【动手学Paddle2.0系列】低配版PP-YOLO实战(一种改进的YOLOV3算法)
低配版PP-YOLO实战
目录
1、数据处理与读取
2、目标检测模型PP-YOLO
3、总结
第一部分:数据处理与读取
一、数据处理
林业病虫害数据集和数据预处理方法介绍
在本课程中,将使用百度与林业大学合作开发的林业病虫害防治项目中用到昆虫数据集。
读取AI识虫数据集标注信息
AI识虫数据集结构如下:
- 提供了2183张图片,其中训练集1693张,验证集245,测试集245张。
- 包含7种昆虫,分别是Boerner、Leconte、Linnaeus、acuminatus、armandi、coleoptera和linnaeus。
- 包含了图片和标注,请读者先将数据解压,并存放在insects目录下。
insects包含train、val和test三个文件夹。train/annotations/xmls目录下存放着图片的标注。每个xml文件是对一张图片的说明,包括图片尺寸、包含的昆虫名称、在图片上出现的位置等信息。
# 解压数据脚本,第一次运行时打开注释,将文件解压到work目录下
# !unzip -q -d /home/aistudio/work /home/aistudio/data/data73985/insects.zip
下面我们将从数据集中读取xml文件,将每张图片的标注信息读取出来。在读取具体的标注文件之前,我们先完成一件事情,就是将昆虫的类别名字(字符串)转化成数字表示的类别。因为神经网络里面计算时需要的输入类型是数值型的,所以需要将字符串表示的类别转化成具体的数字。昆虫类别名称的列表是:[‘Boerner’, ‘Leconte’, ‘Linnaeus’, ‘acuminatus’, ‘armandi’, ‘coleoptera’, ‘linnaeus’],这里我们约定此列表中:'Boerner’对应类别0,'Leconte’对应类别1,…,'linnaeus’对应类别6。使用下面的程序可以得到表示名称字符串和数字类别之间映射关系的字典。
INSECT_NAMES = ['Boerner', 'Leconte', 'Linnaeus',
'acuminatus', 'armandi', 'coleoptera', 'linnaeus']
def get_insect_names():
"""
return a dict, as following,
{'Boerner': 0,
'Leconte': 1,
'Linnaeus': 2,
'acuminatus': 3,
'armandi': 4,
'coleoptera': 5,
'linnaeus': 6
}
It can map the insect name into an integer label.
"""
insect_category2id = {}
for i, item in enumerate(INSECT_NAMES):
print(item)
insect_category2id[item] = i
return insect_category2id
cname2cid = get_insect_names()
cname2cid
Boerner
Leconte
Linnaeus
acuminatus
armandi
coleoptera
linnaeus
{'Boerner': 0,
'Leconte': 1,
'Linnaeus': 2,
'acuminatus': 3,
'armandi': 4,
'coleoptera': 5,
'linnaeus': 6}
调用get_insect_names函数返回一个dict,描述了昆虫名称和数字类别之间的映射关系。下面的程序从annotations/xml目录下面读取所有文件标注信息。
import os
import numpy as np
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def get_annotations(cname2cid, datadir):
filenames = os.listdir(os.path.join(datadir, 'annotations', 'xmls'))
records = []
ct = 0
for fname in filenames:
fid = fname.split('.')[0]
fpath = os.path.join(datadir, 'annotations', 'xmls', fname)
img_file = os.path.join(datadir, 'images', fid + '.jpeg')
tree = ET.parse(fpath)
if tree.find('id') is None:
im_id = np.array([ct])
else:
im_id = np.array([int(tree.find('id').text)])
objs = tree.findall('object')
im_w = float(tree.find('size').find('width').text)
im_h = float(tree.find('size').find('height').text)
gt_bbox = np.zeros((len(objs), 4), dtype=np.float32)
gt_class = np.zeros((len(objs), ), dtype=np.int32)
is_crowd = np.zeros((len(objs), ), dtype=np.int32)
difficult = np.zeros((len(objs), ), dtype=np.int32)
for i, obj in enumerate(objs):
cname = obj.find('name').text
gt_class[i] = cname2cid[cname]
_difficult = int(obj.find('difficult').text)
x1 = float(obj.find('bndbox').find('xmin').text)
y1 = float(obj.find('bndbox').find('ymin').text)
x2 = float(obj.find('bndbox').find('xmax').text)
y2 = float(obj.find('bndbox').find('ymax').text)
x1 = max(0, x1)
y1 = max(0, y1)
x2 = min(im_w - 1, x2)
y2 = min(im_h - 1, y2)
# 这里使用xywh格式来表示目标物体真实框
gt_bbox[i] = [(x1+x2)/2.0 , (y1+y2)/2.0, x2-x1+1., y2-y1+1.]
is_crowd[i] = 0
difficult[i] = _difficult
voc_rec = {
'im_file': img_file,
'im_id': im_id,
'h': im_h,
'w': im_w,
'is_crowd': is_crowd,
'gt_class': gt_class,
'gt_bbox': gt_bbox,
'gt_poly': [],
'difficult': difficult
}
if len(objs) != 0:
records.append(voc_rec)
ct += 1
return records
TRAINDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/train'
TESTDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/test'
VALIDDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/val'
cname2cid = get_insect_names()
records = get_annotations(cname2cid, TRAINDIR)
Boerner
Leconte
Linnaeus
acuminatus
armandi
coleoptera
linnaeus
len(records)
1693
records[1692]
{'im_file': '/home/aistudio/work/insects/train/images/899.jpeg',
'im_id': array([1692]),
'h': 1302.0,
'w': 1302.0,
'is_crowd': array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], dtype=int32),
'gt_class': array([1, 0, 5, 4, 3, 5, 2], dtype=int32),
'gt_bbox': array([[990.5, 429.5, 138. , 192. ],
[822. , 741. , 109. , 139. ],
[625. , 956.5, 37. , 68. ],
[473.5, 975.5, 78. , 70. ],
[468. , 715.5, 55. , 90. ],
[578.5, 705.5, 40. , 64. ],
[528. , 514. , 75. , 81. ]], dtype=float32),
'gt_poly': [],
'difficult': array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], dtype=int32)}
通过上面的程序,将所有训练数据集的标注数据全部读取出来了,存放在records列表下面,其中每一个元素是一张图片的标注数据,包含了图片存放地址,图片id,图片高度和宽度,图片中所包含的目标物体的种类和位置。
前面已经将图片的所有描述信息保存在records中了,其中每一个元素都包含了一张图片的描述,下面的程序展示了如何根据records里面的描述读取图片及标注。
# 数据读取
import cv2
def get_bbox(gt_bbox, gt_class):
# 对于一般的检测任务来说,一张图片上往往会有多个目标物体
# 设置参数MAX_NUM = 50, 即一张图片最多取50个真实框;如果真实
# 框的数目少于50个,则将不足部分的gt_bbox, gt_class和gt_score的各项数值全设置为0
MAX_NUM = 50
gt_bbox2 = np.zeros((MAX_NUM, 4))
gt_class2 = np.zeros((MAX_NUM,))
for i in range(len(gt_bbox)):
gt_bbox2[i, :] = gt_bbox[i, :]
gt_class2[i] = gt_class[i]
if i >= MAX_NUM:
break
return gt_bbox2, gt_class2
def get_img_data_from_file(record):
"""
record is a dict as following,
record = {
'im_file': img_file,
'im_id': im_id,
'h': im_h,
'w': im_w,
'is_crowd': is_crowd,
'gt_class': gt_class,
'gt_bbox': gt_bbox,
'gt_poly': [],
'difficult': difficult
}
"""
im_file = record['im_file']
h = record['h']
w = record['w']
is_crowd = record['is_crowd']
gt_class = record['gt_class']
gt_bbox = record['gt_bbox']
difficult = record['difficult']
img = cv2.imread(im_file)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# check if h and w in record equals that read from img
