RandLA-Net源码解析
前言
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.11236
github:https://github.com/QingyongHu/RandLA-Net
- 本文章以运行S3DIS数据集为例.
- 本文章不是运行指南,仅为阅读源码的笔记。
数据准备
下载数据集解压到/data/S3DIS/Stanford3dDataset_v1.2_Aligned_Version文件夹中。
Stanford3dDataset_v1.2_Aligned_Version文件夹中包含多个Area_*(区域)文件夹。
每个Area(区域)文件夹中包含多个场景文件夹。
每个场景文件夹(以Area_1\conferenceRoom_1为例)中主要包含一个场景点云文件conferenceRoom_1.txt和一个分类点云文件夹Annotations。
conferenceRoom_1.txt中直接以XYZRGB格式储存了整个场景的点云。
-15.609 39.505 2.214 71 64 54
-15.634 39.518 2.198 68 64 52
-15.622 39.514 2.195 70 61 52
-15.621 39.510 2.215 72 65 55
-15.606 39.505 2.211 71 63 52
-15.657 39.524 2.213 76 70 58
-15.549 39.484 2.206 63 53 44
Annotations文件夹中的文件按照不同分类储存了点云,文件名为分类名称,文件内容同样为XYZRGB格式的点云。
data_prepare_s3dis.py
在准备好数据集之后运行data_prepare_s3dis.py进行数据预处理。
预处理会在/data/S3DIS文件夹下生成两个额外的文件夹original_ply和input_0.040。
程序首先将Stanford3dDataset_v1.2_Aligned_Version下的每个场景处理成一个区域名_场景名.ply的文件,放入original_ply文件夹中。其中对XYZ进行了平移,使得X, Y, Z均大于等于0,数据以XYZRGBL(L为label,分类编码的索引)方式储存。
随后对每个区域的每个场景进行如下操作:
- 进行网格下采样,将颜色进行归一化(RGB/255),保存在
input_0.040/区域名_场景名.ply。 - 对下采样后的点云坐标构建KD树,将KD树保存在
input_0.040/区域名_场景名_KDTree.pkl。 - 使用KD树查询每个
原始点最邻近的下采样点的index,将查询到的等同原始点数量的index列表保存在input_0.040/区域名_场景名_proj.pkl。
注意:以下代码为在windows下运行做过部分修改,仅供参考。
from sklearn.neighbors import KDTree
from os.path import join, exists, dirname, abspath
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os, sys, glob, pickle
BASE_DIR = dirname(abspath(__file__))
ROOT_DIR = dirname(BASE_DIR)
sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)
sys.path.append(ROOT_DIR)
from helper_ply import write_ply
from helper_tool import DataProcessing as DP
dataset_path = join(ROOT_DIR, 'data/S3DIS/Stanford3dDataset_v1.2_Aligned_Version')
anno_paths = [line.rstrip() for line in open(join(BASE_DIR, 'meta/anno_paths.txt'))]
anno_paths = [join(dataset_path, p) for p in anno_paths] # 每个Annotations文件夹的绝对路径
gt_class = [x.rstrip() for x in open(join(BASE_DIR, 'meta/class_names.txt'))]
gt_class2label = {cls: i for i, cls in enumerate(gt_class)} # class:n
sub_grid_size = 0.04
original_pc_folder = join(dirname(dataset_path), 'original_ply')
sub_pc_folder = join(dirname(dataset_path), 'input_{:.3f}'.format(sub_grid_size))
os.mkdir(original_pc_folder) if not exists(original_pc_folder) else None
os.mkdir(sub_pc_folder) if not exists(sub_pc_folder) else None
out_format = '.ply'
def convert_pc2ply(anno_path, save_path):
"""
将每个场景压成一个文件,位于data/S3DIS/original_ply中
Convert original dataset files to ply file (each line is XYZRGBL).L:label
We aggregated all the points from each instance in the room.
