } 52 53 @Override 54 public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName arg0) { 55 mBound = false; 56 } 57 }; 58 }
使用一个消息传递器-Using a Messenger
如果你需要你的Service能够与远程进程通信,那么你可以使用一个Messenger为你的服务提供接口。这个方法允许你执行进程间通信(IPC)而不需要使用AIDL(当Service要处理多线程的客户端请求时,AIDL更加适合)。
以下为怎么样使用Messenger的总结:
- Service实现了一个Handler,用来接收每一次客户端发来的请求,并根据请求内容做处理。
- Service通过它的Handler接收每一个Message——更确切的说,是在handleMessage()方法中接收。
通过这种方法,在Service没有客户端能调用的“方法”。而是,客户传递“消息”(Message对象),同时服务在其Handler中接收。
以下为服务使用一个Messenger接口的简单范例:
1 public class MessengerService extends Service { 2 /** Command to the service to display a message */ 3 static final int MSG_SAY_HELLO = 1; /** 4 * Handler of incoming messages from clients. 5 */ 6 class IncomingHandler extends Handler { 7 @Override 8 public void handleMessage(Message msg) { 9 switch (msg.what) { 10 case MSG_SAY_HELLO: 11 Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "hello!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); 12 break; 13 default: 14 super.handleMessage(msg); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 /** 19 * Target we publish for clients to send messages to IncomingHandler. 20 */ 21 final Messenger mMessenger = new Messenger(new IncomingHandler()); 22 23 /** 24 * When binding to the service, we return an interface to our messenger 25 * for sending messages to the service. 26 */ 27 @Override 28 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { 29 Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "binding", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); 30 return mMessenger.getBinder(); 31 } 32 }
注意Handler中的handleMessage()方法,Service接收客户端发来的Message,基于what成员,决定下一步的处理。
客户端所需做的只是基于Service返回的IBinder创建一个Messenger并使用send()方法发送一条消息。例如,以下为一个简单的Activity范例,其绑定到了Service,并向服务传递了MSG_SAY_HELLO消息:
1 public class ActivityMessenger extends Activity { 2 /** Messenger for communicating with the service. */ 3 Messenger mService = null; /** Flag indicating whether we have called bind on the service. */ 4 boolean mBound; 5 /** 6 * Class for interacting with the main interface of the service. 7 */ 8 private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() { 9 public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) { 10 // This is called when the connection with the service has been 11 // established, giving us the object we can use to 12 // interact with the service. We are communicating with the 13 // service using a Messenger, so here we get a client-side 14 // representation of that from the raw IBinder object. 15 mService = new Messenger(service); 16 mBound = true; 17 } 18 19 20 public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) { 21 // This is called when the connection with the service has been 22 // unexpectedly disconnected -- that is, its process crashed. 23 mService = null; 24 mBound = false; 25 } 26 }; 27 28 public void sayHello(View v) { 29 if (!mBound) return; 30 // Create and send a message to the service, using a supported 'what' value 31 Message msg = Message.obtain(null, MessengerService.MSG_SAY_HELLO, 0, 0); 32 try { 33 mService.send(msg); 34 } catch (RemoteException e) { 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 } 38 39 @Override 40 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 41 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 42 setContentView(R.layout.main); 43 } 44 45 @Override 46 protected void onStart() { 47 super.onStart(); 48 // Bind to the service 49 bindService(new Intent(this, MessengerService.class), mConnection, 50 Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); 51 } 52 @Override 53 protected void onStop() { 54 super.onStop(); 55 // Unbind from the service 56 if (mBound) { 57 unbindService(mConnection); 58 mBound = false; 59 } 60 } 61 }
参考文章:
Android Service的绑定 基础概念篇 http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdd/archive/2013/03/24/2979710.html