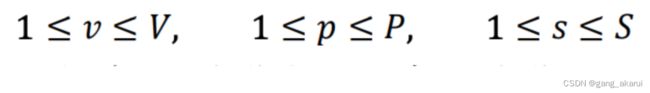量子退火Python实战(1):车辆路径问题(VRP : Vehicle Routing Problem)
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、车辆路径问题(VRP)的QUBO建模
-
- 1.目标变量
- 2.目标函数定义
- 3.约束条件定义
- 二、Python实现VRP的QUBO
-
- 1.引入库
- 2.设置参数和距离矩阵
- 3.QUBO实现
- 4.OpenJij求解QUBO目标变量
- 5.输出求解结果路径
- 总结
前言
提示:本系列主要讲解如何用python实现常见组合优化问题中的QUBO公式:
量子退火作为解决组合优化问题的利器,车辆路径问题(VRP : Vehicle Routing Problem)是最经常被提起的现实应用。该问题的定义和特点如下:
-
车辆路径问题 (VRP) 是优化多辆送货车辆的送货顺序的组合优化问题,是旅行商问题 (TSP) 的推广。
-
这是一个可以应用于各种现实世界问题的问题,例如物流中的货物配送、工厂中的货物搬运,以及按需运输服务中的车辆分配计划。
-
VRP 是一个典型的组合优化问题,也是经典的NP-Hard问题,普通计算机很难在多项式时间内找到精确解。
-
量子退火有望利用量子隧穿效应实时解决 NP-Hard 组合优化问题。
一、车辆路径问题(VRP)的QUBO建模
本章节主要参考以下论文:
齋藤和広, 大山重樹, 梅木智光, 黒川茂莉, 小野智弘, "配送計画問題への量子アニーリング適用に関する初期評価" DEIM2020 D2-4(day1 p25) https://proceedings-of-deim.github.io/DEIM2020/papers/D2-4.pdf
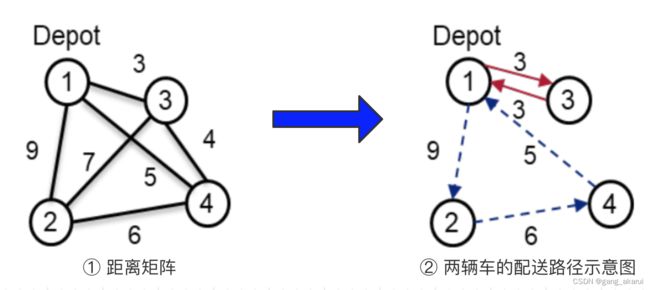
作为一个基本的VRP,我们考虑了当多辆运送车辆访问所有目标基地时,搜索总旅行成本最小的路线的组合优化问题。
我们假设所有的送货车辆都从一个叫做 Depot 的基地出发,并且总是在最后返回到 Depot。移动成本使用基地之间的距离计算。距离矩阵的实现如下:
- VRP的QUBO的定义:
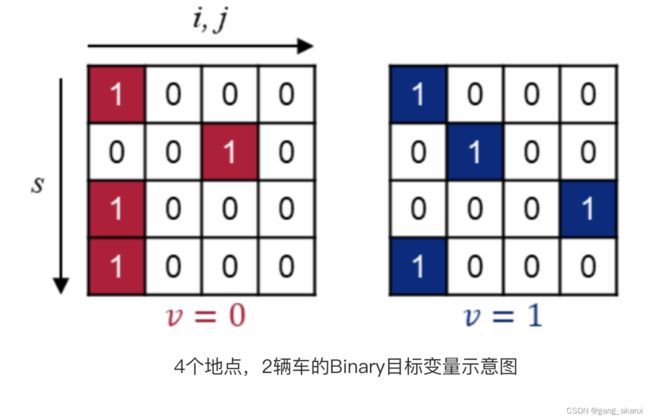
我们把地点1作为Depot,然后假设有2辆车用来配送4个地点。2辆车的配送示意图如下:
其实大家可以可以把VRP问题理解为,有V辆车,V辆车各自负责不重叠的地点子集,所有车辆负责的地点子集的路径总和最小。
所以这里我们有三个参数需要设定:
- V:车辆个数
- P:地点个数
- S:时间步(TSP建模中,我们不需要设置时间步,因为S=P+1)
1.目标变量
- 红色矩阵代表车辆1,从地点1==>地点3==>地点1;
- 蓝色矩阵代表车辆2,从地点1==>地点2==>地点4==>地点1。
2.目标函数定义
3.约束条件定义
-
约束条件
– 条件a:第1个时间步的地点必须是Depot地点
– 条件b:第S个时间步的地点必须是Depot地点
– 条件c:除了Depot地点,剩余地点必须被访问过一次
– 条件d:相同时间步,不同车辆v不能在同一地点p -
H = H o b j + w 1 H a + w 2 H b + w 3 H c + w 4 H d \mathcal{H}=\mathcal{H}_{obj}+w_1 \mathcal{H}_a+w_2 \mathcal{H}_b+w_3 \mathcal{H}_c+w_4 \mathcal{H}_d H=Hobj+w1Ha+w2Hb+w3Hc+w4Hd
-
H o b j = ∑ v = 1 V ∑ i = 1 P ∑ j = 1 P ∑ s = 1 S − 1 d i j x i s ( v ) x j ( s + 1 ) ( v ) \mathcal{H}_{obj}=\sum_{v=1}^V \sum_{i=1}^P \sum_{j=1}^P \sum_{s=1}^{S-1} d_{i j} x_{i s}^{(v)} x_{j(s+1)}^{(v)} Hobj=∑v=1V∑i=1P∑j=1P∑s=1S−1dijxis(v)xj(s+1)(v)
-
H a = ∑ v = 1 V ( 1 − x 11 ( v ) ) 2 \mathcal{H}_a=\sum_{v=1}^V\left(1-x_{11}^{(v)}\right)^2 Ha=∑v=1V(1−x11(v))2
-
H b = ∑ v = 1 V ( 1 − x 1 S ( v ) ) 2 \mathcal{H}_b=\sum_{v=1}^V\left(1-x_{1 S}^{(v)}\right)^2 Hb=∑v=1V(1−x1S(v))2
-
H c = ∑ p = 2 P ( 1 − ∑ v = 1 V ∑ s = 1 S x p s ( v ) ) 2 \mathcal{H}_c=\sum_{p=2}^P\left(1-\sum_{v=1}^V \sum_{s=1}^S x_{p s}^{(v)}\right)^2 Hc=∑p=2P(1−∑v=1V∑s=1Sxps(v))2
-
H d = ∑ v = 1 V ∑ s = 1 s ( 1 − ∑ p = 1 P x p s ( v ) ) 2 \mathcal{H}_d=\sum_{v=1}^V \sum_{s=1}^s\left(1-\sum_{p=1}^P x_{p s}^{(v)}\right)^2 Hd=∑v=1V∑s=1s(1−∑p=1Pxps(v))2
