一般使用#!/bin/bash来解析shell语法,当然还有zsh, ksh等,但一般用的最多的就是bash
一、变量
-e参数:解析echo中的特殊字符,如换行:echo -e "Hello \nWorld"
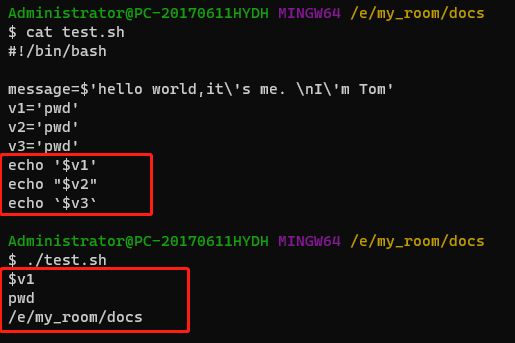
1.1、 单引号 '
如果变量被包含在单引号里面,那么变量不会被解析。$符号会原样输出。
1.2、 双引号 "
双引号会忽略大多数特殊字符,但是不包括$、反引号、\
所以不忽略$意味着Shell在双引号内部可以进行变量名替换
1.3、 反引号 `
反引号要求Shell执行被它括起来的内容
1.4、 read请求输入,同时给多个变量赋值
- 可以使用
read命令一次性给多个变量赋值 read命令每个单词之间使用空格分开-p参数: 提示信息:promptread -p 'Please enter a Fruit and Animal:' fruit animal echo "fruit is $fruit, animal is $animal"-n参数: 限制字符数n是number的首字母
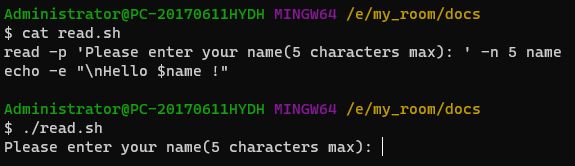
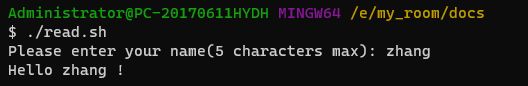
用-n可以限制用户输入的字符串的最大长度(字符数)read -p 'Please enter your name(5 characters max): ' -n 5 name echo -e "\nHello $name !"-t:限制输入时间t是time的首字母-t参数可以限定用户的输入时间(以秒为单位)
超过这个时间,就不读取输入了#!/bin/bash read -p 'Please enter the name (you have 5 seconds): ' -t 5 name echo -e "\nyour name is $name.... !"-s:隐藏输入内容-s是secret的首字母#!/bin/bash read -p 'Please enter the password : ' -s password echo -e "\npassword is $password.... !"1.5、 环境变量
1. 使用
env命令查看所有环境变量shell文件中使用环境变量
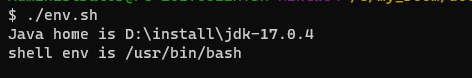
#!/bin/bash echo "Java home is $JAVA_HOME" echo "shell env is $SHELL"2.
export: 自定义环境变量3. 参数变量
我们可以这是使用:
./variable.sh 参数1 参数2 参数3...
| 变量 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| $# | 参数的数目 |
| $0 | 被运行的脚本名称 |
| $1 | 第一个参数 |
| $2 | 第二个参数 |
| $N | 第N个参数 |
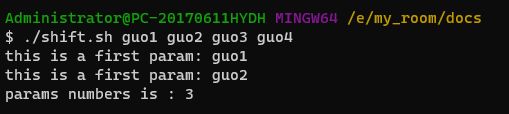
shift : 移位
#!/bin/bash
echo "this is a first param: $1"
shift
echo "this is a first param: $1"
echo "params numbers is : $#"4. 算数运算: let
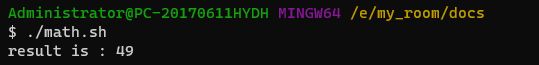
#!/bin/bash
let a="3+4"
# a的平方
let c="$a**2"
echo "result is : $c"5. 数组
#!/bin/bash
array=('apple', 'bonana', 'pear')
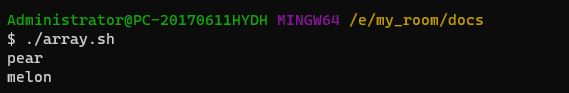
array[3]="melon"
echo "${array[2]}"
echo "${array[3]}"#!/bin/bash
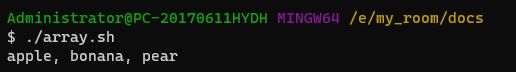
array=('apple', 'bonana', 'pear')
echo "${array[*]}"二、 条件语句
if [ 条件 ]
then
做这个
else
做那个
fi或
if [ 条件 ]; then
做这个
fi或
if [ 条件 ]
then
做这个
elif [ 条件2 ]
then
做事情2
else
做其他事情
fi不同的测试类型
1. 测试字符串
| 条件 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| $string1 = $string2 | 两个字符串是否相等,Shell大小写敏感 |
| $string1 != $string2 | 两个字符串是否不相同 |
| -z $string | 字符串string是否为空,z 是 zero 的缩写 |
| -n $string | 字符串string是否不为空,n 是 not 的缩写 |
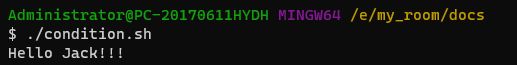
#!/bin/bash
name="Jack"
if [ $name = "Jack" ]
then
echo "Hello $name!!!"
fi#!/bin/bash
name="Jack"
if [ $name = "Jackson" ]
then
echo "Hello $name!!!"
elif [ $name = "Jacky" ]
then
echo "this is Jacky"
else
echo "default is Jack"
fi#!/bin/bash
if [ -z $1 ]
then
echo "No Parameter"
else
echo "There is at least one param!!!"
