Python实现博弈树minmax补全与α-β剪枝算法脚本简介
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、题目
- 二、使用步骤
-
- 1.递归构建博弈树
- 2.α-β剪枝算法
- 3.博弈树可视化
- 4.测试实例
- 5.结果展示
- 6.全部代码
- 总结
前言
使用Python编程实现博弈树的构建,实现利用MinMax方法补全博弈树缺失值,并结合α-β剪枝算法,实现博弈树的剪枝。实现了整体算法与博弈树的可视化。
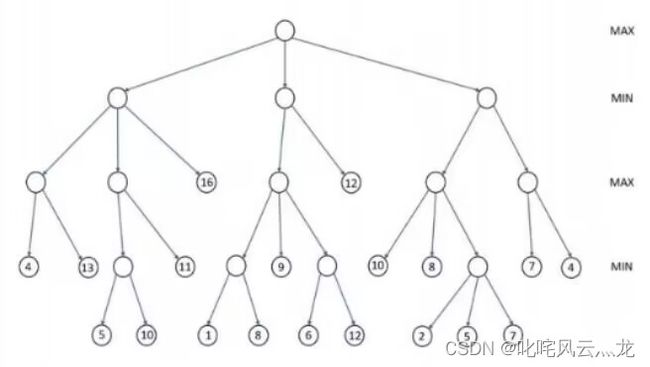
一、题目
二、使用步骤
1.递归构建博弈树
代码如下:
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val: int=0, max: bool=True) -> None:
'''
val: 节点值
max: 是否为max层
childern: 子节点列表
'''
self.val = val # 该节点的值
self.max = max # 该层是否为max层,默认顶层节点为max层
self.children : list = [] # 该节点的子节点
class Tree(object):
def __init__(self) -> None:
'''
data_list: 数据列表
上图所示列表示例:[[[4,13],[[5,10],11],16],[[[1,8],9,[6,12]],12],[[10,8,[2,5,7]],[7,4]]]
其中节点值为一个int型数值,含有其他子节点的构建为列表
'''
self.root = Node() # Node(),根节点
def build_tree(self, data_list, root) -> None:
# 递归构建博弈树
for i in range(len(data_list)):
is_max = root.max
if is_max == True:
is_max = False # min层
else:
is_max = True # max层
if type(data_list[i]) is tuple:
# 该节点为叶节点,直接添加节点值
for val in data_list[i]:
root.children.append(Node(val, is_max))
elif type(data_list[i]) is int:
# 该节点为叶节点,直接添加节点值
root.children.append(Node(data_list[i], is_max))
elif type(data_list[i]) is list:
# 该节点含有子节点,递归创建
if type(data_list[i]) is int:
# 该节点为叶节点,直接添加节点值
root.children.append(Node(data, is_max))
elif type(data_list[i]) is list:
# 该节点含有子节点,递归创建
root.children.append(Node(max=is_max)) # 添加子节点
self.build_tree(data_list[i], root.children[i])
2.α-β剪枝算法
代码如下:
class AlphaBeta(object):
def __init__(self, tree, auto=False) -> None:
'''
tree: 博弈树
auto: 补全全部节点值,默认不补全
选择不补全时,可视化过程为剪枝过程,节点为0的子节点为剪掉的节点
'''
self.tree = tree # 博弈树
self.auto = auto # 补全全部节点值,可选参数,默认不补全
self.deep = 0 # 节点深度
self.alpha = -float('inf')
self.beta = float('inf')
if self.auto:
# 补全博弈树
self.complement_value(self.tree.root)
def get_value(self, node) -> int:
# 获取节点值
return node.val
def is_leaf(self, node) -> bool:
# 判断是否为叶节点
if len(node.children) == 0:
return True
else:
return False
def complement_value(self, node): # 补全博弈树,可选
# 根据MinMax规则补全博弈树
if self.is_leaf(node):
return self.get_value(node)
if self.get_value(node) != 0:
return self.get_value(node)
val_list = []
for child in node.children:
temp = self.complement_value(child)
val_list.append(temp if temp is not None else child.val)
if node.max:
node.val = max(val_list)
else:
node.val = min(val_list)
def max_value(self, node, alpha, beta):
if self.is_leaf(node):
# 当前节点为叶节点
return self.get_value(node)
best = -float('inf') # 初始化无穷小
for child in node.children:
best = max(best, self.min_value(child, alpha, beta))
if best >= beta:
return best
alpha = max(alpha, best)
node.val = best
return best
def min_value(self, node, alpha, beta):
if self.is_leaf(node):
# 当前节点为叶节点
return self.get_value(node)
best = float('inf') # 初始化无穷大
for child in node.children:
best = min(best, self.max_value(child, alpha, beta))
if best <= alpha:
return best
beta = min(beta, best)
node.val = best
return best
def alpha_beta(self):
best = self.max_value(self.tree.root, self.alpha, self.beta)
# return best
for child in self.tree.root.children:
if best == child.val:
return child
3.博弈树可视化
代码如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class ShowTree(object):
def __init__(self, tree) -> None:
'''
tree: 博弈树
'''
self.tree = tree # 博弈树
self.__num_of_leafs = self.get_num_of_leaf(self.tree.root) # 叶节点数量
