从零开始 HRNet_网络的结构和源码
(0)摘要
# 本文重点剖析一下 HRNet 的完整网络结构和网络模块,对每一个网络模块的源码进行分析。同时介绍一下 nn.ModuleList() 。
# 内容
(1)HRNet 源码
(2)网络结构图
# 乱花渐欲迷人眼
(1)HRNet 的源码
# (1)HRNet 是由三个基础块构成的,分别是 Bottleneck、BasicBlock、HighResolutionModule。其中,blocks_dict 其实就是 Bottleneck 和 BasicBlock 。另外, HighResolution 是由 BasicBlock 构成的。有了这个基础,我们分别结合源码,讲解这三个模块。
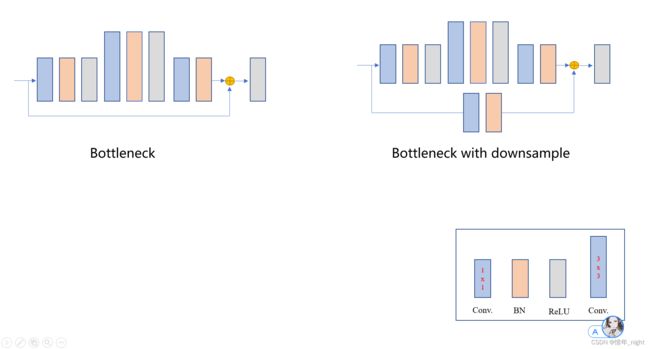
# (2)Bottleneck 模块。
1)源码如下,看看就行了,基本结合图来看就是了。
class Bottleneck(nn.Module): expansion = 4 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None): super(Bottleneck, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM) self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * self.expansion, kernel_size=1, bias=False) self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * self.expansion, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) self.downsample = downsample self.stride = stride def forward(self, x): residual = x out = self.conv1(x) out = self.bn1(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv2(out) out = self.bn2(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv3(out) out = self.bn3(out) if self.downsample is not None: residual = self.downsample(x) out += residual out = self.relu(out) return out2)Bottleneck 网络模型图,结合源码可以看得很清楚。
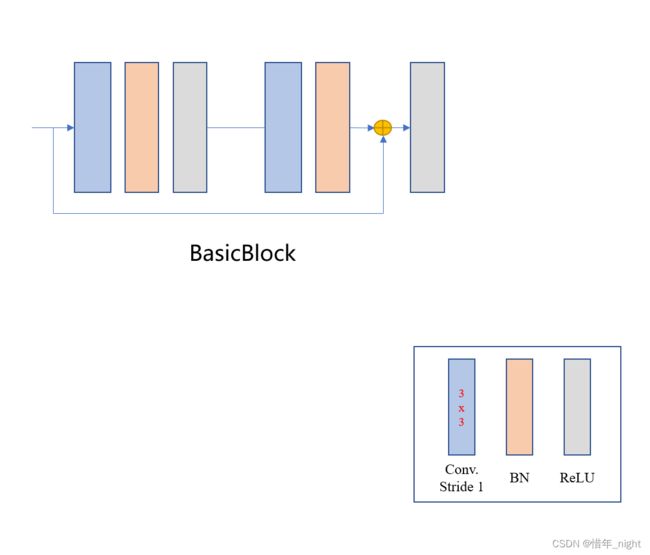
# (3)BasicBlock 模块。
1)网络源码。
class BasicBlock(nn.Module): expansion = 1 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None): super(BasicBlock, self).__init__() self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM) self.downsample = downsample self.stride = stride def forward(self, x): residual = x out = self.conv1(x) out = self.bn1(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv2(out) out = self.bn2(out) if self.downsample is not None: residual = self.downsample(x) out += residual out = self.relu(out) return out2)BasicBlock 模块的网络模型图