:param anno_path: path to annotations. e.g. Area_1/office_2/Annotations/
:param save_path: path to save original point clouds (each line is XYZRGBL)
:return: None
"""
data_list = []
for f in glob.glob(join(anno_path, '*.txt')):
class_name = os.path.basename(f).split('_')[0] # 确定标签
if class_name not in gt_class: # note: in some room there is 'staris' class..
class_name = 'clutter'
pc = pd.read_csv(f, header=None, delim_whitespace=True).values # 读入数据
labels = np.ones((pc.shape[0], 1)) * gt_class2label[class_name] # 将标签转为label
data_list.append(np.concatenate([pc, labels], 1)) # [Nx7] 结合数据和标签
pc_label = np.concatenate(data_list, 0) # Nx7
xyz_min = np.amin(pc_label, axis=0)[0:3] # 获取xyz各自的最小值
pc_label[:, 0:3] -= xyz_min # 平移
xyz = pc_label[:, :3].astype(np.float32)
colors = pc_label[:, 3:6].astype(np.uint8)
labels = pc_label[:, 6].astype(np.uint8)
write_ply(save_path, (xyz, colors, labels), ['x', 'y', 'z', 'red', 'green', 'blue', 'class'])
# save sub_cloud and KDTree file 下采样 和 KD树
sub_xyz, sub_colors, sub_labels = DP.grid_sub_sampling(xyz, colors, labels, sub_grid_size) # 网格下采样,点数 114w -> 8w
sub_colors = sub_colors / 255.0
sub_ply_file = join(sub_pc_folder, save_path.replace('/', '\\').split('\\')[-1][:-4] + '.ply')
write_ply(sub_ply_file, [sub_xyz, sub_colors, sub_labels], ['x', 'y', 'z', 'red', 'green', 'blue', 'class'])
search_tree = KDTree(sub_xyz)
kd_tree_file = join(sub_pc_folder, str(save_path.replace('/', '\\').split('\\')[-1][:-4]) + '_KDTree.pkl')
with open(kd_tree_file, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(search_tree, f)
proj_idx = np.squeeze(search_tree.query(xyz, return_distance=False)) # 查询原始点临近的下采样点index
proj_idx = proj_idx.astype(np.int32)
proj_save = join(sub_pc_folder, str(save_path.replace('/', '\\').split('\\')[-1][:-4]) + '_proj.pkl')
with open(proj_save, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump([proj_idx, labels], f)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Note: there is an extra character in the v1.2 data in Area_5/hallway_6. It's fixed manually.
for annotation_path in anno_paths:
print(annotation_path)
elements = str(annotation_path).replace('/', '\\').split('\\')
out_file_name = elements[-3] + '_' + elements[-2] + out_format
convert_pc2ply(annotation_path, join(original_pc_folder, out_file_name))
main_S3DIS.py
在完成数据预处理后运行main_S3DIS.py,传入gpu编号(默认为0),测试区域(默认为5:即使用Area_5进行测试,其他区域进行训练),模式(train, test, vis),指定预训练模型(仅mode=test时有效)。
例如:
python -B main_S3DIS.py --gpu 0 --mode train --test_area 1
加载数据
程序首先加载数据集,按照Area分为训练组和验证组,整理如下数据。
# Initiate containers S:场景数量,P:原始点云数量,N:下采样后点云数量
self.val_proj = [] # 验证集原始点云投影 Sv*P
self.val_labels = [] # 验证集原始点云标签 Sv*P
self.possibility = {} # 每个点概率 S*N
self.min_possibility = {} # 每个场景最小概率 S
self.input_trees = {'training': [], 'validation': []} # KDTree S
self.input_colors = {'training': [], 'validation': []} # RGB S*N*3
self.input_labels = {'training': [], 'validation': []} # 标签 S*N*1
self.input_names = {'training': [], 'validation': []} # 区域名_场景名 S
self.load_sub_sampled_clouds(cfg.sub_grid_size)
def load_sub_sampled_clouds(self, sub_grid_size):
tree_path = join(self.path, 'input_{:.3f}'.format(sub_grid_size))
for i, file_path in enumerate(self.all_files):
t0 = time.time()
cloud_name = file_path.replace('/', '\\').split('\\')[-1][:-4] # 获取点云名(去除路径去除后缀)
if self.val_split in cloud_name: # 选中的为验证组,其余为训练组
cloud_split = 'validation'
else:
cloud_split = 'training'
# Name of the input files
kd_tree_file = join(tree_path, '{:s}_KDTree.pkl'.format(cloud_name)) # 加载KD树
