驱动程序开发:I2C设备驱动
目录
- Linux下I2C知识点:
-
- Linux下I2C驱动简介
- I2C架构概述
- I2C驱动架构图
- I2C适配器
- I2C设备(client)
- I2C驱动(driver)
- I2C 设备和驱动匹配过程
- 编写AP3216C传感器I2C设备Linux驱动:
-
- 设备树编写操作
- i2c驱动基本框架编写
- 在i2c驱动基本框架下添加字符设备框架
- 使用以上搭建好的框架读取ap3216c传感器数值
Linux下I2C知识点:
Linux下I2C驱动简介
利用linux的I2C驱动体系结构完成其驱动编写优点:①不需要工程师对I2C设备和I2C的适配器(I2C控制器)操作的熟悉。②编写出来的程序可移植性强。③ 对内核的资源可以直接直接使用,因为内核提供的所有I2C设备器以及设备驱动都是基于I2C子系统的格式。 但缺点就是:需要花时间去了解linux中复杂的I2C子系统的操作方法。
I2C架构概述
Linux的I2C体系结构分为3个组成部分:
I2C核心:I2C核心提供了I2C总线驱动和设备驱动的注册,注销方法,I2C通信方法(”algorithm”)上层的,与具体适配器无关的代码以及探测设备,检测设备地址的上层代码等。
I2C总线驱动:I2C总线驱动是对I2C硬件体系结构中适配器端的实现,适配器可由CPU控制,甚至可以直接集成在CPU内部。
I2C设备驱动:I2C设备驱动(也称为客户驱动)是对I2C硬件体系结构中设备端的实现,设备一般挂接在受CPU控制的I2C适配器上,通过I2C适配器与CPU交换数据。
I2C驱动架构图

架构层次分类详情描述:
第一层:提供i2c adapter的硬件驱动,探测、初始化i2c adapter(如申请i2c的io地址和中断号),驱动soc控制的i2c adapter在硬件上产生信号(start、stop、ack)以及处理i2c中断。覆盖图中的硬件实现层。
第二层:提供i2c adapter的algorithm,用具体适配器的xxx_xferf()函数来填充i2c_algorithm的master_xfer函数指针,并把赋值后的i2c_algorithm再赋值给i2c_adapter的algo指针。覆盖图中的访问抽象层、i2c核心层。
第三层:实现i2c设备驱动中的i2c_driver接口,用具体的i2c device设备的attach_adapter()、detach_adapter()方法赋值给i2c_driver的成员函数指针。实现设备device与总线(或者叫adapter)的挂接。覆盖图中的driver驱动层。
第四层:实现i2c设备所对应的具体device的驱动,i2c_driver只是实现设备与总线的挂接,而挂接在总线上的设备则是千差万别的,所以要实现具体设备device的write()、read()、ioctl()等方法,赋值给file_operations,然后注册字符设备(多数是字符设备)。覆盖图中的driver驱动层。
第一层和第二层又叫i2c总线驱动(bus),第三第四属于i2c设备驱动(device driver)。
在linux驱动架构中,几乎不需要驱动开发人员再添加bus,因为linux内核几乎集成所有总线bus,如usb、pci、i2c等等。并且总线bus中的(与特定硬件相关的代码)已由芯片提供商编写完成。
第三第四层与特定device相干的就需要驱动工程师来实现了。
根据驱动分离与分层的思想“总线、设备和驱动模型”,在I2C设备驱动分别对应的结构体:i2c_adapter、i2c_client和i2c_driver。 其中i2c_client 就是描述设备信息的,i2c_driver 描述驱动内容,类似于 platform_driver。
I2C适配器
I2C 总线驱动重点是 I2C 适配器(也就是 SOC 的 I2C 接口控制器)驱动,这里要用到两个重要的数据结构:i2c_adapter 和i2c_algorithm。
Linux 内核将 SOC 的 I2C 适配器(控制器)抽象成i2c_adapter,如下:
struct i2c_adapter {
struct module *owner;//所属模块
unsigned int id;//algorithm的类型,定义于i2c-id.h,
unsigned int class;
const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; //总线通信方法结构体指针
void *algo_data;//algorithm数据
struct rt_mutex bus_lock;//控制并发访问的自旋锁
int timeout;
int retries;//重试次数
struct device dev; //适配器设备
int nr;
char name[48];//适配器名称
struct completion dev_released;//用于同步
struct list_head userspace_clients;//client链表头
};
i2c_algorithm 类型的指针变量 algo,对于一个 I2C 适配器,肯定要对外提供读写 API 函数,设备驱动程序可以使用这些 API 函数来完成读写操作。i2c_algorithm 就是 I2C 适配器与 IIC 设备进行通信的方法,具体来说就是i2c_algorithm中提供的通信函数来控制适配器上产生特定的访问周期。缺少i2c_algorithm的i2c_adapter什么也做不了。
i2c_algorithm结构体,如下:
struct i2c_algorithm {
int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap,struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num); //I2C传输函数指针
int (*smbus_xfer) (struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr, unsigned short flags,
char read_write, u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data); //smbus传输函数指针
/* To determine what the adapter supports */
