深入浅出PyTorch - Pytorch模型定义
深入浅出PyTorch
模型部署及定义
使用seqtoseq模型预测时序数据
Pytorch模型定义
- 深入浅出PyTorch
- 1.数据集
-
- 1.1数据读入
- 1.2数据集预处理
- 2模块化搭建模型
1.数据集
时间序列就是以时间为自变量的一系列数据。本文使用seabon包中的数据。
1.1数据读入
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
sns.get_dataset_names()
flight_data = sns.load_dataset("flights")
1.2数据集预处理
主要有两个部分:1)将数据转为浮点数以方便梯度计算;2)将数据进行标准化/归一化以防止过拟合。
# 归一化
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(-1, 1))
train_data_normalized = scaler.fit_transform(train_data .reshape(-1, 1))
# 转为浮点形式的tensor
train_data_normalized = torch.FloatTensor(train_data_normalized).view(-1)
train_data_normalized
2模块化搭建模型
对于大部分模型结构(比如ResNet、DenseNet等),我们仔细观察就会发现,虽然模型有很多层, 但是其中有很多重复出现的结构。考虑到每一层有其输入和输出,若干层串联成的”模块“也有其输入和输出,如果我们能将这些重复出现的层定义为一个”模块“,每次只需要向网络中添加对应的模块来构建模型,这样将会极大便利模型构建的过程。在自然语言处理及时序数据处理中,具有重要作用的seqtoseq模型就是典型的例子。
seqtoseq模型主要包含编码器与解码器两个部分,其工作原理图如下:
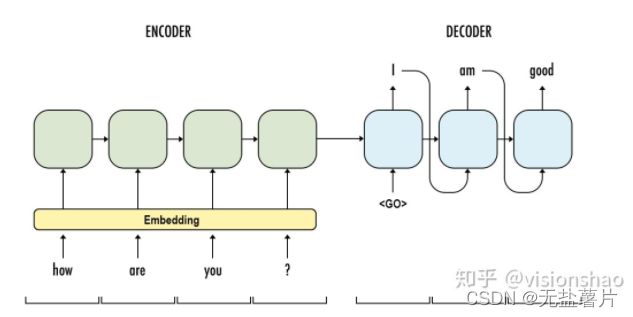
关于该模型的理论详述,可参考https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/57623148
第一部分编码器:
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
input_size = 2,
embedding_size = 128,
hidden_size = 256,
n_layers = 4,
dropout = 0.5):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_size, embedding_size)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embedding_size, hidden_size, n_layers,
dropout = dropout)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, x):
embedded = self.dropout(F.relu(self.linear(x)))
output, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(embedded)
return hidden, cell
第二部分解码器:
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
output_size = 2,
embedding_size = 128,
hidden_size = 256,
n_layers = 4,
dropout = 0.5):
super().__init__()
self.output_size = output_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.embedding = nn.Linear(output_size, embedding_size)
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embedding_size, hidden_size, n_layers, dropout = dropout)
self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, x, hidden, cell):
x = x.unsqueeze(0)
embedded = self.dropout(F.relu(self.embedding(x)))
prediction = self.linear(output.squeeze(0))
return prediction, hidden, cell
使用写好的模型块,可以非常方便地组装seqtoseq模型。可以看到,通过模型块的方式实现了代码复用,整个模型结构定义所需的代码总行数明显减少,代码可读性也得到了提升。
第三部分seqtoseq:
class Seq2Seq(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder, device):
super().__init__()
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
self.device = device
assert encoder.hidden_size == decoder.hidden_size, \
"Hidden dimensions of encoder and decoder must be equal!"
assert encoder.n_layers == decoder.n_layers, \
"Encoder and decoder must have equal number of layers!"
def forward(self, x, y, teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5):
batch_size = x.shape[1]
target_len = y.shape[0]
outputs = torch.zeros(y.shape).to(self.device)
hidden, cell = self.encoder(x)
decoder_input = x[-1, :, :]
for i in range(target_len):
output, hidden, cell = self.decoder(decoder_input, hidden, cell)
outputs[i] = output
teacher_forcing = random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio
decoder_input = y[i] if teacher_forcing else output
return outputs
该部分详述可参考https://curow.github.io/blog/LSTM-Encoder-Decoder/
模型训练完成后,可将训练好的参数进行保存,方便下次直接使用,储存方式主要有两种::存储整个模型(包括结构和权重),和只存储模型权重。更推荐使用第二种,因为若训练保存模型的pytorch版本与迁移后直接使用的pytorch版本相差较大时,直接加载第一种方法保存的模型可能会报错,且保存整个模型所需的空间明显更大。
# 保存整个模型
torch.save(model, save_dir)
# 保存模型权重
torch.save(model.state_dict, save_dir)