sub_ply_file = join(tree_path, '{:s}.ply'.format(cloud_name)) # 加载下采样后的点云数据
data = read_ply(sub_ply_file)
sub_colors = np.vstack((data['red'], data['green'], data['blue'])).T # N*3
sub_labels = data['class'] # N*1
# Read pkl with search tree
with open(kd_tree_file, 'rb') as f:
search_tree = pickle.load(f)
self.input_trees[cloud_split] += [search_tree]
self.input_colors[cloud_split] += [sub_colors]
self.input_labels[cloud_split] += [sub_labels]
self.input_names[cloud_split] += [cloud_name]
size = sub_colors.shape[0] * 4 * 7
print('{:s} {:.1f} MB loaded in {:.1f}s'.format(kd_tree_file.replace('/', '\\').split('\\')[-1], size * 1e-6, time.time() - t0))
print('\nPreparing reprojected indices for testing') # 为测试准备重投影的指标
# Get validation and test reprojected indices 获取验证和测试重投影的指标
for i, file_path in enumerate(self.all_files):
t0 = time.time()
cloud_name = file_path.replace('/', '\\').split('\\')[-1][:-4]
# Validation projection and labels
if self.val_split in cloud_name:
proj_file = join(tree_path, '{:s}_proj.pkl'.format(cloud_name))
with open(proj_file, 'rb') as f:
proj_idx, labels = pickle.load(f)
self.val_proj += [proj_idx]
self.val_labels += [labels]
print('{:s} done in {:.1f}s'.format(cloud_name, time.time() - t0))
初始化输入信息流
主要包括:构建生成器、使用生成器构建数据集、设置MAP函数预处理。
def init_input_pipeline(self):
print('Initiating input pipelines')
cfg.ignored_label_inds = [self.label_to_idx[ign_label] for ign_label in self.ignored_labels] # 设置忽略的分类
gen_function, gen_types, gen_shapes = self.get_batch_gen('training') # 加载生成器
gen_function_val, _, _ = self.get_batch_gen('validation')
self.train_data = tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(gen_function, gen_types, gen_shapes) # 生成器构建数据集
self.val_data = tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(gen_function_val, gen_types, gen_shapes)
self.batch_train_data = self.train_data.batch(cfg.batch_size) # 设置batch_size
self.batch_val_data = self.val_data.batch(cfg.val_batch_size)
map_func = self.get_tf_mapping2()
self.batch_train_data = self.batch_train_data.map(map_func=map_func) # 设置预处理函数
self.batch_val_data = self.batch_val_data.map(map_func=map_func)
self.batch_train_data = self.batch_train_data.prefetch(cfg.batch_size) # 设置预加载下批次文件
self.batch_val_data = self.batch_val_data.prefetch(cfg.val_batch_size)
# 构建一个可重新初始化的迭代器,提供 迭代器输出 和 使用训练组或验证组对其进行初始化 的操作
iter = tf.data.Iterator.from_structure(self.batch_train_data.output_types, self.batch_train_data.output_shapes)
self.flat_inputs = iter.get_next()
self.train_init_op = iter.make_initializer(self.batch_train_data)
self.val_init_op = iter.make_initializer(self.batch_val_data)
构建数据生成器
生成器初始化时执行以下操作:
- 为每个点云生成一个“概率”。(这里的概率使用黑体加粗,因为该概率和我们平时常用的概率意义不同)
- 确定每个场景中点云的最小概率。
生成器提供以下数据处理操作:
- 选择 存在最低概率的场景 中 最低概率的点 ,称为
中心点。 - 对
中心点坐标添加噪声。 - 通过KD树查找
中心点附近一定数量(超参数num_points = 40960)的点(包括原中心点)。若该场景点数量不足,则查找该场景中所有点,这些查找到的点称为被选点。 - 将查找到的
被选点顺序打乱。 - 获取
被选点的坐标,颜色,标签。 - 通过
被选点坐标 - 中心点坐标将被选点中心归零。 - 增加被选点的概率,越接近中心增加的数值越高,以降低这些点再次被选中的概率。
- 若在步骤3中未查找到足够的点,在
被选点中随机重复采点,使其达到参数要求的数量。 - 输出:XYZ,RGB,Label,
被选点的index,场景的index。
# Generate the input data flow
def get_batch_gen(self, split):
if split == 'training':
num_per_epoch = cfg.train_steps * cfg.batch_size
elif split == 'validation':
num_per_epoch = cfg.val_steps * cfg.val_batch_size
self.possibility[split] = []
self.min_possibility[split] = []
# Random initialize 随机初始化
for i, tree in enumerate(self.input_colors[split]):
self.possibility[split] += [np.random.rand(tree.data.shape[0]) * 1e-3] # 为点云的每个原始点生成一个"概率"