u32 (*functionality) (struct i2c_adapter *); //返回适配器支持的功能
};
master_xfer 就是 I2C 适配器的传输函数,用于产生i2c访问周期需要的start stop ack信号,以i2c_msg(即i2c消息)为单位。
发送和接收通信数据。而i2c_msg也非常关键,调用驱动中的发送接收函数需要填充该结构体。
smbus_xfer 就是 SMBUS 总线的传输函数。
functionality就是指适配器所支持的功能。
因为I2C适配器驱动一般都是SOC等原厂家编写好的,所有具体想看I2C适配器驱动程序可以在 drivers/i2c/busses/i2c-imx.c目录找到IMX6ULL对应的I2C适配器驱动,这里不提供展示了。
I2C设备(client)
struct i2c_client {
unsigned short flags;//标志
unsigned short addr; //低7位为芯片地址
char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE];//设备名称
struct i2c_adapter *adapter;//依附的i2c_adapter
struct i2c_driver *driver;//依附的i2c_driver
struct device dev;//设备结构体
int irq;//设备所使用的结构体
struct list_head detected;//链表头
};
一个设备对应一个 i2c_client,每检测到一个 I2C 设备就会给这个 I2C 设备分配一个i2c_client。
I2C驱动(driver)
struct i2c_driver {
unsigned int class;
int (*attach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *);//依附i2c_adapter函数指针
int (*detach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *);//脱离i2c_adapter函数指针
int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *);
int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *);
void (*shutdown)(struct i2c_client *);
int (*suspend)(struct i2c_client *, pm_message_t mesg);
int (*resume)(struct i2c_client *);
void (*alert)(struct i2c_client *, unsigned int data);
int (*command)(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned int cmd, void*arg);//命令列表
struct device_driver driver;
const struct i2c_device_id *id_table;//该驱动所支持的设备ID表
int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, struct i2c_board_info *);
const unsigned short *address_list;
struct list_head clients;
};
当 I2C 设备和驱动匹配成功以后 probe 函数就会执行,和 platform 驱动一样。
device_driver 驱动结构体,如果使用设备树的话,需要设置 device_driver 的of_match_table 成员变量,也就是驱动的兼容(compatible)属性。
id_table 是传统的、未使用设备树的设备匹配 ID 表。
对于我们 I2C 设备驱动编写人来说,重点工作就是构建 i2c_driver,构建完成以后需要向Linux 内核注册这个 i2c_driver。
示例代码 61.1.2.4 i2c_driver 注册流程
1 /* i2c 驱动的 probe 函数 */
2 static int xxx_probe(struct i2c_client *client, const struct i2c_device_id *id)
3 {
4 /* 函数具体程序 */
5 return 0;
6 }
7
8 /* i2c 驱动的 remove 函数 */
9 static int xxx_remove(struct i2c_client *client)
10 {
11 /* 函数具体程序 */
12 return 0;
13 }
14
15 /* 传统匹配方式 ID 列表 */
16 static const struct i2c_device_id xxx_id[] = {
17 {"xxx", 0},
18 {}
19 };
20
21 /* 设备树匹配列表 */
22 static const struct of_device_id xxx_of_match[] = {
23 { .compatible = "xxx" },
24 { /* Sentinel */ }
25 };
26
27 /* i2c 驱动结构体 */
28 static struct i2c_driver xxx_driver = {
29 .probe = xxx_probe,
30 .remove = xxx_remove,
31 .driver = {
32 .owner = THIS_MODULE,
33 .name = "xxx",
34 .of_match_table = xxx_of_match,
35 },
36 .id_table = xxx_id,
37 };
38
39 /* 驱动入口函数 */
40 static int __init xxx_init(void)
41 {
42 int ret = 0;
43
44 ret = i2c_add_driver(&xxx_driver);
45 return ret;
46 }
47
48 /* 驱动出口函数 */
49 static void __exit xxx_exit(void)