assert img.shape[0] == int(h), \
"image height of {} inconsistent in record({}) and img file({})".format(
im_file, h, img.shape[0])
assert img.shape[1] == int(w), \
"image width of {} inconsistent in record({}) and img file({})".format(
im_file, w, img.shape[1])
gt_boxes, gt_labels = get_bbox(gt_bbox, gt_class)
# gt_bbox 用相对值
gt_boxes[:, 0] = gt_boxes[:, 0] / float(w)
gt_boxes[:, 1] = gt_boxes[:, 1] / float(h)
gt_boxes[:, 2] = gt_boxes[:, 2] / float(w)
gt_boxes[:, 3] = gt_boxes[:, 3] / float(h)
return img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, (h, w)
from paddle.vision.transforms import RandomCrop
# RandomCrop是一个python类,需要事先声明
#RandomCrop还需要传入剪切的形状,这里设置为640
# transform = RandomCrop(640)
# # 将图像转换为PIL.Image格式
# srcimg = Image.fromarray(np.array(srcimg))
# # 调用声明好的API实现随机剪切
# img_res = transform(srcimg)
# # 可视化结果
# visualize(srcimg, np.array(img_res))
这里得到的img数据数值需要调整,需要除以255,并且减去均值和方差,再将维度从[H, W, C]调整为[C, H, W]。
def get_img_data(record, size=640):
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, scales = get_img_data_from_file(record)
transform = RandomCrop(size)
img = transform(img)
# img, gt_boxes, gt_labels = image_augment(img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, size)
mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
mean = np.array(mean).reshape((1, 1, -1))
std = np.array(std).reshape((1, 1, -1))
img = (img / 255.0 - mean) / std
img = img.astype('float32').transpose((2, 0, 1))
return img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, scales
TRAINDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/train'
TESTDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/test'
VALIDDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/val'
cname2cid = get_insect_names()
records = get_annotations(cname2cid, TRAINDIR)
record = records[0]
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, scales = get_img_data(record, size=480)
Boerner
Leconte
Linnaeus
acuminatus
armandi
coleoptera
linnaeus
scales
(1268.0, 1268.0)
通过使用飞桨提供的paddle.io.DataLoader API中的num_workers参数设置进程数量,实现多进程读取数据,具体实现代码如下。
import paddle
# 定义数据读取类,继承Paddle.io.Dataset
class TrainDataset(paddle.io.Dataset):
def __init__(self, datadir, mode='train'):
self.datadir = datadir
cname2cid = get_insect_names()
self.records = get_annotations(cname2cid, datadir)
self.img_size = 640 #get_img_size(mode)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
record = self.records[idx]
# print("print: ", record)
img, gt_bbox, gt_labels, im_shape = get_img_data(record, size=self.img_size)
return img, gt_bbox, gt_labels, np.array(im_shape)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.records)
# 创建数据读取类
train_dataset = TrainDataset(TRAINDIR, mode='train')
# 使用paddle.io.DataLoader创建数据读取器,并设置batchsize,进程数量num_workers等参数
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
Boerner
Leconte
Linnaeus
acuminatus
armandi
coleoptera
linnaeus
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, im_shape = next(train_loader())
img.shape, gt_boxes.shape, gt_labels.shape, im_shape.shape
([2, 3, 640, 640], [2, 50, 4], [2, 50], [2, 2])
单阶段目标检测模型PP-YOLO
R-CNN系列算法需要先产生候选区域,再对候选区域做分类和位置坐标的预测,这类算法被称为两阶段目标检测算法。近几年,很多研究人员相继提出一系列单阶段的检测算法,只需要一个网络即可同时产生候选区域并预测出物体的类别和位置坐标。
与R-CNN系列算法不同,YOLO系列算法使用单个网络结构,在产生候选区域的同时即可预测出物体类别和位置,不需要分成两阶段来完成检测任务。另外,YOLO系列算法产生的预测框数目比Faster R-CNN少很多。Faster R-CNN中每个真实框可能对应多个标签为正的候选区域,而YOLO里面每个真实框只对应一个正的候选区域。这些特性使得YOLO系列算法具有更快的速度,能到达实时响应的水平。
Joseph Redmon等人在2015年提出YOLO(You Only Look Once,YOLO)算法,通常也被称为YOLOv1;2016年,他们对算法进行改进,又提出YOLOv2版本;2018年发展出YOLOv3版本。
YOLO系列算法模型设计思想
YOLO系列算法的基本思想可以分成两部分:
- 按一定规则在图片上产生一系列的候选区域,然后根据这些候选区域与图片上物体真实框之间的位置关系对候选区域进行标注。跟真实框足够接近的那些候选区域会被标注为正样本,同时将真实框的位置作为正样本的位置目标。偏离真实框较大的那些候选区域则会被标注为负样本,负样本不需要预测位置或者类别。
- 使用卷积神经网络提取图片特征并对候选区域的位置和类别进行预测。这样每个预测框就可以看成是一个样本,根据真实框相对它的位置和类别进行了标注而获得标签值,通过网络模型预测其位置和类别,将网络预测值和标签值进行比较,就可以建立起损失函数。
YOLO系列算法训练过程的流程图如 图8 所示:
图8:YOLO系列算法训练流程图
- 图8 左边是输入图片,上半部分所示的过程是使用卷积神经网络对图片提取特征,随着网络不断向前传播,特征图的尺寸越来越小,每个像素点会代表更加抽象的特征模式,直到输出特征图,其尺寸减小为原图的 1 32 \frac{1}{32} 321。
- 图8 下半部分描述了生成候选区域的过程,首先将原图划分成多个小方块,每个小方块的大小是 32 × 32 32 \times 32 32×32,然后以每个小方块为中心分别生成一系列锚框,整张图片都会被锚框覆盖到。在每个锚框的基础上产生一个与之对应的预测框,根据锚框和预测框与图片上物体真实框之间的位置关系,对这些预测框进行标注。
- 将上方支路中输出的特征图与下方支路中产生的预测框标签建立关联,创建损失函数,开启端到端的训练过程。
接下来具体介绍流程中各节点的原理和代码实现。
PP-YOLO:一个更快更好的目标检测器
- PP-YOLO的目的是实现一种可以在实际应用场景中直接应用的具有相对平衡的有效性和效率的目标检测器,而不是提出一种新颖的检测模型。
- PP-YOLO:一种基于YOLOv3的新型目标检测器。
- PP-YOLO:尝试结合各种几乎不增加模型参数和FLOPs数量的技巧,以实现在确保速度几乎不变的情况下尽可能提高检测器精度的目标
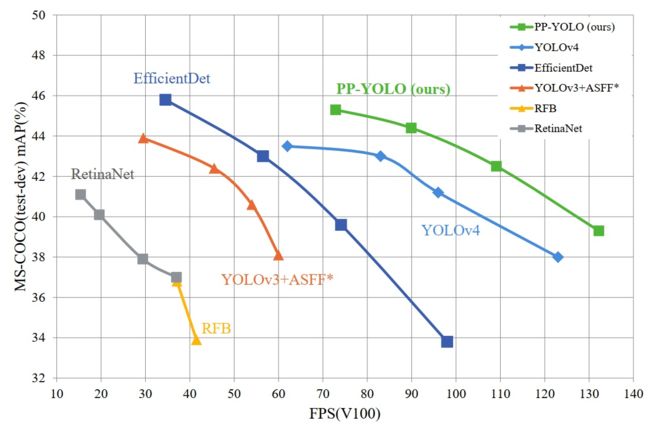
PP-YOLO网络如下图,部分主要模块如下所述:
- Backbone:ResNet50-vd-dcn
- Detection Neck:FPN
- Detection Head:YOLOv3
重磅技巧(tricks):
- Larger Batch Size:196
- EMA
在深度学习中,经常会使用EMA(指数移动平均)这个方法对模型的参数做平均,以求提高测试指标并增加模型鲁棒。
指数移动平均(Exponential Moving Average)也叫权重移动平均(Weighted Moving Average),是一种给予近期数据更高权重的平均方法。
- DropBlock
- IoU Loss
- IoU Aware
在目标检测问题中,模型需要输出目标分类分数和与其对应的目标定位的包围框,在以往的模型中,经常使用分类分数作为目标定位准不准的置信度,并基于此对大量候选目标包围框NMS,现在越来越多的工作发现,分类分数高并不能保证定位精度高。而IoU是直接反应定位准不准的直接指标,可以在目标检测模型的分类和定位任务的基础上添加IoU预测的任务,可以在一定程度上反应定位置信度。
- Grid Sensitive
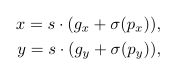
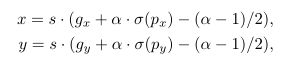
- Matrix NMS
在推理过程中,NMS还会删除与得分高的框的重合度大于一定阈值的其它预测框,这样对于存在两个同类别物体重叠的的图像检测任务来说,就会出现一个物体的预测框把另一个物体的预测框抑制掉的情况,导致漏检。
因此又引入了Soft NMS这个概念,其解决思路并不是粗暴的将与得分高的预测框重合度大于阈值的框直接滤除,而是降低这个预测框的评分,对预测框评分的惩罚系数与这两个框的重合度,也就是IoU正相关,采用这种软化的滤除方式就能有效的避免重叠的同类物体预测框互相冲突的情况,提高检测的精度。