self.min_possibility[split] += [float(np.min(self.possibility[split][-1]))] # 确定最小概率
def spatially_regular_gen(): # 空间正则生成器
# Generator loop
for i in range(num_per_epoch): # 每epoch训练次数 * batch_size
# Choose the cloud with the lowest probability 选择存在最低概率点的点云
cloud_idx = int(np.argmin(self.min_possibility[split]))
# choose the point with the minimum of possibility in the cloud as query point 选择该点云概率最低的点
point_ind = np.argmin(self.possibility[split][cloud_idx])
# Get all points within the cloud from tree structure 从树结构中获取云中的所有点坐标
points = np.array(self.input_trees[split][cloud_idx].data, copy=False)
# Center point of input region 获取该点云的概率最低点(称为中心点)坐标
center_point = points[point_ind, :].reshape(1, -1) # 1*3
# Add noise to the center point 为中心点坐标添加噪声
noise = np.random.normal(scale=cfg.noise_init / 10, size=center_point.shape) # 1*3
pick_point = center_point + noise.astype(center_point.dtype)
# Check if the number of points in the selected cloud is less than the predefined num_points
if len(points) < cfg.num_points: # 检查点云数量是否足够
# Query all points within the cloud 查询云中的所有点
queried_idx = self.input_trees[split][cloud_idx].query(pick_point, k=len(points))[1][0]
else:
# Query the predefined number of points 查询一定数量的点
queried_idx = self.input_trees[split][cloud_idx].query(pick_point, k=cfg.num_points)[1][0]
# Shuffle index 随机打乱点云顺序
queried_idx = DP.shuffle_idx(queried_idx)
# Get corresponding points and colors based on the index 根据索引得到相应的点、颜色、标签
queried_pc_xyz = points[queried_idx]
queried_pc_xyz = queried_pc_xyz - pick_point # 点云居中
queried_pc_colors = self.input_colors[split][cloud_idx][queried_idx]
queried_pc_labels = self.input_labels[split][cloud_idx][queried_idx]
# Update the possibility of the selected points 更新选择的点的概率,距离中心点越近增加越多
dists = np.sum(np.square((points[queried_idx] - pick_point).astype(np.float32)), axis=1)
delta = np.square(1 - dists / np.max(dists))
self.possibility[split][cloud_idx][queried_idx] += delta
self.min_possibility[split][cloud_idx] = float(np.min(self.possibility[split][cloud_idx])) # 更新概率
# up_sampled with replacement 若点数不足,进行上采样(随机重复采样)
if len(points) < cfg.num_points:
queried_pc_xyz, queried_pc_colors, queried_idx, queried_pc_labels = \
DP.data_aug(queried_pc_xyz, queried_pc_colors, queried_pc_labels, queried_idx, cfg.num_points)
if True:
yield (queried_pc_xyz.astype(np.float32), # num_points*3
queried_pc_colors.astype(np.float32), # num_points*3
queried_pc_labels, # num_points
queried_idx.astype(np.int32), # num_points
np.array([cloud_idx], dtype=np.int32)) # int cloud_idx
gen_func = spatially_regular_gen
gen_types = (tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.int32, tf.int32, tf.int32)
gen_shapes = ([None, 3], [None, 3], [None], [None], [None])
return gen_func, gen_types, gen_shapes
MAP(数据预处理)
对生成器生成的数据进行一系列预处理:
- 将生成器生成的点称为
原始点。 - 获取
原始点中每个点的K临近(超参数k=16)的原始点的index,记为原始点knn16原始点。 - 对
原始点进行随机下采样,采样1/sub_sampling_ratio的点,得到下采样点。 原始点knn16原始点进行和3相同的下采样,得到下采样点knn16原始点。- 获取
下采样点中每个点的K=1临近的下采样点,记为下采样点knn1下采样点。 - 使
原始点=下采样点,回到步骤2,直到完成规定次数(超参数num_layers = 5)的下采样。
记录每次循环中的原始点,原始点knn16原始点,下采样点knn16原始点,下采样点knn1下采样点。
返回 记录的这些数据 和 生成器输出的 RGB,Label,被选点的index,场景的index。
@staticmethod
def get_tf_mapping2():
# Collect flat inputs
def tf_map(batch_xyz, batch_features, batch_labels, batch_pc_idx, batch_cloud_idx):
batch_features = tf.concat([batch_xyz, batch_features], axis=-1)
input_points = [] # 原始点
input_neighbors = [] # 原始点KNN16原始点
input_pools = [] # 下采样点KNN16原始点