50 {
51 i2c_del_driver(&xxx_driver);
52 }
53
54 module_init(xxx_init);
55 module_exit(xxx_exit);
i2c_adapter、i2c_client和i2c_driver三个结构体之间的关系 *i2c_driver和i2c_client:
i2c_driver对应一套驱动方法,其主要函数是attach_adapter()和detach_client()。
i2c_client对应真实的i2c物理设备device,每个i2c设备都需要一个i2c_client来描述。
i2c_driver与i2c_client的关系是一对多。一个i2c_driver上可以支持多个同等类型的i2c_client。
i2c_adapter和i2c_client:
i2c_adapter和i2c_client的关系与i2c硬件体系中适配器和设备的关系一致,即i2c_client依附于i2c_adapter,由于一个适配器上可以连接多个i2c设备,所以i2c_adapter中包含依附于它的i2c_client的链表。
从i2c驱动架构图中可以看出,linux内核对i2c架构抽象了一个叫核心层core的中间件,它分离了设备驱动device driver和硬件控制的实现细节(如操作i2c的寄存器),core层不但为上面的设备驱动提供封装后的内核注册函数,而且还为小面的硬件事件提供注册接口(也就是i2c总线注册接口),可以说core层起到了承上启下的作用。
I2C 设备和驱动匹配过程
I2C 设备和驱动的匹配过程是由 I2C 核心来完成的,drivers/i2c/i2c-core.c 就是 I2C 的核心
部分,I2C 核心提供了一些与具体硬件无关的 API 函数,如:
1、i2c_adapter 注册/注销函数
int i2c_add_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adapter)
int i2c_add_numbered_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap)
void i2c_del_adapter(struct i2c_adapter * adap)
2、i2c_driver 注册/注销函数
int i2c_register_driver(struct module *owner, struct i2c_driver *driver)
int i2c_add_driver (struct i2c_driver *driver)
void i2c_del_driver(struct i2c_driver *driver)
设备和驱动的匹配过程也是由 I2C 总线完成的的,I2C 总线的数据结构为 i2c_bus_type,定义在 drivers/i2c/i2c-core.c 文件,i2c_bus_type 内容如下:
示例代码 61.1.2.5 i2c_bus_type 总线
struct bus_type i2c_bus_type = {
.name = "i2c",
.match = i2c_device_match,
.probe = i2c_device_probe,
.remove = i2c_device_remove,
.shutdown = i2c_device_shutdown,
};
.match 就是 I2C 总线的设备和驱动匹配函数,在这里就是 i2c_device_match 这个函数,此函数内容如下:
示例代码 61.1.2.6 i2c_device_match 函数
static int i2c_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev);
struct i2c_driver *driver;
if (!client)
return 0;
/* Attempt an OF style match */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then ACPI style match */
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
driver = to_i2c_driver(drv);
/* match on an id table if there is one */
if (driver->id_table)
return i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client) != NULL;
return 0;
}
of_driver_match_device 函数用于完成设备树设备和驱动匹配。比较 I2C 设备节点的 compatible 属性和 of_device_id 中的 compatible 属性是否相等,如果相当的话就表示 I2C设备和驱动匹配。
acpi_driver_match_device 函数用于 ACPI 形式的匹配。
i2c_match_id 函数用于传统的、无设备树的 I2C 设备和驱动匹配过程。比较 I2C设备名字和 i2c_device_id 的 name 字段是否相等,相等的话就说明 I2C 设备和驱动匹配。
编写AP3216C传感器I2C设备Linux驱动:
设备树编写操作
由原理图可知,UART4_TXD、UART4_RXD分别作为I2C1的SCL和SDA。
在IMX6ULL参考手册可查询到其关系。
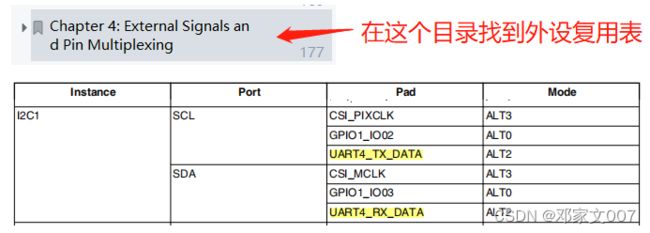
因此需要将UART4_TXD、UART4_RXD这两个引脚分别复用为I2C1_SCL和I2C1_SDA。所以将设备树pinctrl_i2c1子节点设置为如下:
pinctrl_i2c1: i2c1grp {
fsl,pins = <
MX6UL_PAD_UART4_TX_DATA__I2C1_SCL 0x4001b8b0
MX6UL_PAD_UART4_RX_DATA__I2C1_SDA 0x4001b8b0
>;
};
这里对子节点下的第一个属性作为解释:
MX6UL_PAD_UART4_TX_DATA__I2C1_SCL等于“0x020E00B4U, 0x2U, 0x020E05A4U, 0x1U, 0x020E0340U”这一串东西,那么这一串东西又表示为什么呢?