但引入Soft NMS会使推理速度变慢。因此此轮模型优化采用了更优的Matrix NMS:一种并行化进行Soft NMS的实现思路。Matrix NMS通过一个矩阵并行运算的方式计算出任意两个框之间的IoU,例如对某一个预测框B计算抑制系数时,Matrix NMS通过矩阵并行方式计算出所有得分高于B的预测框与预测框B的IoU,然后根据这些IOU和得分高于B的预测框的被抑制概率做近似估算,估算出B的抑制系数,从而实现并行化的计算Soft NMS,在提高检测精度的同时,避免了推理速度的降低。
- CoordConv
即它无法将空间表示转换成笛卡尔空间中的坐标和one-hot像素空间中的坐标。
卷积是等变的,也就是说当每个过滤器应用到输入上时,它不知道每个过滤器在哪。我们可以帮助卷积,让它知道过滤器的位置。这一过程需要在输入上添加两个通道实现,一个在i坐标,另一个在j坐标。我们将这个图层成为CoordConv,如下图所示:
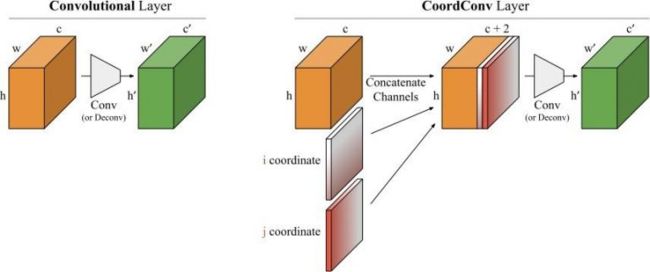
深度学习里的卷积运算是具有平移等变性的,这样可以在图像的不同位置共享统一的卷积核参数,但是这样卷积学习过程中是不能感知当前特征在图像中的坐标的。CoordConv就是通过在卷积的输入特征图中新增对应的通道来表征特征图像素点的坐标,让卷积学习过程中能够一定程度感知坐标来提升检测精度。
- SPP
空间金字塔池化是SPPNet提出的,如下图所示通过多个不同尺度的池化窗口提取不同尺度的池化特征,把特征组合在一起作为输出特征,在骨干网络提取特征后加入空间金字塔池化,能有效的增加特征的感受野,是一种广泛应用的特征提取优化方法。
- Better Pretrain Model
(PS:图中三角为DropBlock、star为SPP、diamonds为CoordConv)
对候选区域进行标注
每个区域可以产生3种不同形状的锚框,每个锚框都是一个可能的候选区域,对这些候选区域我们需要了解如下几件事情:
-
锚框是否包含物体,这可以看成是一个二分类问题,使用标签objectness来表示。当锚框包含了物体时,objectness=1,表示预测框属于正类;当锚框不包含物体时,设置objectness=0,表示锚框属于负类。
-
如果锚框包含了物体,那么它对应的预测框的中心位置和大小应该是多少,或者说上面计算式中的 t x , t y , t w , t h t_x, t_y, t_w, t_h tx,ty,tw,th应该是多少,使用location标签。
-
如果锚框包含了物体,那么具体类别是什么,这里使用变量label来表示其所属类别的标签。
标注锚框包含物体类别的标签
对于objectness=1的锚框,需要确定其具体类别。正如上面所说,objectness标注为1的锚框,会有一个真实框跟它对应,该锚框所属物体类别,即是其所对应的真实框包含的物体类别。这里使用one-hot向量来表示类别标签label。比如一共有10个分类,而真实框里面包含的物体类别是第2类,则label为 ( 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ) (0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0) (0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0)
对上述步骤进行总结,标注的流程如 图15 所示。
图15:标注流程示意图
通过这种方式,我们在每个小方块区域都生成了一系列的锚框作为候选区域,并且根据图片上真实物体的位置,标注出了每个候选区域对应的objectness标签、位置需要调整的幅度以及包含的物体所属的类别。位置需要调整的幅度由4个变量描述 ( t x , t y , t w , t h ) (t_x, t_y, t_w, t_h) (tx,ty,tw,th),objectness标签需要用一个变量描述 o b j obj obj,描述所属类别的变量长度等于类别数C。
对于每个锚框,模型需要预测输出 ( t x , t y , t w , t h , P o b j , P 1 , P 2 , . . . , P C ) (t_x, t_y, t_w, t_h, P_{obj}, P_1, P_2,... , P_C) (tx,ty,tw,th,Pobj,P1,P2,...,PC),其中 P o b j P_{obj} Pobj是锚框是否包含物体的概率, P 1 , P 2 , . . . , P C P_1, P_2,... , P_C P1,P2,...,PC则是锚框包含的物体属于每个类别的概率。接下来让我们一起学习如何通过卷积神经网络输出这样的预测值。
标注锚框的具体程序
上面描述了如何对预锚框进行标注,但读者可能仍然对里面的细节不太了解,下面将通过具体的程序完成这一步骤。
# 标注预测框的objectness
def get_objectness_label(img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, iou_threshold = 0.7,
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
num_classes=7, downsample=32):
"""
img 是输入的图像数据,形状是[N, C, H, W]
gt_boxes,真实框,维度是[N, 50, 4],其中50是真实框数目的上限,当图片中真实框不足50个时,不足部分的坐标全为0
真实框坐标格式是xywh,这里使用相对值
gt_labels,真实框所属类别,维度是[N, 50]
iou_threshold,当预测框与真实框的iou大于iou_threshold时不将其看作是负样本
anchors,锚框可选的尺寸
anchor_masks,通过与anchors一起确定本层级的特征图应该选用多大尺寸的锚框
num_classes,类别数目
downsample,特征图相对于输入网络的图片尺寸变化的比例
"""
img_shape = img.shape
batchsize = img_shape[0]
num_anchors = len(anchors) // 2
input_h = img_shape[2]
input_w = img_shape[3]
# 将输入图片划分成num_rows x num_cols个小方块区域,每个小方块的边长是 downsample
# 计算一共有多少行小方块
num_rows = input_h // downsample
# 计算一共有多少列小方块
num_cols = input_w // downsample
label_objectness = np.zeros([batchsize, num_anchors, num_rows, num_cols])
label_classification = np.zeros([batchsize, num_anchors, num_classes, num_rows, num_cols])
label_location = np.zeros([batchsize, num_anchors, 4, num_rows, num_cols])
scale_location = np.ones([batchsize, num_anchors, num_rows, num_cols])
# 对batchsize进行循环,依次处理每张图片
for n in range(batchsize):
# 对图片上的真实框进行循环,依次找出跟真实框形状最匹配的锚框
for n_gt in range(len(gt_boxes[n])):
gt = gt_boxes[n][n_gt]
gt_cls = gt_labels[n][n_gt]
gt_center_x = gt[0]
gt_center_y = gt[1]
gt_width = gt[2]
gt_height = gt[3]
if (gt_height < 1e-3) or (gt_height < 1e-3):
continue
i = int(gt_center_y * num_rows)
j = int(gt_center_x * num_cols)
ious = []
for ka in range(num_anchors):
bbox1 = [0., 0., float(gt_width), float(gt_height)]
anchor_w = anchors[ka * 2]
anchor_h = anchors[ka * 2 + 1]
bbox2 = [0., 0., anchor_w/float(input_w), anchor_h/float(input_h)]
# 计算iou
iou = box_iou_xywh(bbox1, bbox2)
ious.append(iou)
ious = np.array(ious)
inds = np.argsort(ious)
k = inds[-1]
label_objectness[n, k, i, j] = 1
c = int(gt_cls)
label_classification[n, k, c, i, j] = 1
# for those prediction bbox with objectness =1, set label of location
dx_label = gt_center_x * num_cols - j
dy_label = gt_center_y * num_rows - i
dw_label = np.log(gt_width * input_w / anchors[k*2])
dh_label = np.log(gt_height * input_h / anchors[k*2 + 1])
label_location[n, k, 0, i, j] = dx_label
label_location[n, k, 1, i, j] = dy_label
label_location[n, k, 2, i, j] = dw_label
label_location[n, k, 3, i, j] = dh_label
# scale_location用来调节不同尺寸的锚框对损失函数的贡献,作为加权系数和位置损失函数相乘
scale_location[n, k, i, j] = 2.0 - gt_width * gt_height
# 目前根据每张图片上所有出现过的gt box,都标注出了objectness为正的预测框,剩下的预测框则默认objectness为0
# 对于objectness为1的预测框,标出了他们所包含的物体类别,以及位置回归的目标
return label_objectness.astype('float32'), label_location.astype('float32'), label_classification.astype('float32'), \
scale_location.astype('float32')
# 计算IoU,矩形框的坐标形式为xywh
def box_iou_xywh(box1, box2):
x1min, y1min = box1[0] - box1[2]/2.0, box1[1] - box1[3]/2.0
x1max, y1max = box1[0] + box1[2]/2.0, box1[1] + box1[3]/2.0
s1 = box1[2] * box1[3]
x2min, y2min = box2[0] - box2[2]/2.0, box2[1] - box2[3]/2.0
x2max, y2max = box2[0] + box2[2]/2.0, box2[1] + box2[3]/2.0
s2 = box2[2] * box2[3]
xmin = np.maximum(x1min, x2min)
ymin = np.maximum(y1min, y2min)
xmax = np.minimum(x1max, x2max)
ymax = np.minimum(y1max, y2max)
inter_h = np.maximum(ymax - ymin, 0.)
inter_w = np.maximum(xmax - xmin, 0.)
