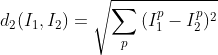图像分类Image Classification
图像分类采用数据驱动(Data-driven approach)方法,每个类别提供若干图像,运行算法学习不同类别的特点,再对新图像进行分类
一、Nearest Neighbor Classifier
将图像A与training data中的每个图像进行对比,选择其中“距离最近”的图像B,将B的类别作为A的类别。“距离”可以采取不同的计算形式,包括:
对于d2,虽然公式中需要取平方根,但在实际计算中,由于我们只需要找到d2最小的图像,而取平方根是单调函数,因此可以省略。
首先进行数据处理,从CIFAR-10中加载数据,并且转换成指定形式
# Xtr为training set中的图像,50000×32×32×3;Ytr为training set图像的label
Xtr,Ytr,Xte,Yte=load_CIFAR10('data/cifar10/')
# 需要将image变形为一维形式50000×(32*32*3),每个image占据一个row
Xtr_rows=Xtr.reshape(Xtr.shape[0],32*32*3)
Ytr_rows=Ytr.reshape(Ytr.shape[0],32*32*3)然后建立NearestNeighbor类,并创建训练函数train和预测函数predict。Nearest Neighor算法在训练数据时不需要做特定的处理,因此train()中只需要拷贝训练数据即可;在预测函数中,则依次将本图像与训练集中所有图像进行比较,计算距离(L1/L2),并选择距离最短的图像所属于的label
import numpy as np
class NearestNeighbor(object):
def __init__(self):
pass
def train(self, X, y):
"""X is N×D where each row is an example.
Y is 1-dimensional of size N """
# the nearest neighbor classifier simply remembers all the training data
self.Xtr=X
self.Ytr=y
def predict(self,X):
"""X is N×D where each row is an example we wish to predict label."""
num_test=X.shape[0]
# lets make sure that the output type matches the input type
Ypred=np.zeros(num_test,dtype=self.ytr.dtype)
# loop over all test rows
for i in range(num_test):
# find the nearest training image to the i'th test image
L1_distances=np.sum(np.abs(self.Xtr-X[i,:]),axis=1)
L2_distances=np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(self.Xtr-X[i,:]),axis=1))
min_index=np.argmin(distances) # get the index with smallest distance
Ypred[i]=self.ytr[min_index]
return Y_pred二、K-Nearest Neighbor Classifier
1. 方法概述
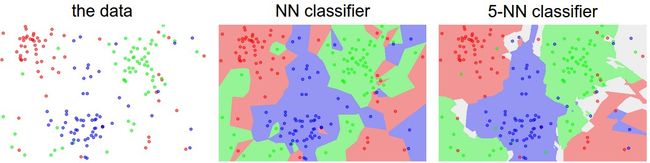
寻找距离最近的K个图像,同时考虑K个图像的类别。如下图,不同颜色的区域之间的分界为dicision boundary,白色区域为模糊分类区(比如结果同时为两个类别)
NN方法下,异常数据点为可能出现的错误预测创建了小的区域,比如大块绿色区域中的红色孤岛,这种情况下红色数据点很可能是异常数据;而K-NN方法下,消除了这些不规则的区域,也很大程度上获得了更好的泛化能力。
2. K的选择
超参数Hyperparameter:包括距离选择方法(L1/L2...),K的选择等等。
需要用于调参的数据集(Validation sets for Hyperparameter tuning)。注意不能直接使用test set,否则会出现overfit的问题,并且test set将无法有效反映模型的性能。通过将test set分成两部分——较小的validation set和test set,以CIFAR-10为例,从test set中50000个数据取出1000个作为validation set即可。
然后用validation set中的数据测试每一个K的值,选择准确率最高的K即可
# we have Xtr_rows, Ytr, Xte_rows, Yte now
Xval_rows=Xtr_rows[:1000,:] # take first 1000 for validation
Yval=Ytr[:1000]
Xtr_rows = Xtr_rows[1000:, :] # keep last 49,000 for train
Ytr = Ytr[1000:]
# find hyperparameters that work best on the validation set
validation_accuracies = []
for k in [1, 3, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100]:
# use a particular value of k and evaluation on validation data
nn = NearestNeighbor()
nn.train(Xtr_rows, Ytr)
# here we assume a modified NearestNeighbor class that can take a k as input
Yval_predict = nn.predict(Xval_rows, k = k)
acc = np.mean(Yval_predict == Yval)
# keep track of what works on the validation set
validation_accuracies.append((k, acc))3. 交叉检验Cross-validation
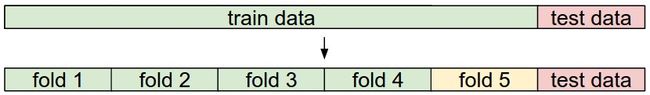
如果training set本身很小,则使用比较复杂的交叉检验法。比如对于5-fold cross-validation,将training set分成5份,4份用于training,一份用于validation;5份数据依次用作validation fold并评价性能,即每个k会受到5个accuracy,最后取平均性能作为选择K的依据。
三、评价
实现简单并且易于理解,并且不需要时间来训练模型;但是在检测时开销很大,每预测一个图像需要遍历整个training set,而在实际使用中往往更看重测试时间。
对于低维度的数据,Nearest Neighbor Classifier比较适合;但对于多维度对象,具有更多的pixel,距离的计算常常是违反直觉的counter-intuitive,比如下图中右侧三个图与左侧第一个图具有相同的L2距离。因为“距离”的计算一般与颜色的分布关系比较大,但我们无法仅仅通过色彩的分布确定图像的类型。
四、总结(KNN算法的实现步骤)
- 数据预处理。PNormalize the features in your data (e.g. one pixel in images) to have zero mean and unit variance. We will cover this in more detail in later sections, and chose not to cover data normalization in this section because pixels in images are usually homogeneous and do not exhibit widely different distributions, alleviating the need for data normalization.
- 如果数据本身是多维的,则可以通过IPCA (wiki ref, CS229ref, blog ref), NCA (wiki ref, blog ref), Random Projections 等方法降低维度
- 随机将training set分成training和validation两个部分,各部分的占比与需要决定的hyperparameters个数有关,个数越多,validation set也越大,一般而言,training占据70-90%。如果不希望validation set过大,或者不太在乎计算开销,也可以采用cross-validation,将training data分成若干个fold。
- 用validation data对各个k进行训练并评价
- 如果kNN classifier运行时间过长,可以使用Approximate Nearest Neighbor library (e.g. FLANN)来加速
- 选择性能最好的hyperparameters。