input_up_samples = [] # 原始点KNN1下采样点
for i in range(cfg.num_layers):
neighbour_idx = tf.py_func(DP.knn_search, [batch_xyz, batch_xyz, cfg.k_n], tf.int32) # KNN
sub_points = batch_xyz[:, :tf.shape(batch_xyz)[1] // cfg.sub_sampling_ratio[i], :] # 下采样部分点
pool_i = neighbour_idx[:, :tf.shape(batch_xyz)[1] // cfg.sub_sampling_ratio[i], :] # KNN得到的也下采样
up_i = tf.py_func(DP.knn_search, [sub_points, batch_xyz, 1], tf.int32) # KNN搜索每个原点最近的下采样点
input_points.append(batch_xyz)
input_neighbors.append(neighbour_idx)
input_pools.append(pool_i)
input_up_samples.append(up_i)
batch_xyz = sub_points # 下采样点作为原始点进行再一次下采样
input_list = input_points + input_neighbors + input_pools + input_up_samples # 结合所有数据和原始数据
input_list += [batch_features, batch_labels, batch_pc_idx, batch_cloud_idx]
return input_list
return tf_map
RandLANet.py
该文件储存网络结构,供main_S3DIS.py调用。
首先我们看到模型快照会储存在results文件夹下
flat_inputs = dataset.flat_inputs # 获取数据集输入
self.config = config
# Path of the result folder 设置存储文件夹
if self.config.saving:
if self.config.saving_path is None:
self.saving_path = time.strftime('results/Log_%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S', time.gmtime())
else:
self.saving_path = self.config.saving_path
makedirs(self.saving_path) if not exists(self.saving_path) else None
其次开始构建网络的输入和各种参数
# 开始构建网络
with tf.variable_scope('inputs'):
self.inputs = dict() # 读取数据集输入
num_layers = self.config.num_layers
self.inputs['xyz'] = flat_inputs[:num_layers]
self.inputs['neigh_idx'] = flat_inputs[num_layers: 2 * num_layers]
self.inputs['sub_idx'] = flat_inputs[2 * num_layers:3 * num_layers]
self.inputs['interp_idx'] = flat_inputs[3 * num_layers:4 * num_layers]
self.inputs['features'] = flat_inputs[4 * num_layers]
self.inputs['labels'] = flat_inputs[4 * num_layers + 1]
self.inputs['input_inds'] = flat_inputs[4 * num_layers + 2]
self.inputs['cloud_inds'] = flat_inputs[4 * num_layers + 3]
self.labels = self.inputs['labels'] # 初始化参数、变量等杂项
self.is_training = tf.placeholder(tf.bool, shape=())
self.training_step = 1
self.training_epoch = 0
self.correct_prediction = 0
self.accuracy = 0
self.mIou_list = [0]
self.class_weights = DP.get_class_weights(dataset.name)
self.Log_file = open('log_train_' + dataset.name + str(dataset.val_split) + '.txt', 'a')
网络核心结构
with tf.variable_scope('layers'):
self.logits = self.inference(self.inputs, self.is_training)
在这个函数inference()中,就是网络的核心结构
首先使用一个全连接层将特征数据变换为B*N*1*8
随后叠加上多层(超参数 num_layers=5)的dilated_res_block(),每层dilated_res_block()之后还进行random_sample()。
Encoder
def inference(self, inputs, is_training):
d_out = self.config.d_out
feature = inputs['features'] # B*N*3(RGB)
feature = tf.layers.dense(feature, 8, activation=None, name='fc0') # B*N*8
feature = tf.nn.leaky_relu(tf.layers.batch_normalization(feature, -1, 0.99, 1e-6, training=is_training))
feature = tf.expand_dims(feature, axis=2) # B*N*1*8
# ###########################Encoder############################
f_encoder_list = []
for i in range(self.config.num_layers):
f_encoder_i = self.dilated_res_block(feature, inputs['xyz'][i], inputs['neigh_idx'][i], d_out[i],
'Encoder_layer_' + str(i), is_training)
f_sampled_i = self.random_sample(f_encoder_i, inputs['sub_idx'][i])
feature = f_sampled_i
if i == 0:
f_encoder_list.append(f_encoder_i)
f_encoder_list.append(f_sampled_i)
# ###########################Encoder############################
feature = helper_tf_util.conv2d(f_encoder_list[-1], f_encoder_list[-1].get_shape()[3].value, [1, 1],
'decoder_0',
[1, 1], 'VALID', True, is_training) # B*N*1*1024
...