intersection = inter_h * inter_w
union = s1 + s2 - intersection
iou = intersection / union
return iou
# 读取数据
import paddle
# reader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, drop_last=True)
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, im_shape = next(train_loader())
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, im_shape = img.numpy(), gt_boxes.numpy(), gt_labels.numpy(), im_shape.numpy()
# 计算出锚框对应的标签
label_objectness, label_location, label_classification, scale_location = get_objectness_label(img,
gt_boxes, gt_labels,
iou_threshold = 0.7,
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
num_classes=7, downsample=32)
img.shape, gt_boxes.shape, gt_labels.shape, im_shape.shape
((2, 3, 640, 640), (2, 50, 4), (2, 50), (2, 2))
label_objectness.shape, label_location.shape, label_classification.shape, scale_location.shape
((2, 3, 20, 20), (2, 3, 4, 20, 20), (2, 3, 7, 20, 20), (2, 3, 20, 20))
三、卷积神经网络提取特征
在上一节图像分类的课程中,我们已经学习过了通过卷积神经网络提取图像特征。通过连续使用多层卷积和池化等操作,能得到语义含义更加丰富的特征图。在检测问题中,也使用卷积神经网络逐层提取图像特征,通过最终的输出特征图来表征物体位置和类别等信息。
在提取特征的过程中通常会使用步幅大于1的卷积或者池化,导致后面的特征图尺寸越来越小,特征图的步幅等于输入图片尺寸除以特征图尺寸。例如:C0的尺寸是 20 × 20 20\times20 20×20,原图尺寸是 640 × 640 640\times640 640×640,则C0的步幅是 640 20 = 32 \frac{640}{20}=32 20640=32。同理,C1的步幅是16,C2的步幅是8。
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import numpy as np
import paddle
from paddle import ParamAttr
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.nn.functional as F
from paddle.nn import Conv2D, BatchNorm, Linear, Dropout
from paddle.nn import AdaptiveAvgPool2D, MaxPool2D, AvgPool2D
from paddle.nn.initializer import Uniform
import math
__all__ = [
"ResNet18_vd", "ResNet34_vd", "ResNet50_vd", "ResNet101_vd", "ResNet152_vd"
]
class ConvBNLayer(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
num_channels,
num_filters,
filter_size,
stride=1,
groups=1,
is_vd_mode=False,
act=None,
lr_mult=1.0,
name=None):
super(ConvBNLayer, self).__init__()
self.is_vd_mode = is_vd_mode
self._pool2d_avg = AvgPool2D(
kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, ceil_mode=True)
self._conv = Conv2D(
in_channels=num_channels,
out_channels=num_filters,
kernel_size=filter_size,
stride=stride,
padding=(filter_size - 1) // 2,
groups=groups,
weight_attr=ParamAttr(
name=name + "_weights", learning_rate=lr_mult),
bias_attr=False)
if name == "conv1":
bn_name = "bn_" + name
else:
bn_name = "bn" + name[3:]
self._batch_norm = BatchNorm(
num_filters,
act=act,
param_attr=ParamAttr(
name=bn_name + '_scale', learning_rate=lr_mult),
bias_attr=ParamAttr(
bn_name + '_offset', learning_rate=lr_mult),
moving_mean_name=bn_name + '_mean',
moving_variance_name=bn_name + '_variance')
def forward(self, inputs):
if self.is_vd_mode:
inputs = self._pool2d_avg(inputs)
y = self._conv(inputs)
y = self._batch_norm(y)
return y
class ConvBNLayer_dcn(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
num_channels,
num_filters,
filter_size,
stride=1,
groups=1,
is_vd_mode=False,
act=None,
lr_mult=1.0,
name=None):
super(ConvBNLayer_dcn, self).__init__()
self.is_vd_mode = is_vd_mode
self._pool2d_avg = AvgPool2D(
kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, ceil_mode=True)
self._offsets = Conv2D(
in_channels=num_channels,
out_channels=18,
kernel_size=filter_size,
stride=stride,
padding=(filter_size - 1) // 2,
groups=groups,
weight_attr=ParamAttr(
name=name + "_weights1", learning_rate=lr_mult),
bias_attr=False)
self._mask = Conv2D(
in_channels=num_channels,
out_channels=9,
kernel_size=filter_size,
stride=stride,
padding=(filter_size - 1) // 2,
groups=groups,
weight_attr=ParamAttr(
name=name + "_weights2", learning_rate=lr_mult),
bias_attr=False)
self._conv_dcn = paddle.vision.ops.DeformConv2D(
in_channels=num_channels,
out_channels=num_filters,
kernel_size=filter_size,
stride=stride,
padding=(filter_size - 1) // 2,
groups=groups,
weight_attr=ParamAttr(
name=name + "_weights3", learning_rate=lr_mult),
bias_attr=False)
if name == "conv1":
bn_name = "bn_" + name
else:
bn_name = "bn" + name[3:]
self._batch_norm = BatchNorm(
num_filters,
act=act,
param_attr=ParamAttr(
name=bn_name + '_scale', learning_rate=lr_mult),
bias_attr=ParamAttr(
bn_name + '_offset', learning_rate=lr_mult),
moving_mean_name=bn_name + '_mean',
moving_variance_name=bn_name + '_variance')
def forward(self, inputs):
if self.is_vd_mode:
inputs = self._pool2d_avg(inputs)
offset = self._offsets(inputs)
mask = self._mask(inputs)
y = self._conv_dcn(inputs, offset, mask)
y = self._batch_norm(y)
return y
class BottleneckBlock_dcn(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
num_channels,
num_filters,
stride,
shortcut=True,
if_first=False,
lr_mult=1.0,
name=None):
super(BottleneckBlock_dcn, self).__init__()
self.conv0 = ConvBNLayer(
num_channels=num_channels,
num_filters=num_filters,
filter_size=1,
act='relu',
lr_mult=lr_mult,
name=name + "_branch2a_dcn")
self.conv1 = ConvBNLayer_dcn(
num_channels=num_filters,
num_filters=num_filters,
filter_size=3,
stride=stride,
act='relu',
lr_mult=lr_mult,
name=name + "_branch2b_dcn")
self.conv2 = ConvBNLayer(
num_channels=num_filters,
num_filters=num_filters * 4,
filter_size=1,
act=None,
lr_mult=lr_mult,
name=name + "_branch2c_dcn")
if not shortcut:
self.short = ConvBNLayer(
num_channels=num_channels,
num_filters=num_filters * 4,
filter_size=1,
stride=1,
is_vd_mode=False if if_first else True,
lr_mult=lr_mult,
name=name + "_branch1_dcn")
self.shortcut = shortcut
def forward(self, inputs):
y = self.conv0(inputs)
conv1 = self.conv1(y)
conv2 = self.conv2(conv1)
if self.shortcut:
short = inputs
else:
short = self.short(inputs)
y = paddle.add(x=short, y=conv2)
y = F.relu(y)
return y
class ResNet_vd(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
layers=50,
class_dim=1000,
lr_mult_list=[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0]):
super(ResNet_vd, self).__init__()
self.layers = layers
supported_layers = [18, 34, 50, 101, 152, 200]
assert layers in supported_layers, \
"supported layers are {} but input layer is {}".format(
supported_layers, layers)
self.lr_mult_list = lr_mult_list
assert isinstance(self.lr_mult_list, (
list, tuple
)), "lr_mult_list should be in (list, tuple) but got {}".format(
type(self.lr_mult_list))
assert len(
self.lr_mult_list
) == 5, "lr_mult_list length should should be 5 but got {}".format(
len(self.lr_mult_list))
if layers == 18:
depth = [2, 2, 2, 2]
elif layers == 34 or layers == 50:
depth = [3, 4, 6, 3]
elif layers == 101:
depth = [3, 4, 23, 3]
elif layers == 152:
depth = [3, 8, 36, 3]
elif layers == 200:
depth = [3, 12, 48, 3]
num_channels = [64, 256, 512,
1024] if layers >= 50 else [64, 64, 128, 256]
num_filters = [64, 128, 256, 512]
self.conv1_1 = ConvBNLayer(
num_channels=3,
num_filters=32,
filter_size=3,
stride=2,
act='relu',
lr_mult=self.lr_mult_list[0],
name="conv1_1")
self.conv1_2 = ConvBNLayer(
num_channels=32,
