PaperNotes(6)-GAN/DCGAN/WGAN/WGAN-GP/WGAN-SN-网络结构/实验效果
GAN模型网络结构+实验效果演化
- 1.GAN
-
- 1.1网络结构
- 1.2实验结果
- 2.DCGAN
-
- 2.1网络结构
- 2.2实验结果
- 3.WGAN
-
- 3.1网络结构
- 3.2实验结果
- 4.WGAN-GP
-
- 4.1网络结构
- 4.2实验结果
- 5.WGAN-SN
-
- 5.1网络结构
- 5.2实验结果
- 小结
1.GAN
文章: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1406.2661.pdf
代码: Pylearn2, theano, https://github.com/goodfeli/adversarial
1.1网络结构
多层感知机器(没有在文章中找到)
G: ReLU, sigmoid
D:maxout, dropout
1.2实验结果
1.数据集:MNIST,the Toronto Face Database (TFD) , CIFAR-10
2.Gaussian Parzen window 拟合样本,输出对应的log-likelihood.
3.直接展示了在三个图像集合上的效果,最右遍一列显示的是与第二列最相似的训练样本(具体如何衡量相近,需要查论文)

a) MNIST,b) TFD, c) CIFAR-10 (fully connected model), d) CIFAR-10 (convolutional discriminatorand “deconvolutional” generator)
训练次数呢?
这时候的cifar数据集基本不能看·
2.DCGAN
文章:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.06434.pdf
代码:https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/dcgan_faces_tutorial.html,pytorch 官网DCAGAN教程,示例是人脸图像生成
2.1网络结构
P3:网络结构表
1.去除所有的poling层
2.D,G中都使用batchnorm
3.移除全联接结构
4.G激活函数:ReLU+Tanh(最后一层)
5.D激活函数:LeakyReLU(所有层)
2.2实验结果
Lsun–视觉效果,300万张图像
Cifar10-分类实验
人脸加减法实验
3.WGAN
文章:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1701.07875.pdf
代码:https://github.com/martinarjovsky/WassersteinGAN,作者github 提供的代码,pytorch
3.1网络结构
p9:以DCGAN为baseline, baseline 损失使用-logD 技巧
lipschitz约束实现:clip D网络参数
3.2实验结果
Lsun-bedromm 稳定性视觉实验
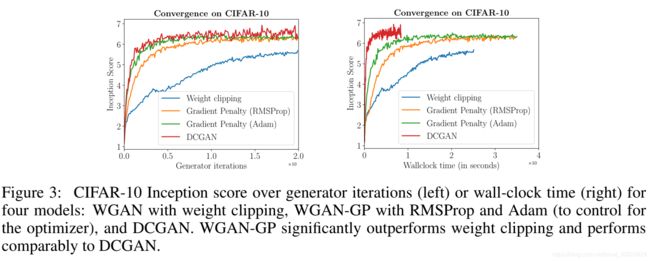
WGAN本身是为了提高GAN模型训练的稳定性而生的。文章强调的两个优点啊:有意义的loss+稳定训练过程。同一作者的后续文章(improved Training of Wasserstein GANs) 图3,展示了clip 版本WGAN IS指标确实比不上DCGAN。
4.WGAN-GP
文章:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.00028.pdf
代码:https://github.com/igul222/improved_wgan_training,作者github 提供的代码,tensorflow(明明是同一个作者写的平台还不一样)
自己复现代码时使用的是:https://github.com/eriklindernoren/PyTorch-GAN/tree/master/implementations WGAN_GP中写的GP方法。
4.1网络结构
1.G网络带BN,D网络不实用Batch normalization, 转而使用 layer Normalization
2.clip 会使优化变得困难,惩罚D网络的梯度,使其不至于太大
3.在cifar-10 数据集合上D和G都使用resnet 结构
4.2实验结果
WGAN-GP能看出来一个轮廓,算是比较好的一个视觉效果了。
本人用pytroch 复现WGAN_GP ,参考了作者梯度惩罚的源码(https://github.com/igul222/improved_wgan_training.)主体代码是在WGAN的基础上(https://github.com/martinarjovsky/WassersteinGAN),注释了CLIP部分的代码,在D损失函数的计算上增加了梯度惩罚项目(计算方式参考了网上的实现博文)。虽然生成的图像视觉指标轮廓不错,但是IS曲线(与baseline-WGAN 相比)并没特别的优势。
现在WGAN实现的时候,D网络的更新次数在100/5之间切换,直接换成5 试一试
仓库:https://github.com/caogang/wgan-gp (1000star)是pytorch复现的WGAN_GP具体效果没有考察。
// 梯度惩罚的计算法函数
def compute_gradient_penalty(D, real_samples, fake_samples):
"""Calculates the gradient penalty loss for WGAN GP"""
# Random weight term for interpolation between real and fake samples
alpha = torch.Tensor(np.random.random((real_samples.size(0), 1, 1, 1))).cuda()