fi2. 测试数字
| 条件 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| $num1 -eq $num2 | 两个数字是否相等 |
| $num1 -ne $num2 | 是否不相等 |
| $num1 -lt $num2 | 小于 |
| $num1 -le $num2 | 小于等于 |
| $num1 -gt $num2 | 大于 |
| $num1 -ge $num2 | 大于 |
3. 测试文件
| 条件 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| -e $file | 文件是否存在,e 是 exist 的缩写 |
| -d $file | 文件是否是一个目录, d 是 dir 的缩写 |
| -f $file | 是否是一个文件,f 是 file 缩写 |
| -L $file | 文件是否是一个符号链接文件,L 是 link 的缩写 |
| -r $file | 文件是否可读, r -> read |
| -w $file | 文件是否可写,w -> write |
| -x $file | 文件是否可执行, x -> executable |
| $file1 -nt $file | 文件file1是否比file2更新,nt -> newer than |
| $file1 -ot $file2 | 文件file1是否比file2更旧,ot -> older than |
多个测试条件 && ||
#!/bin/bash
if [ $# -ge 1 ] && [ $1 = 'love' ]
then
echo "Great !"
echo "You know the password"
else
echo "You do not know the password"
ficase条件判断
#!/bin/bash
case $1 in
"Jack")
echo "Hello Jack !!!"
;;
"Tom")
echo "Hello Tom !!!"
;;
"LiLi")
echo "Hello LiLi"
# ;; 类似Java中的break
;;
# *)类似Java中的default
*)
echo "Sorry, I do not know you !"
esac逻辑或 |
#!/bin/bash
case $1 in
"dog" | "cat" | "pig")
echo "It is a animal !!!"
;;
"pigeon" | "swallow")
echo "It is a bird !!!"
;;
*)
echo "I do not know what it is"
;;
esac3. 循环语句
3.1 while 循环
while [ 条件测试 ]
do
做某些事
done或
while [ 条件测试 ]; do
做某些事
done示例
#!/bin/bash
while [ -z $response ] || [ $response != 'yes' ]
do
read -p 'Say yes: ' response
done3.2 until 循环
与while刚好相反,until表示直到条件满足就结束循环
#!/bin/bash
until [ "$response" = 'yes' ]
do
read -p 'Say yes: ' response
done3.3 for 循环
#!/bin/bash
for animal in 'dog' 'cat' 'pig'
do
echo "Animal is $animal"
done循环遍历 ls 命令查询的文件
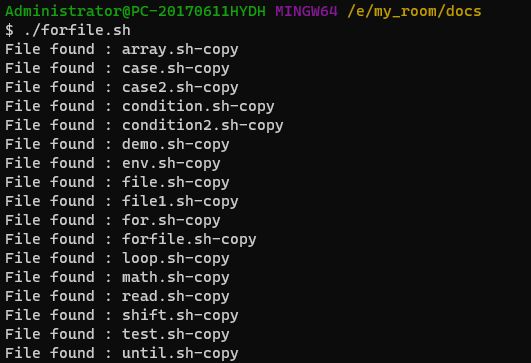
#!/bin/bash
for file in `ls`
do
echo "File found : $file"
done循环便利所有目录
for dir in `ls -al | grep "^d"`
do
echo "File found : $dir-copy"
done循环遍历所有以.sh结尾的文件
#!/bin/bash
for file in `ls *.sh`
do
echo "File found : $file-copy"
done3.4、 seq 序列
#!/bin/bash
# 其中2为步长
for i in `seq 1 2 10`
do
echo "$i"
done4. 函数
函数名后面的括号里不加任何参数
函数的完整定义必须置于函数的调用之前
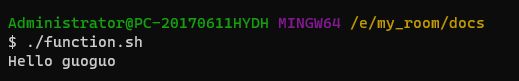
#!/bin/bash
print_something () {
echo "Hello $1"
}
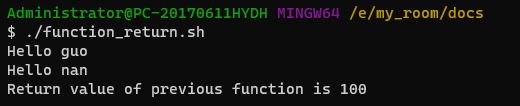
print_something guoguo有返回值的函数
#!/bin/bash
print_something () {
echo Hello $1
return 100
}
print_something guo
print_something nan
echo Return value of previous function is $?查看文件中内容的行数
#!/bin/bash
lines_in_file () {
cat $1 | wc -l
}
line_nums=$(lines_in_file $1)
echo The file $1 has $line_nums lines4.1、变量作用范围
默认来说,一个变量是全局的(global)
如果要顶一个局部变量,需要用local关键字
#!/bin/bash
local_global () {
local var1='local 1'
echo Inside function : var1 is $var1, var2 is : $var2
var1='Change again'
var2='2 Change again'
}
var1='global 1'
var2='global 2'
echo Before function call: var1 is $var1, var2 is $var2
local_global
echo After function call: var1 is $var1, var2 is $var24.2、 重载命令
command命令
重载:就是把函数的名字取成与我们通常在命令行中的命令相同的名字
#!/bin/bash
ls () {
command ls -lh
}
ls5、Shell实战练习
#!/bin/bash
if [ -z $1 ]
then
echo "Please enter the file of dir !"
exit
fi
if [ ! -e $1 ]
then
echo "Please make sure that the file of dir exists !"
exit
fi
statistics () {
for char in {a..z}
do
# >> tmp.txt输出到tmp.txt文件中
echo "$char - `grep -io "$char" $1 | wc -l`" | tr /a-z/ /A-Z/ >> tmp.txt
done
# -rn(r:倒叙,n:按数字排序),
# -k 2(根据哪几列进行排序,根据第2列排序)
# -t(指定分隔符)
sort -rn -k 2 -t - tmp.txt
rm tmp.txt
}
statistics $1