num_filters=32,
filter_size=3,
stride=1,
act='relu',
lr_mult=self.lr_mult_list[0],
name="conv1_2")
self.conv1_3 = ConvBNLayer(
num_channels=32,
num_filters=64,
filter_size=3,
stride=1,
act='relu',
lr_mult=self.lr_mult_list[0],
name="conv1_3")
self.pool2d_max = MaxPool2D(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.block_list = []
if layers >= 50:
for block in range(len(depth)):
shortcut = False
for i in range(depth[block]):
if layers in [101, 152, 200] and block == 2:
if i == 0:
conv_name = "res" + str(block + 2) + "a"
else:
conv_name = "res" + str(block + 2) + "b" + str(i)
else:
conv_name = "res" + str(block + 2) + chr(97 + i)
if layers in [34, 50] and block != 3:
bottleneck_block = self.add_sublayer(
'bb_%d_%d' % (block, i),
BottleneckBlock(
num_channels=num_channels[block]
if i == 0 else num_filters[block] * 4,
num_filters=num_filters[block],
stride=2 if i == 0 and block != 0 else 1,
shortcut=shortcut,
if_first=block == i == 0,
lr_mult=self.lr_mult_list[block + 1],
name=conv_name))
self.block_list.append(bottleneck_block)
shortcut = True
elif block == 3 :
bottleneck_block = self.add_sublayer(
'bb_%d_%d' % (block, i),
BottleneckBlock_dcn(
num_channels=num_channels[block]
if i == 0 else num_filters[block] * 4,
num_filters=num_filters[block],
stride=2 if i == 0 and block != 0 else 1,
shortcut=shortcut,
if_first=block == i == 0,
lr_mult=self.lr_mult_list[block + 1],
name=conv_name))
self.block_list.append(bottleneck_block)
shortcut = True
else:
for block in range(len(depth)):
shortcut = False
for i in range(depth[block]):
conv_name = "res" + str(block + 2) + chr(97 + i)
basic_block = self.add_sublayer(
'bb_%d_%d' % (block, i),
BasicBlock(
num_channels=num_channels[block]
if i == 0 else num_filters[block],
num_filters=num_filters[block],
stride=2 if i == 0 and block != 0 else 1,
shortcut=shortcut,
if_first=block == i == 0,
name=conv_name,
lr_mult=self.lr_mult_list[block + 1]))
self.block_list.append(basic_block)
shortcut = True
def forward(self, inputs):
y = self.conv1_1(inputs)
y = self.conv1_2(y)
y = self.conv1_3(y)
y = self.pool2d_max(y)
blocks = []
for block in self.block_list:
y = block(y)
blocks.append(y)
# y = blocks[-1]
return blocks[-1], blocks[-4], blocks[-10]
def ResNet34_vd(**args):
model = ResNet_vd(layers=34, **args)
return model
def ResNet50_vd(**args):
model = ResNet_vd(layers=50, **args)
return model
# # 查看Darknet53网络输出特征图
# import numpy as np
# backbone = ResNet50_vd()
# x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
# x = paddle.to_tensor(x)
# C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
# print(C0.shape, C1.shape, C2.shape)
上面这段示例代码,指定输入数据的形状是 ( 1 , 3 , 640 , 640 ) (1, 3, 640, 640) (1,3,640,640),则3个层级的输出特征图的形状分别是 C 0 ( 1 , 1024 , 20 , 20 ) C0 (1, 1024, 20, 20) C0(1,1024,20,20), C 1 ( 1 , 512 , 40 , 40 ) C1 (1, 512, 40, 40) C1(1,512,40,40)和 C 2 ( 1 , 256 , 80 , 80 ) C2 (1, 256, 80, 80) C2(1,256,80,80)。
四、根据输出特征图计算预测框位置和类别
PP-YOLO中对每个预测框计算逻辑如下:
-
预测框是否包含物体。也可理解为objectness=1的概率是多少,可以用网络输出一个实数 x x x,可以用 S i g m o i d ( x ) Sigmoid(x) Sigmoid(x)表示objectness为正的概率 P o b j P_{obj} Pobj
-
预测物体位置和形状。物体位置和形状 t x , t y , t w , t h t_x, t_y, t_w, t_h tx,ty,tw,th可以用网络输出4个实数来表示 t x , t y , t w , t h t_x, t_y, t_w, t_h tx,ty,tw,th
-
预测物体类别。预测图像中物体的具体类别是什么,或者说其属于每个类别的概率分别是多少。总的类别数为C,需要预测物体属于每个类别的概率 ( P 1 , P 2 , . . . , P C ) (P_1, P_2, ..., P_C) (P1,P2,...,PC),可以用网络输出C个实数 ( x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x C ) (x_1, x_2, ..., x_C) (x1,x2,...,xC),对每个实数分别求Sigmoid函数,让 P i = S i g m o i d ( x i ) P_i = Sigmoid(x_i) Pi=Sigmoid(xi),则可以表示出物体属于每个类别的概率。
对于一个预测框,网络需要输出 ( 5 + C ) (5 + C) (5+C)个实数来表征它是否包含物体、位置和形状尺寸以及属于每个类别的概率。
由于我们在每个小方块区域都生成了K个预测框,则所有预测框一共需要网络输出的预测值数目是:
[ K ( 5 + C ) ] × m × n [K(5 + C)] \times m \times n [K(5+C)]×m×n
还有更重要的一点是网络输出必须要能区分出小方块区域的位置来,不能直接将特征图连接一个输出大小为 [ K ( 5 + C ) ] × m × n [K(5 + C)] \times m \times n [K(5+C)]×m×n的全连接层。
建立输出特征图与预测框之间的关联
现在观察特征图,经过多次卷积核池化之后,其步幅stride=32, 640 × 480 640 \times 480 640×480大小的输入图片变成了 20 × 15 20\times15 20×15的特征图;而小方块区域的数目正好是 20 × 15 20\times15 20×15,也就是说可以让特征图上每个像素点分别跟原图上一个小方块区域对应。这也是为什么我们最开始将小方块区域的尺寸设置为32的原因,这样可以巧妙的将小方块区域跟特征图上的像素点对应起来,解决了空间位置的对应关系。
图17:特征图C0与小方块区域形状对比
下面需要将像素点 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)与第i行第j列的小方块区域所需要的预测值关联起来,每个小方块区域产生K个预测框,每个预测框需要 ( 5 + C ) (5 + C) (5+C)个实数预测值,则每个像素点相对应的要有 K ( 5 + C ) K(5 + C) K(5+C)个实数。为了解决这一问题,对特征图进行多次卷积,并将最终的输出通道数设置为 K ( 5 + C ) K(5 + C) K(5+C),即可将生成的特征图与每个预测框所需要的预测值巧妙的对应起来。当然,这种对应是为了将骨干网络提取的特征对接输出层来形成Loss。实际中,这几个尺寸可以随着任务数据分布的不同而调整,只要保证特征图输出尺寸(控制卷积核和下采样)和输出层尺寸(控制小方块区域的大小)相同即可。
骨干网络的输出特征图是C0,下面的程序是对C0进行多次卷积以得到跟预测框相关的特征图P0。
import paddle.fluid.layers as L
import paddle
class SPP(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, seq='asc'):
super(SPP, self).__init__()
assert seq in ['desc', 'asc']
self.seq = seq
self.max_pool1 = paddle.nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2)
self.max_pool2 = paddle.nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=9, stride=1, padding=4)
self.max_pool3 = paddle.nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=13, stride=1, padding=6)
def __call__(self, x):
x_1 = x
x_2 = self.max_pool1(x)
x_3 = self.max_pool2(x)
x_4 = self.max_pool3(x)
if self.seq == 'desc':
out = L.concat([x_4, x_3, x_2, x_1], axis=1)
else:
out = L.concat([x_1, x_2, x_3, x_4], axis=1)
return out
class DropBlock(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, block_size, keep_prob, name):
super(DropBlock, self).__init__()
self.block_size = block_size
self.keep_prob = keep_prob
self.name = name
def forward(self, x):
if not self.training or self.keep_prob == 1:
return x
else:
gamma = (1. - self.keep_prob) / (self.block_size**2)
for s in x.shape[2:]:
gamma *= s / (s - self.block_size + 1)
matrix = paddle.cast(paddle.rand(x.shape, x.dtype) < gamma, x.dtype)
mask_inv = F.max_pool2d(
matrix, self.block_size, stride=1, padding=self.block_size // 2)
mask = 1. - mask_inv
y = x * mask * (mask.numel() / mask.sum())
return y
import paddle
import paddle.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
class ConvBNLayer_d(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, ch_in, ch_out,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, groups=1,
padding=0, act="leaky"
):
super(ConvBNLayer_d, self).__init__()
self.conv = paddle.nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=ch_in,
out_channels=ch_out,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
groups=groups,
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Normal(0., 0.02)),
bias_attr=False)
self.batch_norm = paddle.nn.BatchNorm2D(
num_features=ch_out,
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Normal(0., 0.02),
regularizer=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.)),
bias_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Constant(0.0),
regularizer=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.)))
self.act = act
def forward(self, inputs):
out = self.conv(inputs)
out = self.batch_norm(out)
if self.act == 'leaky':
out = F.leaky_relu(x=out, negative_slope=0.1)
return out
class YoloDetectionBlock(paddle.nn.Layer):
# define YOLOv3 detection head
# 使用多层卷积和BN提取特征
def __init__(self,ch_in,ch_out,is_test=True):
super(YoloDetectionBlock, self).__init__()
assert ch_out % 2 == 0, \
"channel {} cannot be divided by 2".format(ch_out)
self.conv0 = ConvBNLayer_d(
ch_in=ch_in,
ch_out=ch_out,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
# self.CoordConv = CoordConv()
self.conv1 = ConvBNLayer_d(
ch_in=ch_out,
ch_out=ch_out*2,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1)
self.spp = SPP()
self.conv2 = ConvBNLayer_d(
ch_in=ch_out*8,
ch_out=ch_out,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
self.DropBlock = DropBlock(block_size=5, keep_prob=0.9, name='le')
self.conv3 = ConvBNLayer_d(
ch_in=ch_out,
ch_out=ch_out*2,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1)
self.route = ConvBNLayer_d(
ch_in=ch_out*2,
ch_out=ch_out,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
self.tip = ConvBNLayer_d(
ch_in=ch_out,
ch_out=ch_out*2,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1)
def forward(self, inputs):
out = self.conv0(inputs)
out = self.conv1(out)
out = self.spp(out)
# print('******************', out.shape)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.DropBlock(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
# print('&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&', out.shape)
route = self.route(out)
tip = self.tip(route)
return route, tip
# 定义上采样模块
class Upsample(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, scale=2):
super(Upsample,self).__init__()
self.scale = scale
def forward(self, inputs):
# get dynamic upsample output shape
shape_nchw = paddle.shape(inputs)
shape_hw = paddle.slice(shape_nchw, axes=[0], starts=[2], ends=[4])
shape_hw.stop_gradient = True
in_shape = paddle.cast(shape_hw, dtype='int32')
out_shape = in_shape * self.scale
out_shape.stop_gradient = True
# reisze by actual_shape
out = paddle.nn.functional.interpolate(
x=inputs, scale_factor=self.scale, mode="NEAREST")
return out
class YOLOv3(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, num_classes=7):
super(YOLOv3,self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
# 提取图像特征的骨干代码
self.block = ResNet50_vd()
self.block_outputs = []
self.yolo_blocks = []
self.route_blocks_2 = []
# 生成3个层级的特征图P0, P1, P2
for i in range(3):
# 添加从ci生成ri和ti的模块
yolo_block = self.add_sublayer(
"yolo_detecton_block_%d" % (i),
YoloDetectionBlock(
ch_in=1024//(2**i)*2 if i==0 else 1024//(2**i)*2 + 512//(2**i),
ch_out = 512//(2**i)))
self.yolo_blocks.append(yolo_block)
num_filters = 3 * (self.num_classes + 5)
# 添加从ti生成pi的模块,这是一个Conv2D操作,输出通道数为3 * (num_classes + 5)
block_out = self.add_sublayer(
"block_out_%d" % (i),
paddle.nn.Conv2D(in_channels=512//(2**i)*2,
out_channels=num_filters,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Normal(0., 0.02)),
bias_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Constant(0.0),
regularizer=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.))))
self.block_outputs.append(block_out)
if i < 2:
# 对ri进行卷积
route = self.add_sublayer("route2_%d"%i,
ConvBNLayer_d(ch_in=512//(2**i),
ch_out=256//(2**i),
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0))
self.route_blocks_2.append(route)
# 将ri放大以便跟c_{i+1}保持同样的尺寸
self.upsample = Upsample()
def forward(self, inputs):
outputs = []
blocks = self.block(inputs)
for i, block in enumerate(blocks):
if i > 0:
# 将r_{i-1}经过卷积和上采样之后得到特征图,与这一级的ci进行拼接
block = paddle.concat([route, block], axis=1)
# 从ci生成ti和ri
route, tip = self.yolo_blocks[i](block)
# 从ti生成pi
block_out = self.block_outputs[i](tip)
# 将pi放入列表
outputs.append(block_out)
if i < 2:
# 对ri进行卷积调整通道数
route = self.route_blocks_2[i](route)
# 对ri进行放大,使其尺寸和c_{i+1}保持一致
route = self.upsample(route)
return outputs
def get_loss(self, outputs, gtbox, gtlabel, gtscore=None,
anchors = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
anchor_masks = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
ignore_thresh=0.7,
use_label_smooth=False):
"""
使用paddle.vision.ops.yolo_loss,直接计算损失函数,过程更简洁,速度也更快
"""
self.losses = []
downsample = 32
for i, out in enumerate(outputs): # 对三个层级分别求损失函数
anchor_mask_i = anchor_masks[i]
loss = paddle.vision.ops.yolo_loss(
x=out, # out是P0, P1, P2中的一个
gt_box=gtbox, # 真实框坐标
gt_label=gtlabel, # 真实框类别
gt_score=gtscore, # 真实框得分,使用mixup训练技巧时需要,不使用该技巧时直接设置为1,形状与gtlabel相同
anchors=anchors, # 锚框尺寸,包含[w0, h0, w1, h1, ..., w8, h8]共9个锚框的尺寸
anchor_mask=anchor_mask_i, # 筛选锚框的mask,例如anchor_mask_i=[3, 4, 5],将anchors中第3、4、5个锚框挑选出来给该层级使用
class_num=self.num_classes, # 分类类别数
ignore_thresh=ignore_thresh, # 当预测框与真实框IoU > ignore_thresh,标注objectness = -1
downsample_ratio=downsample, # 特征图相对于原图缩小的倍数,例如P0是32, P1是16,P2是8
use_label_smooth=False) # 使用label_smooth训练技巧时会用到,这里没用此技巧,直接设置为False
self.losses.append(paddle.mean(loss)) #mean对每张图片求和
downsample = downsample // 2 # 下一级特征图的缩放倍数会减半
return sum(self.losses) # 对每个层级求和
import time
import os
import paddle
from work.EMA import ExponentialMovingAverage
ANCHORS = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
ANCHOR_MASKS = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
IGNORE_THRESH = .7
NUM_CLASSES = 7
def get_lr(base_lr = 0.0001, lr_decay = 0.1):
bd = [10000, 20000]
lr = [base_lr, base_lr * lr_decay, base_lr * lr_decay * lr_decay]
learning_rate = paddle.optimizer.lr.PiecewiseDecay(boundaries=bd, values=lr)
return learning_rate
if __name__ == '__main__':
TRAINDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/train'
TESTDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/test'
VALIDDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/val'
paddle.set_device("gpu:0")
# 创建数据读取类
train_dataset = TrainDataset(TRAINDIR, mode='train')
valid_dataset = TrainDataset(VALIDDIR, mode='valid')
test_dataset = TrainDataset(VALIDDIR, mode='valid')
# 使用paddle.io.DataLoader创建数据读取器,并设置batchsize,进程数量num_workers等参数
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=4, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, drop_last=True, use_shared_memory=False)
valid_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(valid_dataset, batch_size=4, shuffle=False, num_workers=0, drop_last=False, use_shared_memory=False)
model = YOLOv3(num_classes = NUM_CLASSES) #创建模型
learning_rate = get_lr()
opt = paddle.optimizer.Momentum(
learning_rate=learning_rate,
momentum=0.9,
weight_decay=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.0005),
parameters=model.parameters()) #创建优化器
# opt = paddle.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate, weight_decay=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.0005), parameters=model.parameters())
# ema = None
# if use_ema:
# ema = ExponentialMovingAverage(model, ema_decay)
# ema.register()
MAX_EPOCH = 3
for epoch in range(MAX_EPOCH):
for i, data in enumerate(train_loader()):
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, img_scale = data
gt_scores = np.ones(gt_labels.shape).astype('float32')
gt_scores = paddle.to_tensor(gt_scores).astype('float32')
img = paddle.to_tensor(img).astype('float32')
gt_boxes = paddle.to_tensor(gt_boxes).astype('float32')
gt_labels = paddle.to_tensor(gt_labels).astype('int32')
# print(type(gt_scores))
# print(type(img))
# print(type(gt_boxes))
# print(type(gt_labels))
outputs = model(img) #前向传播,输出[P0, P1, P2]
loss = model.get_loss(outputs, gt_boxes, gt_labels, gtscore=gt_scores,
anchors = ANCHORS,
anchor_masks = ANCHOR_MASKS,
ignore_thresh=IGNORE_THRESH,
use_label_smooth=False) # 计算损失函数
loss.backward() # 反向传播计算梯度
opt.step() # 更新参数
opt.clear_grad()
# if use_ema:
# ema.update()
if i % 10 == 0:
timestring = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.localtime(time.time()))
print('{}[TRAIN]epoch {}, iter {}, output loss: {}'.format(timestring, epoch, i, loss.numpy()))
# save params of model
if (epoch % 3 == 0) or (epoch == MAX_EPOCH -1):
paddle.save(model.state_dict(), 'yolo_epoch{}'.format(epoch))
# 每个epoch结束之后在验证集上进行测试
# if use_ema:
# ema.apply()
model.eval()
for i, data in enumerate(valid_loader()):
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, img_scale = data
gt_scores = np.ones(gt_labels.shape).astype('float32')
gt_scores = paddle.to_tensor(gt_scores).astype('float32')
img = paddle.to_tensor(img).astype('float32')
gt_boxes = paddle.to_tensor(gt_boxes).astype('float32')
gt_labels = paddle.to_tensor(gt_labels).astype('int32')
outputs = model(img)
loss = model.get_loss(outputs, gt_boxes, gt_labels, gtscore=gt_scores,
anchors = ANCHORS,
anchor_masks = ANCHOR_MASKS,
ignore_thresh=IGNORE_THRESH,
use_label_smooth=False)
if i % 1 == 0:
timestring = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.localtime(time.time()))
print('{}[VALID]epoch {}, iter {}, output loss: {}'.format(timestring, epoch, i, loss.numpy()))
model.train()
预测
class YOLOv3(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, num_classes=7):
super(YOLOv3,self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
# 提取图像特征的骨干代码
self.block = ResNet50_vd()
self.block_outputs = []
self.yolo_blocks = []
self.route_blocks_2 = []
# 生成3个层级的特征图P0, P1, P2
for i in range(3):
# 添加从ci生成ri和ti的模块
yolo_block = self.add_sublayer(
"yolo_detecton_block_%d" % (i),
YoloDetectionBlock(
ch_in=1024//(2**i)*2 if i==0 else 1024//(2**i)*2 + 512//(2**i),
ch_out = 512//(2**i)))
self.yolo_blocks.append(yolo_block)
num_filters = 3 * (self.num_classes + 5)
# 添加从ti生成pi的模块,这是一个Conv2D操作,输出通道数为3 * (num_classes + 5)
block_out = self.add_sublayer(
"block_out_%d" % (i),
paddle.nn.Conv2D(in_channels=512//(2**i)*2,
out_channels=num_filters,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Normal(0., 0.02)),
bias_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Constant(0.0),
regularizer=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.))))
self.block_outputs.append(block_out)
if i < 2:
# 对ri进行卷积
route = self.add_sublayer("route2_%d"%i,
ConvBNLayer_d(ch_in=512//(2**i),
ch_out=256//(2**i),
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0))
self.route_blocks_2.append(route)
# 将ri放大以便跟c_{i+1}保持同样的尺寸
self.upsample = Upsample()
def forward(self, inputs):
outputs = []
blocks = self.block(inputs)
for i, block in enumerate(blocks):
if i > 0:
# 将r_{i-1}经过卷积和上采样之后得到特征图,与这一级的ci进行拼接
block = paddle.concat([route, block], axis=1)
# 从ci生成ti和ri
route, tip = self.yolo_blocks[i](block)
# 从ti生成pi
block_out = self.block_outputs[i](tip)
# 将pi放入列表
outputs.append(block_out)
if i < 2:
# 对ri进行卷积调整通道数
route = self.route_blocks_2[i](route)
# 对ri进行放大,使其尺寸和c_{i+1}保持一致
route = self.upsample(route)
return outputs
def get_loss(self, outputs, gtbox, gtlabel, gtscore=None,
anchors = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
anchor_masks = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
ignore_thresh=0.7,
use_label_smooth=False):
"""
使用paddle.vision.ops.yolo_loss,直接计算损失函数,过程更简洁,速度也更快
"""
self.losses = []
downsample = 32
for i, out in enumerate(outputs): # 对三个层级分别求损失函数
anchor_mask_i = anchor_masks[i]
loss = paddle.vision.ops.yolo_loss(
x=out, # out是P0, P1, P2中的一个
gt_box=gtbox, # 真实框坐标
gt_label=gtlabel, # 真实框类别
gt_score=gtscore, # 真实框得分,使用mixup训练技巧时需要,不使用该技巧时直接设置为1,形状与gtlabel相同
anchors=anchors, # 锚框尺寸,包含[w0, h0, w1, h1, ..., w8, h8]共9个锚框的尺寸
anchor_mask=anchor_mask_i, # 筛选锚框的mask,例如anchor_mask_i=[3, 4, 5],将anchors中第3、4、5个锚框挑选出来给该层级使用
class_num=self.num_classes, # 分类类别数
ignore_thresh=ignore_thresh, # 当预测框与真实框IoU > ignore_thresh,标注objectness = -1
downsample_ratio=downsample, # 特征图相对于原图缩小的倍数,例如P0是32, P1是16,P2是8
use_label_smooth=False) # 使用label_smooth训练技巧时会用到,这里没用此技巧,直接设置为False
self.losses.append(paddle.mean(loss)) #mean对每张图片求和
downsample = downsample // 2 # 下一级特征图的缩放倍数会减半
return sum(self.losses) # 对每个层级求和
def get_pred(self,
outputs,
im_shape=None,
anchors = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
anchor_masks = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
valid_thresh = 0.01):
downsample = 32
total_boxes = []
total_scores = []
for i, out in enumerate(outputs):
anchor_mask = anchor_masks[i]
anchors_this_level = []
for m in anchor_mask:
anchors_this_level.append(anchors[2 * m])
anchors_this_level.append(anchors[2 * m + 1])
boxes, scores = paddle.vision.ops.yolo_box(
x=out,
img_size=im_shape,
anchors=anchors_this_level,
class_num=self.num_classes,
conf_thresh=valid_thresh,
downsample_ratio=downsample,
name="yolo_box" + str(i))
total_boxes.append(boxes)
total_scores.append(
paddle.transpose(
scores, perm=[0, 2, 1]))
downsample = downsample // 2
yolo_boxes = paddle.concat(total_boxes, axis=1)
yolo_scores = paddle.concat(total_scores, axis=2)
return yolo_boxes, yolo_scores
# 画图展示目标物体边界框
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
from matplotlib.image import imread
import math
# 定义画矩形框的程序
def draw_rectangle(currentAxis, bbox, edgecolor = 'k', facecolor = 'y', fill=False, linestyle='-'):
# currentAxis,坐标轴,通过plt.gca()获取
# bbox,边界框,包含四个数值的list, [x1, y1, x2, y2]
# edgecolor,边框线条颜色
# facecolor,填充颜色
# fill, 是否填充
# linestype,边框线型
# patches.Rectangle需要传入左上角坐标、矩形区域的宽度、高度等参数
rect=patches.Rectangle((bbox[0], bbox[1]), bbox[2]-bbox[0]+1, bbox[3]-bbox[1]+1, linewidth=1,
edgecolor=edgecolor,facecolor=facecolor,fill=fill, linestyle=linestyle)
currentAxis.add_patch(rect)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
filename = 'work/insects/test/images/3122.jpeg'
im = imread(filename)
plt.imshow(im)
currentAxis=plt.gca()
# 预测框位置
boxes = np.array([[4.21716537e+01, 1.28230896e+02, 2.26547668e+02, 6.00434631e+02],
[3.18562988e+02, 1.23168472e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.05688416e+02],
[2.62704697e+01, 1.39430557e+02, 2.20587097e+02, 6.38959656e+02],
[4.24965363e+01, 1.42706665e+02, 2.25955185e+02, 6.35671204e+02],
[2.37462646e+02, 1.35731537e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.31451294e+02],
[3.19390472e+02, 1.29295090e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.33003845e+02],
[3.28933838e+02, 1.22736115e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.39000000e+02],
[4.44292603e+01, 1.70438187e+02, 2.26841858e+02, 6.39000000e+02],
[2.17988785e+02, 3.02472412e+02, 4.06062927e+02, 6.29106628e+02],
[2.00241089e+02, 3.23755096e+02, 3.96929321e+02, 6.36386108e+02],
[2.14310303e+02, 3.23443665e+02, 4.06732849e+02, 6.35775269e+02]])
# 预测框得分
scores = np.array([0.5247661 , 0.51759845, 0.86075854, 0.9910175 , 0.39170712,
0.9297706 , 0.5115228 , 0.270992 , 0.19087596, 0.64201415, 0.879036])
# 画出所有预测框
for box in boxes:
draw_rectangle(currentAxis, box)
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/cbook/__init__.py:2349: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working
if isinstance(obj, collections.Iterator):
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/cbook/__init__.py:2366: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working
return list(data) if isinstance(data, collections.MappingView) else data
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-JXaC9nUI-1620785238388)(output_50_1.png)]
# 画图展示目标物体边界框
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
from matplotlib.image import imread
import math
# 定义画矩形框的程序
def draw_rectangle(currentAxis, bbox, edgecolor = 'k', facecolor = 'y', fill=False, linestyle='-'):
# currentAxis,坐标轴,通过plt.gca()获取
# bbox,边界框,包含四个数值的list, [x1, y1, x2, y2]
# edgecolor,边框线条颜色
# facecolor,填充颜色
# fill, 是否填充
# linestype,边框线型
# patches.Rectangle需要传入左上角坐标、矩形区域的宽度、高度等参数
rect=patches.Rectangle((bbox[0], bbox[1]), bbox[2]-bbox[0]+1, bbox[3]-bbox[1]+1, linewidth=1,
edgecolor=edgecolor,facecolor=facecolor,fill=fill, linestyle=linestyle)
currentAxis.add_patch(rect)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
filename = 'work/insects/test/images/3122.jpeg'
im = imread(filename)
plt.imshow(im)
currentAxis=plt.gca()
boxes = np.array([[4.21716537e+01, 1.28230896e+02, 2.26547668e+02, 6.00434631e+02],
[3.18562988e+02, 1.23168472e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.05688416e+02],
[2.62704697e+01, 1.39430557e+02, 2.20587097e+02, 6.38959656e+02],
[4.24965363e+01, 1.42706665e+02, 2.25955185e+02, 6.35671204e+02],
[2.37462646e+02, 1.35731537e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.31451294e+02],
[3.19390472e+02, 1.29295090e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.33003845e+02],
[3.28933838e+02, 1.22736115e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.39000000e+02],
[4.44292603e+01, 1.70438187e+02, 2.26841858e+02, 6.39000000e+02],
[2.17988785e+02, 3.02472412e+02, 4.06062927e+02, 6.29106628e+02],
[2.00241089e+02, 3.23755096e+02, 3.96929321e+02, 6.36386108e+02],
[2.14310303e+02, 3.23443665e+02, 4.06732849e+02, 6.35775269e+02]])
scores = np.array([0.5247661 , 0.51759845, 0.86075854, 0.9910175 , 0.39170712,
0.9297706 , 0.5115228 , 0.270992 , 0.19087596, 0.64201415, 0.879036])
left_ind = np.where((boxes[:, 0]<60) * (boxes[:, 0]>20))
left_boxes = boxes[left_ind]
left_scores = scores[left_ind]