# (4)HighResolutionModule 网络模块。
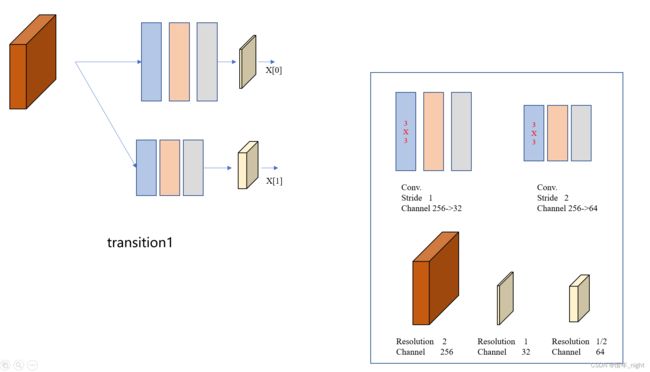
1)讲这个模块之前,我们要先讲一下 transition1 和 transition 2 还有 transition 3的模块,分别以 transition1 对应 stage 2、transition 2 对应 stage 3、transition 3 对应 stage 4 来讲解,具体的代码不讲了。下面是 transition 1 的网络模块。
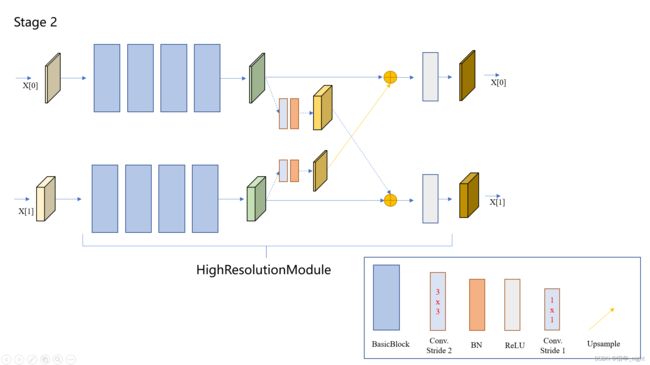
对应的 stage 2 模块,同时也引出了第一个属于 Stage2 的 HighResolutionModule 模块。
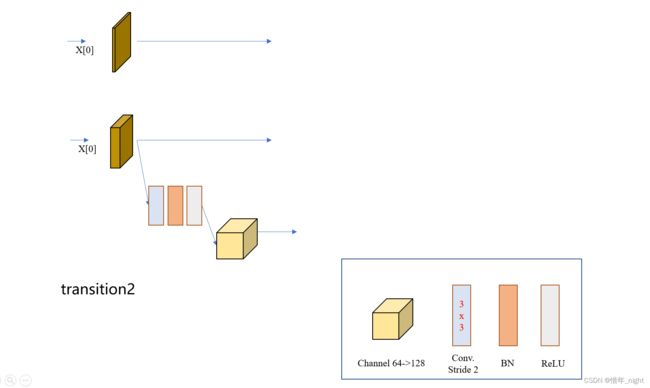
2)下面是 transition 2 的网络模块。
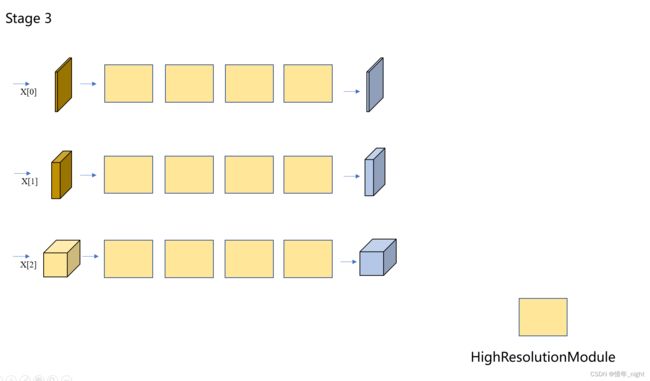
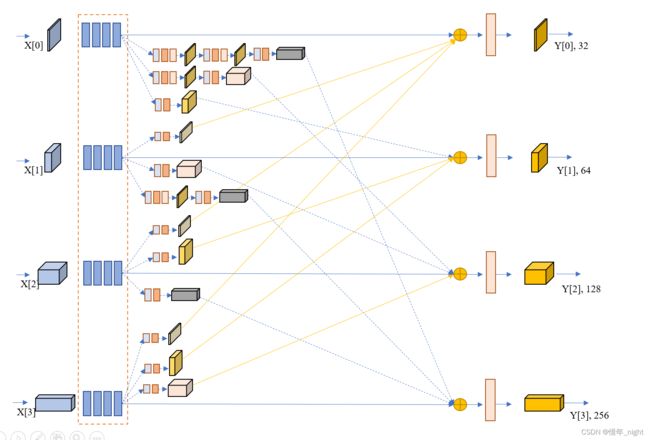
针对于 stage3 阶段的 HighResolutionModule 模块,根据研读源码的结果,stage3 阶段一共有 4 个 HighResolutionModule 模块。
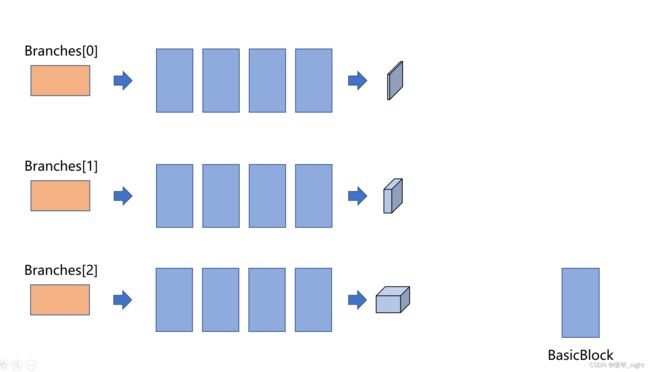
branch 模块的结构图。
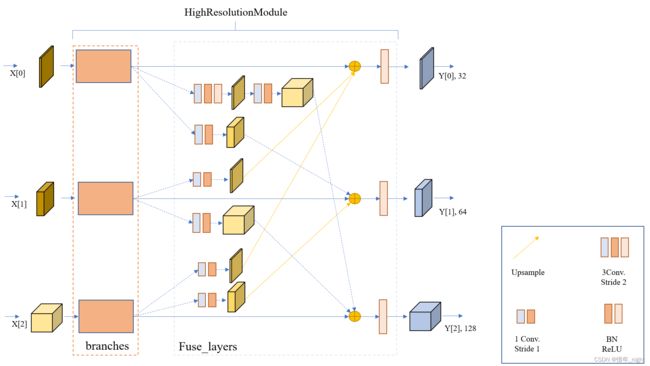
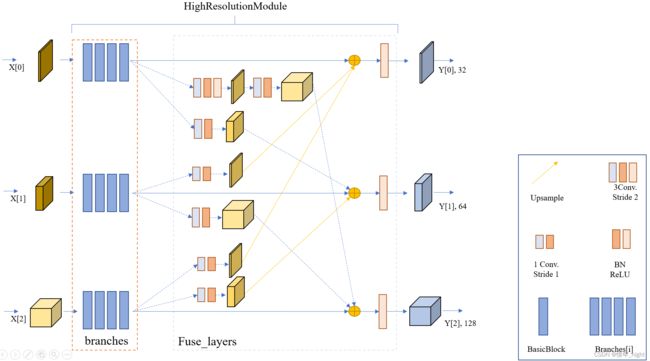
结合上面两个的结果,我们可以看到实际的 HighResolutionModule 模块。
于是根据上面的结果,就有了正儿八经的 stage 3 的网络结构图。
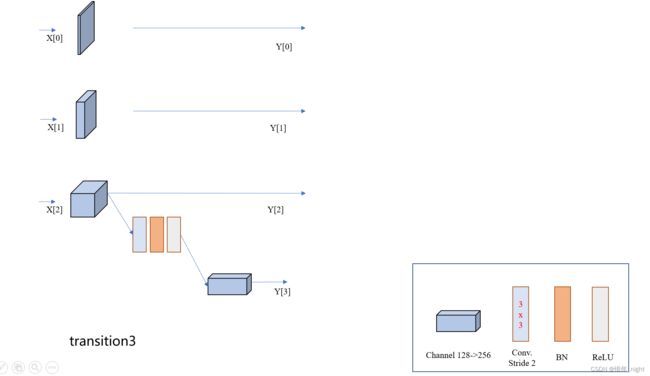
3)下面是 transition3 部分的结构。
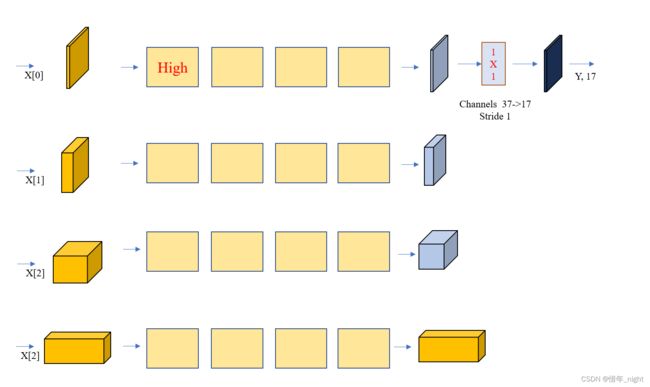
与 stage3 阶段的 HighResolutionModule 模块类似,stage4 的其实就是多一个分支进行尺度融合而已。当然,源码中 stage4 只有三个 HighResolutionModule 模块。
stage 4 阶段的网络模块和最后的 final_layers 层的网络结构图。这也就是最后阶段的网络结构。
4)HighResolutionModule 源码。
class HighResolutionModule(nn.Module): def __init__(self, num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_inchannels, num_channels, fuse_method, multi_scale_output=True): super(HighResolutionModule, self).__init__() self._check_branches( num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_inchannels, num_channels) self.num_inchannels = num_inchannels self.fuse_method = fuse_method self.num_branches = num_branches self.multi_scale_output = multi_scale_output self.branches = self._make_branches( num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_channels) self.fuse_layers = self._make_fuse_layers() self.relu = nn.ReLU(True) def _check_branches(self, num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_inchannels, num_channels): if num_branches != len(num_blocks): error_msg = 'NUM_BRANCHES({}) <> NUM_BLOCKS({})'.format( num_branches, len(num_blocks)) logger.error(error_msg) raise ValueError(error_msg) if num_branches != len(num_channels): error_msg = 'NUM_BRANCHES({}) <> NUM_CHANNELS({})'.format( num_branches, len(num_channels)) logger.error(error_msg) raise ValueError(error_msg) if num_branches != len(num_inchannels): error_msg = 'NUM_BRANCHES({}) <> NUM_INCHANNELS({})'.format( num_branches, len(num_inchannels)) logger.error(error_msg) raise ValueError(error_msg) def _make_one_branch(self, branch_index, block, num_blocks, num_channels, stride=1): downsample = None if stride != 1 or \ self.num_inchannels[branch_index] != num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion: downsample = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d( self.num_inchannels[branch_index], num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False ), nn.BatchNorm2d( num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM ), ) layers = [] layers.append( block( self.num_inchannels[branch_index], num_channels[branch_index], stride, downsample ) ) self.num_inchannels[branch_index] = \ num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion for i in range(1, num_blocks[branch_index]): layers.append( block( self.num_inchannels[branch_index], num_channels[branch_index] ) ) return nn.Sequential(*layers) def _make_branches(self, num_branches, block, num_blocks, num_channels): branches = [] for i in range(num_branches): branches.append( self._make_one_branch(i, block, num_blocks, num_channels) ) return nn.ModuleList(branches) def _make_fuse_layers(self): if self.num_branches == 1: return None num_branches = self.num_branches num_inchannels = self.num_inchannels fuse_layers = [] for i in range(num_branches if self.multi_scale_output else 1): fuse_layer = [] for j in range(num_branches): if j > i: fuse_layer.append( nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d( num_inchannels[j], num_inchannels[i], 1, 1, 0, bias=False ), nn.BatchNorm2d(num_inchannels[i]), nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2**(j-i), mode='nearest') ) ) elif j == i: fuse_layer.append(None) else: conv3x3s = [] for k in range(i-j): if k == i - j - 1: num_outchannels_conv3x3 = num_inchannels[i] conv3x3s.append( nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d( num_inchannels[j], num_outchannels_conv3x3, 3, 2, 1, bias=False ), nn.BatchNorm2d(num_outchannels_conv3x3) ) ) else: num_outchannels_conv3x3 = num_inchannels[j] conv3x3s.append( nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d( num_inchannels[j], num_outchannels_conv3x3, 3, 2, 1, bias=False ), nn.BatchNorm2d(num_outchannels_conv3x3), nn.ReLU(True) ) ) fuse_layer.append(nn.Sequential(*conv3x3s)) fuse_layers.append(nn.ModuleList(fuse_layer)) return nn.ModuleList(fuse_layers) def get_num_inchannels(self): return self.num_inchannels def forward(self, x): if self.num_branches == 1: return [self.branches[0](x[0])] # (2) self.num_branches = 2 # (3) self.num_branches = 3 # (4) self.num_branches = 4 for i in range(self.num_branches): # (2) i = 0, 1 # self.branches[0](x[0]) # self.branches[1](x[1]) # (3) i = 0, 1, 2 # x[0] = self.branches[0](x[0]) # x[1] = self.branches[1](x[1]) # x[2] = self.branches[2](x[2]) # (4) i = 0, 1, 2, 3 # x[0] = self.branches[0](x[0]) # x[1] = self.branches[1](x[1]) # x[2] = self.branches[2](x[2]) # x[3] = self.branches[3](x[3]) x[i] = self.branches[i](x[i]) x_fuse = [] # (2) self.fuse_layers = 2 # (3) self.fuse_layers = 3 # (4) self.fuse_layers = 4 for i in range(len(self.fuse_layers)): # (2) i = 0, 1 # i = 0, y = x[0] # i = 1, y = self.fuse_layers[1][0](x[0]) # # (3) i = 0, 1, 2 # i = 0, y = x[0] # i = 1, y = self.fuse_layers[1][0](x[0]) # i = 2, y = self.fuse_layers[2][0](x[0]) # # (4) i = 0, 1, 2, 3 # i = 0, y = x[0] # i = 1, y = self.fuse_layers[1][0](x[0]) # i = 2, y = self.fuse_layers[2][0](x[0]) # i = 3, y = self.fuse_layers[3][0](x[0]) y = x[0] if i == 0 else self.fuse_layers[i][0](x[0]) # (2) j = 1 # # (3) i = 0, j = 1, 2 # i = 1, j = 1, 2 # i = 2, j = 1, 2 # # (4) i = 0, j = 1, 2, 3 # i = 1, j = 1, 2, 3 # i = 2, j = 1, 2, 3 for j in range(1, self.num_branches): # (2) i = 1 走这个 # # (3) i = 1, j = 1 走这个 # i = 2, j = 2 走这个 # # (4) i = 1, j = 1 走这个 # i = 2, j = 2 走这个 # i = 3, j = 3 走这个 if i == j: # (2) i=1, j=1, y = self.fuse_layers[1][0](x[0]) + x[1] # # (3) i=1, j=1, y = self.fuse_layers[1][0](x[0]) + x[1] # i=2, j=2, y = {self.fuse_layers[2][0](x[0]) + self.fuse_layers[2][1](x[1])}2,1 + x[2] # # (4) i=1, j=1, y = self.fuse_layers[1][0](x[0]) + x[1] # i=2, j=2, y = {self.fuse_layers[2][0](x[0]) + self.fuse_layers[2][1](x[1])}2,1 + x[2] # i=3, j=3, y = {{self.fuse_layers[3][0](x[0]) + self.fuse_layers[3][1](x[1])}3,1 + self.fuse_layers[3][2](x[2])}3,3 + x[3] y = y + x[j] # (2) i = 0 走这个 # # (3) i = 0, j = 1 走这个 # i = 0, j = 2 走这个 # i = 1, j = 2 走这个 # i = 2, j = 1 走这个 # # (4) i = 0, j = 1 走这个 # i = 0, j = 2 走这个 # i = 0, j = 3 走这个 # i = 1, j = 2 走这个 # i = 1, j = 3 走这个 # i = 2, j = 1 走这个 # i = 2, j = 3 走这个 # i = 3, j = 1 走这个 # i = 3, j = 2 走这个 else: # (2) y = x[0] + self.fuse_layers[0][1](x[1]) # # (3) i=0, j=1, y = x[0] + self.fuse_layers[0][1](x[1]) # i=0, j=2, y = {x[0] + self.fuse_layers[0][1](x[1])}0,1 + self.fuse_layers[0][2](x[2]) # i=1, j=2, y = {self.fuse_layers[1][0](x[0]) + x[1]}1,1 + self.fuse_layers[1][2](x[2]) # i=2, j=1, y = self.fuse_layers[2][0](x[0]) + self.fuse_layers[2][1](x[1]) # # (4) i=0, j=1, y = x[0] + self.fuse_layers[0][1](x[1]) # i=0, j=2, y = {x[0] + self.fuse_layers[0][1](x[1])}0,1 + self.fuse_layers[0][2](x[2]) # i=0, j=3, y = {{x[0] + self.fuse_layers[0][1](x[1])}0,1 + self.fuse_layers[0][2](x[2])}0,3 + self.fuse_layers[0][3](x[3]) # i=1, j=2, y = {self.fuse_layers[1][0](x[0]) + x[1]}1,1 + self.fuse_layers[1][2](x[2]) # i=1, j=3, y = {{self.fuse_layers[1][0](x[0]) + x[1]}1,1 + self.fuse_layers[1][2](x[2])}1,3 + self.fuse_layers[1][3](x[3]) # i=2, j=1, y = self.fuse_layers[2][0](x[0]) + self.fuse_layers[2][1](x[1]) # i=3, j=1, y = self.fuse_layers[3][0](x[0]) + self.fuse_layers[3][1](x[1]) # i=3, j=2, y = {self.fuse_layers[3][0](x[0]) + self.fuse_layers[3][1](x[1])}3,1 + self.fuse_layers[3][2](x[2]) y = y + self.fuse_layers[i][j](x[j]) x_fuse.append(self.relu(y)) return x_fuse
# 欢迎大家批评指正!!!
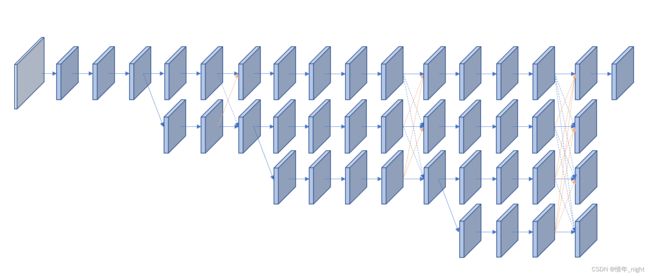
(2)HRNet 简略图
# 结合源码可以看到,HRNet 的简略图是这样的
#