dilated_res_block
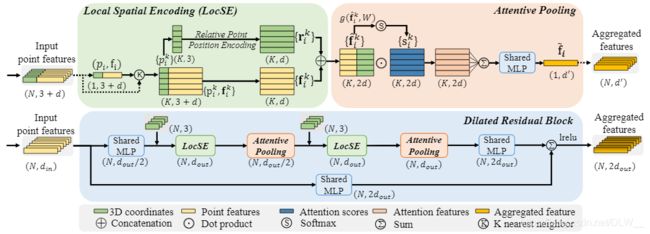
这是作者论文中给出的dilated_res_block流程图,该流程图省略了部分细节,结合下面的building_block流程图能更加清晰的看出网络结构。(默认相关点数量k_n = 16)
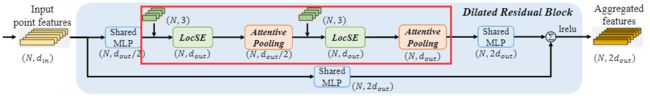

def dilated_res_block(self, feature, xyz, neigh_idx, d_out, name, is_training):
f_pc = helper_tf_util.conv2d(feature, d_out // 2, [1, 1], name + 'mlp1', [1, 1], 'VALID', True, is_training) # B*N*1*d/2
f_pc = self.building_block(xyz, f_pc, neigh_idx, d_out, name + 'LFA', is_training)
f_pc = helper_tf_util.conv2d(f_pc, d_out * 2, [1, 1], name + 'mlp2', [1, 1], 'VALID', True, is_training,
activation_fn=None)
shortcut = helper_tf_util.conv2d(feature, d_out * 2, [1, 1], name + 'shortcut', [1, 1], 'VALID',
activation_fn=None, bn=True, is_training=is_training)
return tf.nn.leaky_relu(f_pc + shortcut)
def building_block(self, xyz, feature, neigh_idx, d_out, name, is_training):
d_in = feature.get_shape()[-1].value # B*N*1*d/2
f_xyz = self.relative_pos_encoding(xyz, neigh_idx) # B*N*16*10 对点的相关位置信息进行编码
f_xyz = helper_tf_util.conv2d(f_xyz, d_in, [1, 1], name + 'mlp1', [1, 1], 'VALID', True, is_training)# B*N*16*d/2
f_neighbours = self.gather_neighbour(tf.squeeze(feature, axis=2), neigh_idx) # B*N*16*d/2 获取点的相关颜色信息
f_concat = tf.concat([f_neighbours, f_xyz], axis=-1) # B*N*16*d 连接颜色信息和位置信息
f_pc_agg = self.att_pooling(f_concat, d_out // 2, name + 'att_pooling_1', is_training)# B*N*1*d/2 对相关信息进行基于自注意力的池化
f_xyz = helper_tf_util.conv2d(f_xyz, d_out // 2, [1, 1], name + 'mlp2', [1, 1], 'VALID', True, is_training)# B*N*16*d/2
f_neighbours = self.gather_neighbour(tf.squeeze(f_pc_agg, axis=2), neigh_idx) # B*N*16*d/2 再次获取点的相关特征信息
f_concat = tf.concat([f_neighbours, f_xyz], axis=-1) # B*N*16*d 连接特征信息和位置信息
f_pc_agg = self.att_pooling(f_concat, d_out, name + 'att_pooling_2', is_training) # B*N*1*d 注意力池化
return f_pc_agg # B*N*1*d
def relative_pos_encoding(self, xyz, neigh_idx): # 编码相关点的距离,方位,原始点坐标和相关点坐标
neighbor_xyz = self.gather_neighbour(xyz, neigh_idx) # B*N*16*3
xyz_tile = tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(xyz, axis=2), [1, 1, tf.shape(neigh_idx)[-1], 1]) # B*N*16*3
relative_xyz = xyz_tile - neighbor_xyz # 计算每个点相关点的相对坐标 B*N*16*3
relative_dis = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(relative_xyz), axis=-1, keepdims=True)) # 距离 B*N*16*1
relative_feature = tf.concat([relative_dis, relative_xyz, xyz_tile, neighbor_xyz], axis=-1)
return relative_feature # B*N*16*10=距离B*N*16*1+相关点方位B*N*16*3+点坐标B*N*16*3+相关点坐标B*N*16*3
@staticmethod
def gather_neighbour(pc, neighbor_idx):
# gather the coordinates or features of neighboring points 获取索引的坐标或特征
batch_size = tf.shape(pc)[0]
num_points = tf.shape(pc)[1]
d = pc.get_shape()[2].value
index_input = tf.reshape(neighbor_idx, shape=[batch_size, -1]) # batch_size * num_point*16
features = tf.batch_gather(pc, index_input) # 进行索引
features = tf.reshape(features, [batch_size, num_points, tf.shape(neighbor_idx)[-1], d])
return features # B*N*16*d
random_sample
random_sample的内容比较简单,毕竟在数据预处理的时候就把每层的随机下采样做了,现在只需要做些索引工作就行了。
@staticmethod
def random_sample(feature, pool_idx):
"""
:param feature: [B, N, d] input features matrix
:param pool_idx: [B, N', max_num] N' < N, N' is the selected position after pooling
:return: pool_features = [B, N', d] pooled features matrix
"""
feature = tf.squeeze(feature, axis=2) # B*N*d
num_neigh = tf.shape(pool_idx)[-1] # 16
d = feature.get_shape()[-1]
batch_size = tf.shape(pool_idx)[0]
pool_idx = tf.reshape(pool_idx, [batch_size, -1])
pool_features = tf.batch_gather(feature, pool_idx)
pool_features = tf.reshape(pool_features, [batch_size, -1, num_neigh, d]) # B*N'*16*d
pool_features = tf.reduce_max(pool_features, axis=2, keepdims=True)
return pool_features # B*N'*1*d
Decoder
首先进行和Encoder相反的操作:多层上采样和反卷积。
随后进行多次卷积处理(其中包含一次droupout),最终得到B*N*class的点云分类矩阵。
# ###########################Decoder############################
f_decoder_list = []
for j in range(self.config.num_layers):
f_interp_i = self.nearest_interpolation(feature, inputs['interp_idx'][-j - 1]) # 特征向上索引 B*N+*1*1024
f_decoder_i = helper_tf_util.conv2d_transpose(tf.concat([f_encoder_list[-j - 2], f_interp_i], axis=3), # B*N*1*1.5d
f_encoder_list[-j - 2].get_shape()[-1].value, [1, 1],
'Decoder_layer_' + str(j), [1, 1], 'VALID', bn=True,
is_training=is_training) # 反卷积 B*N*1*0.5d
feature = f_decoder_i
f_decoder_list.append(f_decoder_i)
# ###########################Decoder############################
f_layer_fc1 = helper_tf_util.conv2d(f_decoder_list[-1], 64, [1, 1], 'fc1', [1, 1], 'VALID', True, is_training) # B*N*1*64
f_layer_fc2 = helper_tf_util.conv2d(f_layer_fc1, 32, [1, 1], 'fc2', [1, 1], 'VALID', True, is_training) # B*N*1*32
f_layer_drop = helper_tf_util.dropout(f_layer_fc2, keep_prob=0.5, is_training=is_training, scope='dp1')
f_layer_fc3 = helper_tf_util.conv2d(f_layer_drop, self.config.num_classes, [1, 1], 'fc', [1, 1], 'VALID', False,
is_training, activation_fn=None) # B*N*1*13
f_out = tf.squeeze(f_layer_fc3, [2])
return f_out # B*N*class
loss
如果指定了要忽略的类型,在开始计算loss前要处理这些点。
#####################################################################
# Ignore the invalid point (unlabeled) when calculating the loss #
#####################################################################
with tf.variable_scope('loss'):
self.logits = tf.reshape(self.logits, [-1, config.num_classes])
self.labels = tf.reshape(self.labels, [-1])
# Boolean mask of points that should be ignored
ignored_bool = tf.zeros_like(self.labels, dtype=tf.bool)
for ign_label in self.config.ignored_label_inds:
ignored_bool = tf.logical_or(ignored_bool, tf.equal(self.labels, ign_label))
# Collect logits and labels that are not ignored
valid_idx = tf.squeeze(tf.where(tf.logical_not(ignored_bool)))
valid_logits = tf.gather(self.logits, valid_idx, axis=0)
valid_labels_init = tf.gather(self.labels, valid_idx, axis=0)
# Reduce label values in the range of logit shape
reducing_list = tf.range(self.config.num_classes, dtype=tf.int32)
inserted_value = tf.zeros((1,), dtype=tf.int32)
for ign_label in self.config.ignored_label_inds:
reducing_list = tf.concat([reducing_list[:ign_label], inserted_value, reducing_list[ign_label:]], 0)
valid_labels = tf.gather(reducing_list, valid_labels_init)
self.loss = self.get_loss(valid_logits, valid_labels, self.class_weights)
这里的pre_cal_weights是预计算出的每个类别的点数,将其作为反权重乘以对应分类的loss可以防止 “当点云中某个类别特别多,神经网络就只选择预测那个类别以达到一个局部最优解” 的现象。
def get_loss(self, logits, labels, pre_cal_weights):
# calculate the weighted cross entropy according to the inverse frequency 根据反频率计算加权交叉熵
class_weights = tf.convert_to_tensor(pre_cal_weights, dtype=tf.float32)
one_hot_labels = tf.one_hot(labels, depth=self.config.num_classes) # N*C
weights = tf.reduce_sum(class_weights * one_hot_labels, axis=1) # N * sum(C*W)
unweighted_losses = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=one_hot_labels) # 计算交叉熵
weighted_losses = unweighted_losses * weights # N * sum(C*W)*L
output_loss = tf.reduce_mean(weighted_losses)
return output_loss
优化器配置
最后是配置优化器,各种显示参数。
with tf.variable_scope('optimizer'):
self.learning_rate = tf.Variable(config.learning_rate, trainable=False, name='learning_rate')
self.train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(self.learning_rate).minimize(self.loss)
self.extra_update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)
with tf.variable_scope('results'):
self.correct_prediction = tf.nn.in_top_k(valid_logits, valid_labels, 1)
self.accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(self.correct_prediction, tf.float32))
self.prob_logits = tf.nn.softmax(self.logits)
tf.summary.scalar('learning_rate', self.learning_rate)
tf.summary.scalar('loss', self.loss)
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', self.accuracy)
my_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES)
self.saver = tf.train.Saver(my_vars, max_to_keep=100)
c_proto = tf.ConfigProto()
c_proto.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
self.sess = tf.Session(config=c_proto)
self.merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
self.train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(config.train_sum_dir, self.sess.graph)
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
train
def train(self, dataset):
log_out('****EPOCH {}****'.format(self.training_epoch), self.Log_file)
self.sess.run(dataset.train_init_op)
while self.training_epoch < self.config.max_epoch:
t_start = time.time()
try:
ops = [self.train_op,
self.extra_update_ops,
self.merged,
self.loss,
self.logits,
self.labels,
self.accuracy]
_, _, summary, l_out, probs, labels, acc = self.sess.run(ops, {self.is_training: True})
self.train_writer.add_summary(summary, self.training_step)
t_end = time.time()
if self.training_step % 50 == 0:
message = 'Step {:08d} L_out={:5.3f} Acc={:4.2f} ''---{:8.2f} ms/batch'
log_out(message.format(self.training_step, l_out, acc, 1000 * (t_end - t_start)), self.Log_file)
self.training_step += 1
except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
m_iou = self.evaluate(dataset)
if m_iou > np.max(self.mIou_list):
# Save the best model
snapshot_directory = join(self.saving_path, 'snapshots')
makedirs(snapshot_directory) if not exists(snapshot_directory) else None
self.saver.save(self.sess, snapshot_directory + './snap', global_step=self.training_step)
self.mIou_list.append(m_iou)
log_out('Best m_IoU is: {:5.3f}'.format(max(self.mIou_list)), self.Log_file)
self.training_epoch += 1
self.sess.run(dataset.train_init_op)
# Update learning rate
op = self.learning_rate.assign(tf.multiply(self.learning_rate,
self.config.lr_decays[self.training_epoch]))
self.sess.run(op)
log_out('****EPOCH {}****'.format(self.training_epoch), self.Log_file)
except tf.errors.InvalidArgumentError as e:
print('Caught a NaN error :')
print(e.error_code)
print(e.message)
print(e.op)
print(e.op.name)
print([t.name for t in e.op.inputs])
print([t.name for t in e.op.outputs])
a = 1 / 0
print('finished')
self.sess.close()