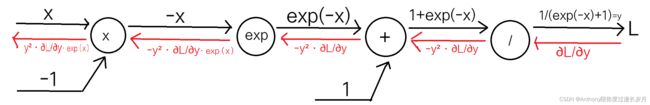“深度学习”学习日记。误差反向传播法--加法层、乘法层、激活函数层的实现
2023.1.16
1、加法层、乘法层:
前两篇文章都在讲述理论,今天实现代码操作:关于加法节点,乘法节点的内容在这篇文章。
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72675651/article/details/128695488
在以后的学习中,将把构建神经网络的“层”实现为一个类。这里的“层”是指神经网络中功能的单位。
这样写感觉到可以让代码变得美观一点,而更容易找出错误并修改
class Addyer: # 加法节点
def __init__(self):
pass
def forward(self, x, y):
out = x + y
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = dout * 1
dy = dout * 1
return dx, dy
class Mullyer: # 乘法节点
def __init__(self): # __init__() 中会初始化实例变量
self.x = None
self.y = None
def forward(self, x, y):
self.x = y
self.y = x
out = x * y
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = dout * self.x
dy = dout * self.y
return dx, dy现在用代码实现了,加法层和乘法层,所以我们用代码解决这个问题:
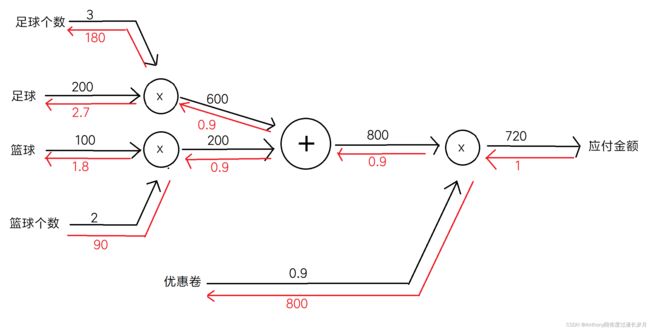
利用反向传播法,求解,篮球、足球分别对应付金额上涨1元的影响是多少?
代码实现:
class Addyer: # 加法节点
def __init__(self):
pass
def forward(self, x, y):
out = x + y
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = dout * 1
dy = dout * 1
return dx, dy
class Mullyer: # 乘法节点
def __init__(self): # __init__() 中会初始化实例变量
self.x = None
self.y = None
def forward(self, x, y):
self.x = y
self.y = x
out = x * y
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = dout * self.x
dy = dout * self.y
return dx, dy
discout = 0.9
basketball = 100 # b
football = 200 # f
basketball_num = 2
footbal_num = 3
# 求解问题时 因为乘法层的反向传播需要正向传播的参数
m = Mullyer()
m1 = Mullyer()
m2 = Mullyer()
a = Addyer()
b_price = m2.forward(basketball, basketball_num)
f_price = m1.forward(football, footbal_num)
b_f_price = a.forward(b_price, f_price)
final_price = m.forward(discout, b_f_price)
print(final_price) # 720
# 求解 应付金额上涨1元 delta=1
# 篮球得影响
delta = 1
ddiscount, db_f_price = m.backward(delta)
dbaskbetball1, dfootball1 = a.backward(db_f_price)
dbaskbetball, dbaskbetball_num = m2.backward(dbaskbetball1)
dfootball, dfootball_num = m1.backward(dfootball1)
print(db_f_price) # 800
print(dfootball1) # 0.9
print(dbaskbetball, dbaskbetball_num) # 1.8 90.0
print(dfootball, dfootball_num) # 2.7 180.0综上,计算图中层的函数计算层实现计算复杂导数的代码简单,接下来要学习激活函数层的代码实现;
2,激活函数层:
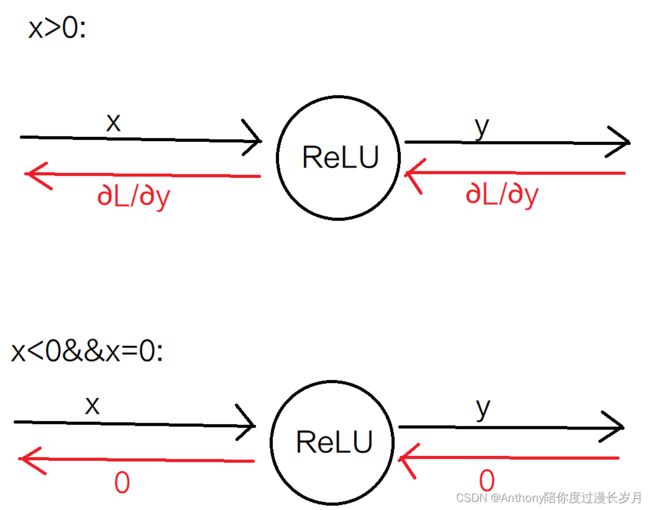
在正向传播时,如果x大于0,则反向传播时,上游的x会原封不动的传递给下游;反之,正向传播时,如果x小于等于0的话,则反向传播中传给下游的信号将停在此处。
用计算图表示:
import numpy as np
class ReLU:
def __init__(self):
self.mask = None
def forward(self, x):
self.mask = (x <= 0)
out = x.copy()
out[self.mask] = 0
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dout[self.mask] = 0
dx = dout
return dx
arr = np.arange(-3, 3).reshape(2, 3)
print(arr)
a = ReLU()
print(a.forward(arr))
mask = (arr <= 0)
print(mask)输出结果:
[[-3 -2 -1]
[ 0 1 2]]
[[0 0 0]
[0 1 2]]
[[ True True True]
[ True False False]]
通过输出结果,我们可以很清楚的知道mask的作用是一个开关 , 一个bool值开关。因此,反向传播中会使用正向传播保存的mask,True为0,false为1。
我们们使用网络的学习,这一部分学习过ReLU函数不适合作为激活函数 https://blog.csdn.net/m0_72675651/article/details/128602009
所以我们接下来来实现sigmoid函数
回忆一下sigmoid函数:![]()
正先传播的话是这样:
反向传播时有大学问,得分解详细讲述:
“ + 节点”: 学习过他有上游会原封不动得传递到下游;
“exp 节点”:在正向传播时表示y=exp(x),由指数函数的数学解析式可得 ![]() ;
;
“ x 节点”: 我们得将正向传播的值翻转后再做乘法运算;
用计算图表示:
import numpy as np
class Sigmoid:
def __init__(self):
self.out = None
def forward(self, x):
out = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
self.out = out
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = dout * (1.0 - self.out) * self.out
return dx
arr = np.arange(-3, 3).reshape(2, 3)
s = Sigmoid()
s1=s.forward(arr)
print(s.forward(arr))
print(s.backward(arr))输出结果:
[[0.04742587 0.11920292 0.26894142]
[0.5 0.73105858 0.88079708]]
[[-0.13552998 -0.20998717 -0.19661193]
[ 0. 0.19661193 0.20998717]]
在正向传播时,用到了实例out,在反向传播时我们也用到了实例out,这样我们可以先进行一次正向传播,保存实例变量out