二、Python实现VRP的QUBO
本章节主要来自以下代码库:https://github.com/yskmt2018/quantum2020/blob/master/vehicle_routing_problem.ipynb
1.引入库
import math
import pyqubo
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from openjij import SQASampler
2.设置参数和距离矩阵
# 车辆个数
V = 3
# 地点个数
L = len(distance[0])
# 最大时间步
S = 10
# 距离矩阵
distance = np.array([
[0, 548, 776, 696, 582, 274, 502, 194, 308, 194, 536, 502, 452, 1020, 393, 208, 1196, 983, 427, 482, 479, 517],
[548, 0, 684, 308, 194, 502, 730, 354, 696, 742, 1084, 594, 1102, 298, 741, 582, 712, 1085, 1024, 202, 220, 1050],
[776, 684, 0, 992, 878, 502, 274, 810, 468, 742, 400, 1278, 1152, 819, 510, 514, 399, 537, 579, 509, 285, 555],
[696, 308, 992, 0, 114, 650, 878, 502, 844, 890, 1232, 514, 300, 263, 593, 153, 801, 1128, 729, 1230, 317, 946],
[582, 194, 878, 114, 0, 536, 764, 388, 730, 776, 1118, 400, 511, 886, 168, 514, 396, 594, 886, 190, 729, 1042],
[274, 502, 502, 650, 536, 0, 228, 308, 194, 240, 582, 776, 270, 343, 716, 535, 1269, 410, 1177, 494, 1133, 651],
[502, 730, 274, 878, 764, 228, 0, 536, 194, 468, 354, 1004, 144, 353, 408, 220, 636, 514, 1180, 1146, 130, 648],
[194, 354, 810, 502, 388, 308, 536, 0, 342, 388, 730, 468, 476, 1296, 338, 1100, 1125, 986, 710, 320, 279, 460],
[308, 696, 468, 844, 730, 194, 194, 342, 0, 274, 388, 810, 263, 138, 145, 740, 1251, 1262, 402, 569, 189, 877],
[194, 742, 742, 890, 776, 240, 468, 388, 274, 0, 342, 536, 1190, 757, 293, 580, 1195, 124, 268, 505, 309, 602],
[536, 1084, 400, 1232, 1118, 582, 354, 730, 388, 342, 0, 878, 369, 161, 306, 1074, 1110, 1130, 347, 163, 817, 637],
[502, 594, 1278, 514, 400, 776, 1004, 468, 810, 536, 878, 0, 381, 1041, 1004, 1251, 406, 578, 1231, 584, 727, 902],
[452, 1102, 1152, 300, 511, 270, 144, 476, 263, 1190, 369, 381, 0, 720, 1011, 991, 957, 233, 758, 934, 1054, 154],
[1020, 298, 819, 263, 886, 343, 353, 1296, 138, 757, 161, 1041, 720, 0, 156, 958, 1202, 919, 401, 685, 716, 994],
[393, 741, 510, 593, 168, 716, 408, 338, 145, 293, 306, 1004, 1011, 156, 0, 798, 270, 298, 618, 246, 766, 957],
[208, 582, 514, 153, 514, 535, 220, 1100, 740, 580, 1074, 1251, 991, 958, 798, 0, 1244, 516, 710, 1086, 946, 1098],
[1196, 712, 399, 801, 396, 1269, 636, 1125, 1251, 1195, 1110, 406, 957, 1202, 270, 1244, 0, 1112, 1031, 1106, 785, 913],
[983, 1085, 537, 1128, 594, 410, 514, 986, 1262, 124, 1130, 578, 233, 919, 298, 516, 1112, 0, 593, 109, 649, 1150],
[427, 1024, 579, 729, 886, 1177, 1180, 710, 402, 268, 347, 1231, 758, 401, 618, 710, 1031, 593, 0, 676, 785, 602],
[482, 202, 509, 1230, 190, 494, 1146, 320, 569, 505, 163, 584, 934, 685, 246, 1086, 1106, 109, 676, 0, 394, 263],
[479, 220, 285, 317, 729, 1133, 130, 279, 189, 309, 817, 727, 1054, 716, 766, 946, 785, 649, 785, 394, 0, 826],
[517, 1050, 555, 946, 1042, 651, 648, 460, 877, 602, 637, 902, 154, 994, 957, 1098, 913, 1150, 602, 263, 826, 0],
])
3.QUBO实现
- H o b j = ∑ v = 1 V ∑ i = 1 P ∑ j = 1 P ∑ s = 1 S − 1 d i j x i s ( v ) x j ( s + 1 ) ( v ) \mathcal{H}_{obj}=\sum_{v=1}^V \sum_{i=1}^P \sum_{j=1}^P \sum_{s=1}^{S-1} d_{i j} x_{i s}^{(v)} x_{j(s+1)}^{(v)} Hobj=∑v=1V∑i=1P∑j=1P∑s=1S−1dijxis(v)xj(s+1)(v)
def build_objective(x: pyqubo.array.Array) -> pyqubo.core.express.AddList:
H = sum(distance[l_from][l_to] * x[v][s][l_from] * x[v][s+1][l_to]
for v in range(V)
for s in range(S-1)
for l_from in range(L)
for l_to in range(L)
)
return H
- H a = ∑ v = 1 V ( 1 − x 11 ( v ) ) 2 \mathcal{H}_a=\sum_{v=1}^V\left(1-x_{11}^{(v)}\right)^2 Ha=∑v=1V(1−x11(v))2
def build_depot_start_rule(x: pyqubo.array.Array) -> pyqubo.core.express.Constraint:
H = pyqubo.Constraint(
sum((x[v][0][0] - 1)**2 for v in range(V)),
'w_0')
return H
- H b = ∑ v = 1 V ( 1 − x 1 S ( v ) ) 2 \mathcal{H}_b=\sum_{v=1}^V\left(1-x_{1 S}^{(v)}\right)^2 Hb=∑v=1V(1−x1S(v))2
def build_depot_end_rule(x: pyqubo.array.Array) -> pyqubo.core.express.Constraint:
H = pyqubo.Constraint(
sum((x[v][S-1][0] - 1)**2 for v in range(V)),
'w_1')
return H
- H c = ∑ p = 2 P ( 1 − ∑ v = 1 V ∑ s = 1 S x p s ( v ) ) 2 \mathcal{H}_c=\sum_{p=2}^P\left(1-\sum_{v=1}^V \sum_{s=1}^S x_{p s}^{(v)}\right)^2 Hc=∑p=2P(1−∑v=1V∑s=1Sxps(v))2
def build_vehicle_stay_rule(x: pyqubo.array.Array) -> pyqubo.core.express.Constraint:
H = pyqubo.Constraint(
sum(
(sum(x[v][s][l] for l in range(L)) - 1)**2
for v in range(V)
for s in range(S)),
'w_2')
return H
- H d = ∑ v = 1 V ∑ s = 1 s ( 1 − ∑ p = 1 P x p s ( v ) ) 2 \mathcal{H}_d=\sum_{v=1}^V \sum_{s=1}^s\left(1-\sum_{p=1}^P x_{p s}^{(v)}\right)^2 Hd=∑v=1V∑s=1s(1−∑p=1Pxps(v))2
def build_location_visit_rule(x: pyqubo.array.Array) -> pyqubo.core.express.Constraint:
H = pyqubo.Constraint(
sum(
(sum(x[v][s][l] for v in range(V) for s in range(S)) - 1)**2
for l in range(1, L)),
'w_3')
return H
- H = H o b j + w 1 H a + w 2 H b + w 3 H c + w 4 H d \mathcal{H}=\mathcal{H}_{obj}+w_1 \mathcal{H}_a+w_2 \mathcal{H}_b+w_3 \mathcal{H}_c+w_4 \mathcal{H}_d H=Hobj+w1Ha+w2Hb+w3Hc+w4Hd
# Vehicle Routing
x = pyqubo.Array.create('x', shape=(V,S,L), vartype='BINARY')
%%time
H = build_objective(x) + \
pyqubo.Placeholder('w_1') * build_depot_start_rule(x) + \
pyqubo.Placeholder('w_2') * build_depot_end_rule(x) + \
pyqubo.Placeholder('w_3') * build_vehicle_stay_rule(x) + \
pyqubo.Placeholder('w_4') * build_location_visit_rule(x)
feed_dict = {'w_1': 1000,
'w_2': 1000,
'w_3': 1000,
'w_4': 1000}
model = H.compile()
qubo, constant = model.to_qubo(feed_dict=feed_dict)
4.OpenJij求解QUBO目标变量
OpenJij(GitHub链接)是使用普通计算机提供SQA(Simulated Quantum Annealing)API来求解,经常用来搭配OpenJij使用。
sampler = SQASampler(trotter=20, num_reads=10)
response = sampler.sample_qubo(qubo)
5.输出求解结果路径
def extract_samples(response) -> (list, list):
solutions = []
energies = []
for record in response.record:
sol, num_occ = record[0], record[2]
solution, broken, energy = model.decode_solution(dict(zip(response.variables, sol)), vartype='BINARY', feed_dict=feed_dict)
if len(broken) == 0:
solutions += [solution] * num_occ
energies += [energy] * num_occ
return solutions, energies
solutions, energies = extract_samples(response)
def vehicle_movement(solution: list) -> list:
vehicles = []
for v in range(V):
solution_sorted = sorted(solution['x'][v].items(), key=lambda x:x[0])
s = [i[1] for i in solution_sorted]
df = pd.DataFrame(s).astype(int)
df.columns = [chr(l) for l in range(65, 65+L)]
vehicles.append(df)
return vehicles
best_solution = solutions[energies.index(min(energies))]
best_vehicles = vehicle_movement(best_solution)
def highlight_positive(val: int) -> str:
if val == 1:
return 'color: {}; font-weight: bold'.format('red')
else:
return 'color: {}'.format('gray')
for v in range(V):
display_html('vehicle-{}'.format(v+1) + best_vehicles[v].style.applymap(highlight_positive)._repr_html_() + '
', raw=True)
总结
本文讲解以最短距离为优化目标的VRP的求解,约束条件也比较简单,真正的应用里,也有以最短时间为优化目标的,也有很多考率以下约束条件的:
- 优先送货服务
- 车辆载货量有限制
- 指定时间配送
至于建模以上类似的约束条件,下面两篇文章可以给大家一些启示:
-
A Hybrid Solution Method for the Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem Using a Quantum Annealer
https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.07403 -
Quantum Annealing of Vehicle Routing Problem with Time, State and Capacity https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.06322
下一篇讲解,护士工作时间排班问题。