self.__tree_depth = self.get_tree_depth(self.tree.root) # 树深度
# 初始化箭头格式
self.arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
@property
def num_of_leafs(self):
return self.__num_of_leafs
@property
def tree_depth(self):
return self.__tree_depth
def get_num_of_leaf(self, node):
# 获取叶节点数量
num_of_leafs = 0
if len(node.children) == 0:
# 该节点为叶节点,叶节点数量+1
num_of_leafs += 1
else:
for child in node.children:
num_of_leafs += self.get_num_of_leaf(child)
return num_of_leafs
def get_tree_depth(self, node):
# 获取树的最大深度
max_tree_depth = 0
if len(node.children) == 0:
# 该节点为叶节点,深度为1
max_tree_depth += 1
else:
for child in node.children:
this_depth = 1 + self.get_tree_depth(child)
if this_depth > max_tree_depth:
max_tree_depth = this_depth
return max_tree_depth
def box(self, node):
# 设置文本框样式
if node.max:
boxstyle = "square"
else:
boxstyle = "circle"
return dict(boxstyle=boxstyle,fc="0.8")
def plot_node(self, node, centerPt, parentPt):
node_type = self.box(node)
# node_type = dict(boxstyle="round4",fc="0.8")
ShowTree.plot.ax1.annotate(node.val, xy=parentPt, \
xycoords='axes fraction',
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',\
va="center",ha="center", bbox=node_type, arrowprops=self.arrow_args)
@staticmethod
def plot_tree(tree, node, parentPt):
numLeafs = ShowTree.get_num_of_leaf(tree, node) # 计算树的宽度
depth = ShowTree.get_tree_depth(tree, node) # 计算树的高度
# 输入的第一个节点
first_node = node
cntrPt = (ShowTree.plot_tree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs)) / 2.0 / ShowTree.plot_tree.totalW, ShowTree.plot_tree.yOff)
# 叶子节点
ShowTree.plot_node(tree, first_node, cntrPt, parentPt)
# 减少y的便偏移
ShowTree.plot_tree.yOff = ShowTree.plot_tree.yOff - 1.0 / ShowTree.plot_tree.totalD
for child in node.children:
if len(child.children) == 0:
ShowTree.plot_tree.xOff = ShowTree.plot_tree.xOff + 1.0 / ShowTree.plot_tree.totalW
ShowTree.plot_node(tree, child, (ShowTree.plot_tree.xOff, ShowTree.plot_tree.yOff), cntrPt)
else:
ShowTree.plot_tree(tree, child, cntrPt)
ShowTree.plot_tree.yOff = ShowTree.plot_tree.yOff + 1.0 / ShowTree.plot_tree.totalD
@staticmethod
def plot(tree):
'''
tree: 需要绘制的树,类型为ShowTree()
'''
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
# Clear figure清除所有轴,但是窗口打开,这样它可以被重复使用
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
ShowTree.plot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops)
# ShowTree.plot_node(show_tree, show_tree.tree.root, (0.5,0.1),(0.1,0.5))
ShowTree.plot_tree.totalW = float(ShowTree.get_num_of_leaf(tree, tree.tree.root))
ShowTree.plot_tree.totalD = float(ShowTree.get_tree_depth(tree, tree.tree.root))
ShowTree.plot_tree.xOff = -0.5 / ShowTree.plot_tree.totalW
ShowTree.plot_tree.yOff = 1.0
ShowTree.plot_tree(tree, tree.tree.root,(0.5, 1.0))
plt.show()
4.测试实例
代码如下:
if __name__ == '__main__':
data = [[[4,13],[[5,10],11],16],[[[1,8],9,[6,12]],12],[[10,8,[2,5,7]],[7,4]]] # 初始博弈树值列表
tree = Tree() # 实例化空树
tree.build_tree(data, tree.root) # 递归构建博弈树
alpha_beta = AlphaBeta(tree, auto=True) # α-β剪枝
best = alpha_beta.alpha_beta() # 获取结果
print(best.val)
from plot_tree import ShowTree
show_tree = ShowTree(tree) # 实例化博弈树可视化算法
show_tree.plot(show_tree) # 可视化博弈树
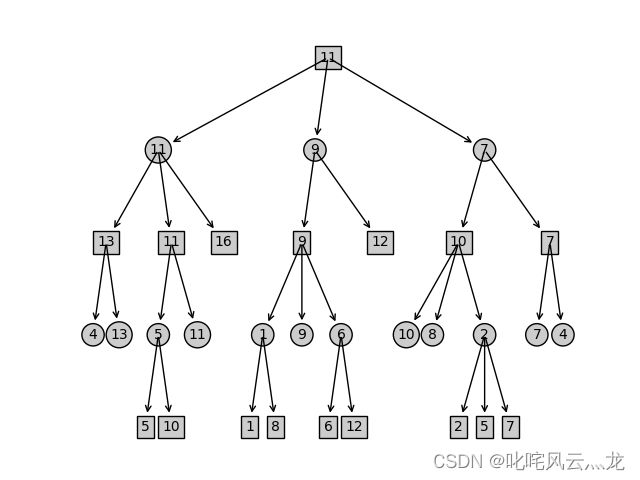
5.结果展示
6.全部代码
全部代码如下alpha_beta.zip
总结
利用Python编程实现了α-β剪枝算法,并利用matplotlib实现了博弈树的可视化。