colors = ['r', 'g', 'b', 'k']
# 画出最终保留的预测框
inds = [3, 5, 10]
for i in range(3):
box = boxes[inds[i]]
draw_rectangle(currentAxis, box, edgecolor=colors[i])
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-1Fm3gQk8-1620785238389)(output_51_0.png)]
# 非极大值抑制
def nms(bboxes, scores, score_thresh, nms_thresh, pre_nms_topk, i=0, c=0):
"""
nms
"""
inds = np.argsort(scores)
inds = inds[::-1]
keep_inds = []
while(len(inds) > 0):
cur_ind = inds[0]
cur_score = scores[cur_ind]
# if score of the box is less than score_thresh, just drop it
if cur_score < score_thresh:
break
keep = True
for ind in keep_inds:
current_box = bboxes[cur_ind]
remain_box = bboxes[ind]
iou = box_iou_xyxy(current_box, remain_box)
if iou > nms_thresh:
keep = False
break
if i == 0 and c == 4 and cur_ind == 951:
print('suppressed, ', keep, i, c, cur_ind, ind, iou)
if keep:
keep_inds.append(cur_ind)
inds = inds[1:]
return np.array(keep_inds)
# 多分类非极大值抑制
def multiclass_nms(bboxes, scores, score_thresh=0.01, nms_thresh=0.45, pre_nms_topk=1000, pos_nms_topk=100):
"""
This is for multiclass_nms
"""
batch_size = bboxes.shape[0]
class_num = scores.shape[1]
rets = []
for i in range(batch_size):
bboxes_i = bboxes[i]
scores_i = scores[i]
ret = []
for c in range(class_num):
scores_i_c = scores_i[c]
keep_inds = nms(bboxes_i, scores_i_c, score_thresh, nms_thresh, pre_nms_topk, i=i, c=c)
if len(keep_inds) < 1:
continue
keep_bboxes = bboxes_i[keep_inds]
keep_scores = scores_i_c[keep_inds]
keep_results = np.zeros([keep_scores.shape[0], 6])
keep_results[:, 0] = c
keep_results[:, 1] = keep_scores[:]
keep_results[:, 2:6] = keep_bboxes[:, :]
ret.append(keep_results)
if len(ret) < 1:
rets.append(ret)
continue
ret_i = np.concatenate(ret, axis=0)
scores_i = ret_i[:, 1]
if len(scores_i) > pos_nms_topk:
inds = np.argsort(scores_i)[::-1]
inds = inds[:pos_nms_topk]
ret_i = ret_i[inds]
rets.append(ret_i)
return rets
# 计算IoU,矩形框的坐标形式为xyxy,这个函数会被保存在box_utils.py文件中
def box_iou_xyxy(box1, box2):
# 获取box1左上角和右下角的坐标
x1min, y1min, x1max, y1max = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
# 计算box1的面积
s1 = (y1max - y1min + 1.) * (x1max - x1min + 1.)
# 获取box2左上角和右下角的坐标
x2min, y2min, x2max, y2max = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
# 计算box2的面积
s2 = (y2max - y2min + 1.) * (x2max - x2min + 1.)
# 计算相交矩形框的坐标
xmin = np.maximum(x1min, x2min)
ymin = np.maximum(y1min, y2min)
xmax = np.minimum(x1max, x2max)
ymax = np.minimum(y1max, y2max)
# 计算相交矩形行的高度、宽度、面积
inter_h = np.maximum(ymax - ymin + 1., 0.)
inter_w = np.maximum(xmax - xmin + 1., 0.)
intersection = inter_h * inter_w
# 计算相并面积
union = s1 + s2 - intersection
# 计算交并比
iou = intersection / union
return iou
# 读取单张测试图片
def single_image_data_loader(filename, test_image_size=608, mode='test'):
"""
加载测试用的图片,测试数据没有groundtruth标签
"""
batch_size= 1
def reader():
batch_data = []
img_size = test_image_size
file_path = os.path.join(filename)
img = cv2.imread(file_path)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
H = img.shape[0]
W = img.shape[1]
img = cv2.resize(img, (img_size, img_size))
mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
mean = np.array(mean).reshape((1, 1, -1))
std = np.array(std).reshape((1, 1, -1))
out_img = (img / 255.0 - mean) / std
out_img = out_img.astype('float32').transpose((2, 0, 1))
img = out_img #np.transpose(out_img, (2,0,1))
im_shape = [H, W]
batch_data.append((image_name.split('.')[0], img, im_shape))
if len(batch_data) == batch_size:
yield make_test_array(batch_data)
batch_data = []
return reader
# 定义画图函数
INSECT_NAMES = ['Boerner', 'Leconte', 'Linnaeus',
'acuminatus', 'armandi', 'coleoptera', 'linnaeus']
# 定义画矩形框的函数
def draw_rectangle(currentAxis, bbox, edgecolor = 'k', facecolor = 'y', fill=False, linestyle='-'):
# currentAxis,坐标轴,通过plt.gca()获取
# bbox,边界框,包含四个数值的list, [x1, y1, x2, y2]
# edgecolor,边框线条颜色
# facecolor,填充颜色
# fill, 是否填充
# linestype,边框线型
# patches.Rectangle需要传入左上角坐标、矩形区域的宽度、高度等参数
rect=patches.Rectangle((bbox[0], bbox[1]), bbox[2]-bbox[0]+1, bbox[3]-bbox[1]+1, linewidth=1,
edgecolor=edgecolor,facecolor=facecolor,fill=fill, linestyle=linestyle)
currentAxis.add_patch(rect)
# 定义绘制预测结果的函数
def draw_results(result, filename, draw_thresh=0.5):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
im = imread(filename)
plt.imshow(im)
currentAxis=plt.gca()
colors = ['r', 'g', 'b', 'k', 'y', 'c', 'purple']
for item in result:
box = item[2:6]
label = int(item[0])
name = INSECT_NAMES[label]
if item[1] > draw_thresh:
draw_rectangle(currentAxis, box, edgecolor = colors[label])
plt.text(box[0], box[1], name, fontsize=12, color=colors[label])
import json
import paddle
ANCHORS = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
ANCHOR_MASKS = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
VALID_THRESH = 0.01
NMS_TOPK = 400
NMS_POSK = 100
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
NUM_CLASSES = 7
if __name__ == '__main__':
image_name = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/test/images/2599.jpeg'
params_file_path = '/home/aistudio/yolo_epoch0.pdparams'
model = YOLOv3(num_classes=NUM_CLASSES)
model_state_dict = paddle.load(params_file_path)
model.load_dict(model_state_dict)
model.eval()
total_results = []
test_loader = single_image_data_loader(image_name, mode='test')
for i, data in enumerate(test_loader()):
img_name, img_data, img_scale_data = data
img = paddle.to_tensor(img_data)
img_scale = paddle.to_tensor(img_scale_data)
outputs = model.forward(img)
bboxes, scores = model.get_pred(outputs,
im_shape=img_scale,
anchors=ANCHORS,
anchor_masks=ANCHOR_MASKS,
valid_thresh = VALID_THRESH)
bboxes_data = bboxes.numpy()
scores_data = scores.numpy()
results = multiclass_nms(bboxes_data, scores_data,
score_thresh=VALID_THRESH,
nms_thresh=NMS_THRESH,
pre_nms_topk=NMS_TOPK,
pos_nms_topk=NMS_POSK)
result = results[0]
, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
ANCHOR_MASKS = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
VALID_THRESH = 0.01
NMS_TOPK = 400
NMS_POSK = 100
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
NUM_CLASSES = 7
if __name__ == '__main__':
image_name = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/test/images/2599.jpeg'
params_file_path = '/home/aistudio/yolo_epoch0.pdparams'
model = YOLOv3(num_classes=NUM_CLASSES)
model_state_dict = paddle.load(params_file_path)
model.load_dict(model_state_dict)
model.eval()
total_results = []
test_loader = single_image_data_loader(image_name, mode='test')
for i, data in enumerate(test_loader()):
img_name, img_data, img_scale_data = data
img = paddle.to_tensor(img_data)
img_scale = paddle.to_tensor(img_scale_data)
outputs = model.forward(img)
bboxes, scores = model.get_pred(outputs,
im_shape=img_scale,
anchors=ANCHORS,
anchor_masks=ANCHOR_MASKS,
valid_thresh = VALID_THRESH)
bboxes_data = bboxes.numpy()
scores_data = scores.numpy()
results = multiclass_nms(bboxes_data, scores_data,
score_thresh=VALID_THRESH,
nms_thresh=NMS_THRESH,
pre_nms_topk=NMS_TOPK,
pos_nms_topk=NMS_POSK)
result = results[0]
draw_results(result, image_name, draw_thresh=0.5)
我在AI Studio上获得至尊等级,点亮8个徽章,来互关呀~