①0x020E00B4U指的是SW_PAD_CTL_PAD_UART4_TX_DATA SW PAD Control Register寄存器地址。而0x2U为设置该寄存器的值,这里是指选择一种iomux模式用于pad,那么0x2U选择的是0010 ALT2 — Select mux mode: ALT2 mux port: I2C1_SCL of instance: i2c1。
②0x020E05A4U指的是I2C1_SCL_SELECT_INPUT DAISY Register寄存器地址。而0x1U为设置该寄存器的值,这里选择的是01 UART4_TX_DATA_ALT2 — Selecting Pad: UART4_TX_DATA for Mode: ALT2。
③0x020E0340U指的是SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_UART4_TX_DATA SW MUX Control Register寄存器,它是用于设置电器属性的,这里可以发现出,该寄存器地址后面没跟有寄存器设置值,因为这个寄存器设置值需要我们去配置,因此这个寄存器的设置值实质就是该子节点的属性值里的0x4001b8b0。
其次,需要在.dts设备树文件中的i2c1节点上追加i2c1子节点,如下:
&i2c1 {
clock-frequency = <100000>; /* I2C频率100KHz */
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_i2c1>;
status = "okay";
ap3216c@1e { /* 后面的'1e'为ap3216c器件地址 */
compatible = "alientek,ap3216c"; /* 兼容属性 */
reg = <0x1e>; /* ap3216c器件地址 */
};
};
最后,使用“make dtbs”重新编译设备树,在/sys/bus/i2c/devices 目录下看到一个名为“0-001e”的子目录,使用“cat 0-001e/name”命令可以查看到其设备名字“ap3216c”,如下图:

i2c驱动基本框架编写
这里参考在前面给出的“i2c_driver 注册流程”编写最基本的i2c驱动框架,编写后,如下:
/*
* 根据linux内核的程序查找所使用函数的对应头文件。
*/
#include 通过“make”命令编译生成.ko文件,然后加载驱动,在“cd /sys/bus/i2c/drivers/”目录下查找到名为“ap3216c”的驱动。
在i2c驱动基本框架下添加字符设备框架
ap3216c.c
/*
* 根据linux内核的程序查找所使用函数的对应头文件。
*/
#include 测试APP(ap3216cAPP.c)
#include
* ./ap3216cAPP /dev/ap3216c
*/
/*
* @description : main 主程序
* @param - argc : argv 数组元素个数
* @param - argv : 具体参数
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd, ret;
char *filename;
int data;
/* 判断输入的元素个数 */
if(argc != 2) {
printf("ERROR USAGE!\r\n");
return -1;
}
filename = argv[1]; //获取驱动文件的路径
fd = open(filename,O_RDWR); //根据文件路径以读写方式打开文件
if(fd < 0) {
printf("file %s open failed!\r\n",filename);
return -1;
}
ret = read(fd,&data,sizeof(data));
close(fd);
return 0;
}
操作命令测试:
~# depmod
~# modprobe ap3216c.ko
~# ls /dev/ap3216c -l
~# ./ap3216cAPP /dev/ap3216c
可查看现象
使用以上搭建好的框架读取ap3216c传感器数值
ap3216c.c
/*
* 根据linux内核的程序查找所使用函数的对应头文件。
*/
#include ap3216cAPP.c
#include
* ./ap3216cAPP /dev/ap3216c
*/
/*
* @description : main 主程序
* @param - argc : argv 数组元素个数
* @param - argv : 具体参数
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd, ret;
char *filename;
unsigned short data[3];
unsigned short ir,als,ps;
/* 判断输入的元素个数 */
if(argc != 2) {
printf("ERROR USAGE!\r\n");
return -1;
}
filename = argv[1]; //获取驱动文件的路径
fd = open(filename,O_RDWR); //根据文件路径以读写方式打开文件
if(fd < 0) {
printf("file %s open failed!\r\n",filename);
return -1;
}
while(1) {
ret = read(fd,&data,sizeof(data));
if(ret < 0) {
return -1;
}
ir = data[0];
als = data[1];
ps = data[2];
printf("AP3216C ir=%d, als=%d, ps=%d\r\n",ir,als,ps);
usleep(200000);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
验证操作:
~# depmod
~# modprobe ap3216c.ko
~# ./ap3216cAPP /dev/ap3216c
现象:

