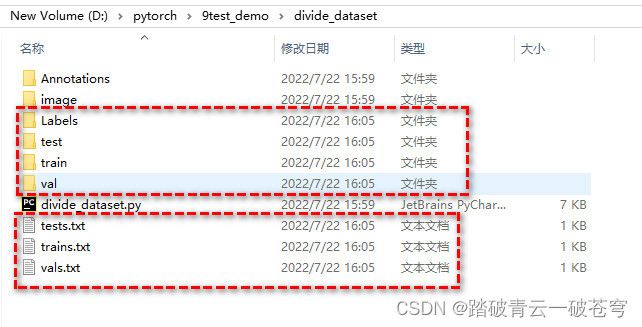
适用于Yolov5数据集划分的脚本代码(train, test, val)
将现有的数据集以及对应的xml文件按照【比例】如:7:2:1划分为训练集、验证集和测试集,并生成对应的txt文件(yolov5可识别的格式)
import os
import random
import shutil
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
random.seed(666)
LIST_FILE=['train', 'val', 'test']
CLASS = ["1", "2", "roll_bad"]
def dir_exist(str_dir_path):
'''
func:judge file is or not exist
:param str_dir_path: file path
:return:
'''
if not os.path.exists(str_dir_path):
os.makedirs(str_dir_path)
def divide_filename(file_name):
'''
func:divide filename to pre_name and expandname
example:'1.jpeg' --> '1', '.jpeg'
:param file_name:
:return:
'''
image_pre, exp_format = os.path.splitext(file_name)
return image_pre, exp_format
def file_expand(item_name, file_type):
'''
func:judge is belong to adaptive expand_name file
example:item_name = '1.jpeg' file_type = '.jpeg'
:param item_name:
:param file_type:file expand name
:return:item_name
'''
if item_name.endswith(file_type):
return item_name
else:
print("not exist the {} file".format(item_name))
return
def read_file(file_path, str_exp_name):
'''
func:List of file names corresponding to file types.
:param file_path:
:param str_exp_name:
:return:
'''
temp = os.listdir(file_path)
# ['20210318085956.xml', '20210318090005_90.xml', ...]
list_total = []
for item in temp:
true_item = file_expand(item, str_exp_name)
list_total.append(true_item)
return list_total
def compute_count(file_path, train_percent, test_percent, str_exp_name):
total_num = len(read_file(file_path, str_exp_name))
list_index = range(total_num) # []
# 训练样本的数量
train_samples_count = int(total_num * train_percent)
dis_order = random.sample(list_index, total_num) # 从 列表中抽取随机num个数值,打乱列表顺序
list_train = random.sample(dis_order, train_samples_count) # 从随机num个数值中抽取train_samples_count个数值
test_samples_count = int(total_num * test_percent)
dis_order_not_in_train = [i for i in dis_order if i not in list_train]
list_test = random.sample(dis_order_not_in_train, test_samples_count)
list_val = [i for i in dis_order_not_in_train if i not in list_test]
return list_train, list_val, list_test
# normalization
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / size[0]
dh = 1. / size[1]
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def convert_annotation(xml_file_path, file_name_pre, save_labels_path):
# 目标文件路径
in_file = open(xml_file_path +'/' + '{}.xml'.format(file_name_pre), 'rb')
# 转换后的txt文件路径
out_file = open(save_labels_path + '/' + '{}.txt'.format(file_name_pre), 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in CLASS or float(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = CLASS.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
def copy_to_target_file(source_file_path,
LIST_FILE,
copy_to_path,
save_txt_file_path,
xml_file_path,
save_labels_path,
list_train,
list_val,
list_test,
str_exp_name):
# copy process
list_file = read_file(source_file_path, str_exp_name)
for file_name in LIST_FILE:
dir_exist(save_txt_file_path)
txt_file = open(save_txt_file_path+ '/'+ '{}s.txt'.format(file_name), 'w')
if file_name == 'train':
list_index = list_train
elif file_name == 'val':
list_index = list_val
elif file_name == 'test':
list_index = list_test
# judge exist or not ['train', 'val', 'test'] file
dir_exist(copy_to_path + '/' + file_name)
for i in list_index:
# img_file_name:1yw.jpeg
img_file_name = list_file[int(i)]
# copy file from src_path to target_path
shutil.copy(source_file_path + '/' + img_file_name, copy_to_path + '/' + file_name)
image_pre, exp_format = divide_filename(img_file_name)
txt_file.write(source_file_path + '/' + img_file_name + '\n')
convert_annotation(xml_file_path, image_pre, save_labels_path)
txt_file.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
'''
str_exp_name
xmlfilepath:xml文件所在路径
saveBasePath:保存目标路径
save_txt_file_path:保存txt文件路径
'''
str_exp_name = '.jpeg'
source_file_path = 'D:/pytorch/9test_demo/divide_dataset/image'
target_save_path = 'D:/pytorch/9test_demo/divide_dataset'
save_image_path_to_txt_file = 'D:/pytorch/9test_demo/divide_dataset'
xml_file_path = 'D:/pytorch/9test_demo/divide_dataset/Annotations'
save_labels_path = 'D:/pytorch/9test_demo/divide_dataset/Labels'
dir_exist(save_labels_path)
# 生成长度为0到total_num的列表
train_percent = 0.7
test_percent = 0.1
list_train, list_val, list_test = compute_count(source_file_path, train_percent, test_percent, str_exp_name)
copy_to_target_file(source_file_path,
LIST_FILE,
target_save_path,
save_image_path_to_txt_file,
xml_file_path,
save_labels_path,
list_train,
list_val,
list_test,
str_exp_name)