# Get random interpolation between real and fake samples
# print(real_samples.size(),fake_samples.size())
# interpolates = (alpha * real_samples + ((1 - alpha) * fake_samples)).requires_grad_(True)
interpolates = (alpha * fake_samples + ((1 - alpha) * real_samples)).requires_grad_(True)
d_interpolates = D(interpolates)
# d_interpolates = d_interpolates.resize(d_interpolates.size()[0],1)
fake = Variable(torch.Tensor(real_samples.shape[0], 1).fill_(1.0), requires_grad=False).cuda()
# Get gradient w.r.t. interpolates
gradients = torch.autograd.grad(
outputs=d_interpolates,
inputs=interpolates,
grad_outputs=fake,
create_graph=True,
retain_graph=True,
only_inputs=True,
)[0]
gradients = gradients.view(gradients.size(0), -1)
gradient_penalty = ((gradients.norm(2, dim=1) - 1) ** 2).mean()
return gradient_penalty
...
// 判别器的损失函数的计算
gradient_penalty = utils.compute_gradient_penalty(netD,inputv_real,inputv_fake)
gradient_penalty *= lambda_gp
gradient_penalty.backward()
errD = errD_real - errD_fake - gradient_penalty
optimizerD.step()
d_iterations += 1
5.WGAN-SN
文章:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1802.05957.pdf
代码:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.utils.spectral_norm.html?highlight=nn%20utils%20spectra#torch.nn.utils.spectral_norm,pytorch 官网上实现了D网络参数谱正则化的代码,直接在定义层的时候调用就可以了。
5.1网络结构
D卷积结构,没有BN
G卷积结构+BN
(没有LN的情况)
5.2实验结果
cifar-10 上的结构,虽然也只能是看一个大致轮廓,但是,效果还是比较好的。
小结
1.BN 在mini-batch 较小或者RNN等动态网络里效果不好,因为少量样本的均值和方差无法反应整体的情况。BN强调了mini-batch 样本之间的联系。D网络本身是将一个输入映射到一个得分输出,不应该考虑样本之间的联系,所以不应该使用BN,在WGAN-GP中转而使用layer-normalization,对同一个样本的各个通道做归一化。
2.网络越深,其生成能力越强,WGAN-GP论文中cifar-10 IS可以达到7左右,WGAN-Sn中也可以达到6.41,都是因为网络结构不同,所以在浅层只有卷积的G(DCGAN,WGAN)想要达到那么高的IS一般是不可能的。
3.尝试人脸生成数据集合the Toronto Face Database (TFD)
4.整理一下各个实验的G训练次数。
5.stack gan 的网络结构基本还行。在做GP实验的时候,至少得吧BN该成LN,再看看SN中是如何做的。
涉及WGAN的论文总共三篇:
WGAN前作:Towards Principled Methods for Training Generative Adversarial Networks
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.04862
WGAN:Wasserstein GAN
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.07875
WGAN后作:Improved Training of Wasserstein GANs
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.00028v3
都是神人Ishaan Gulrajani 写的,连GAN之父Ian Goodfellow都十分惊叹WGAN的改进内容。
神员各种类型GAN代码实现(TensorFlow框架):https://github.com/LynnHo/AttGAN-Tensorflow
这三篇论文理论性都比较强,尤其是第一篇,涉及到比较多的理论公式推导。知乎郑华滨的两个论述,Wasserstein GAN最新进展:从weight clipping到gradient penalty,更加先进的Lipschitz限制手法在理论方面已经做了一个很好的介绍。不过对于很多数学不太好的同学(包括我自己),看着还是不太好理解,所以这里尽量站在做工程的角度,理一下这三篇文章的思路,这样可以对作者的思路有一个比较清晰的理解。