MATLAB对音频信号抽样、量化、编码、2PSK调制解调还原音频信号
将一个mp3文件的信号抽样到8kHz,采用非均匀量化和律15折线编码,通过2PSK调制,经过加入高斯白噪声的信道后经2PSK解调和信号重建还原mp3信号文件。
目录
- 代码
- 结果
代码
main.m
clear
%读取文件,60s-70s
T=10;
fs=44100;
[xr,fs]=audioread('music.mp3',[60*fs,70*fs]);%fs=44100
xr=xr(:,1);t=0:1/44100:T;t=t';
%抽样到8k
fs1=8000;sdt=1/fs1;t1=0:sdt:T;t1=t1';xr1=zeros(8000*T+1,1);
for i=0:8000*T
xr1(i+1)=xr(floor(i*44100/8000+1));
end
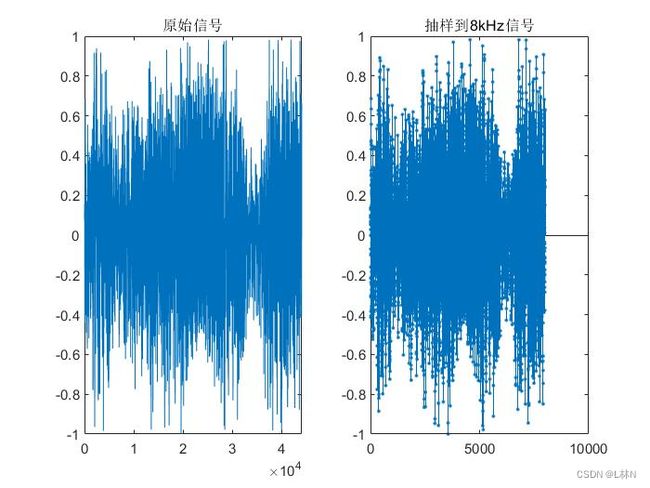
figure(1)
subplot(121);plot(xr);title('原始信号');
subplot(122);stem(xr1,'.');title('抽样到8kHz信号');
%非均匀量化,PCM编码
code=PCMcode(xr1);
max_xr=max(abs(xr1));
figure(2)
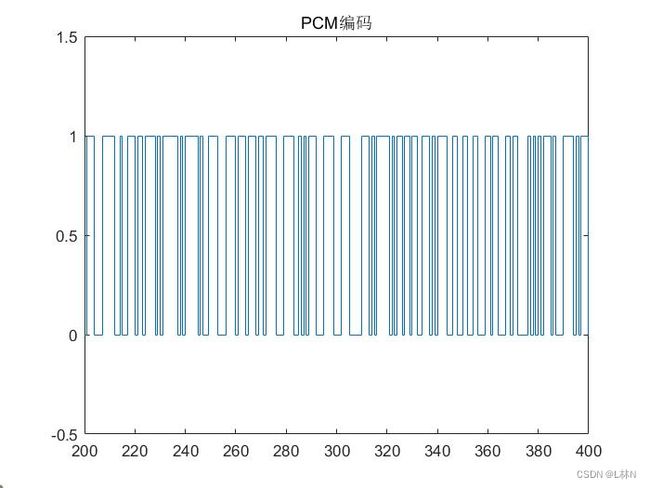
stairs(code);axis([200 400 -0.5 1.5]);title('PCM编码');
%2PSK调制
%双极性基带信号
code2=2*code-1;
%产生载波信号
len=length(code2);
j=50*len;
t2=linspace(0,8*T,j);t3=linspace(0,8*T,len);
st1=t2;
for n=1:len
if code2(n)<0
for m=j/len*(n-1)+1:j/len*n
st1(m)=-1;
end
else
for m=j/len*(n-1)+1:j/len*n
st1(m)=1;
end
end
end
st1=st1';
s1=sin(2*pi*fs1*t2);s1=s1';
figure(3)
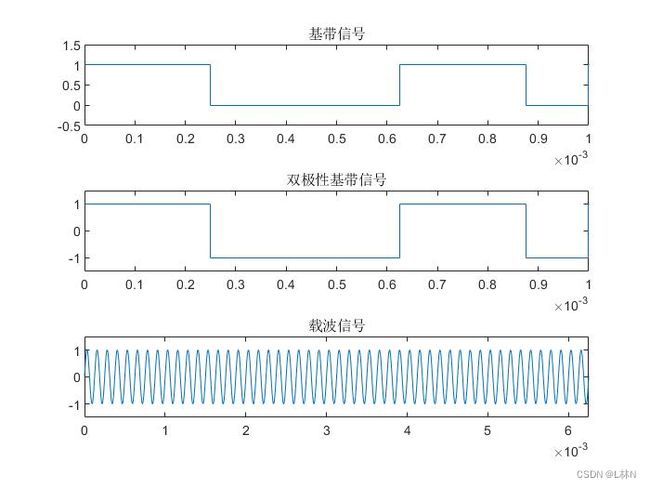
subplot(311);stairs(t3,code);axis([0 T/8000*8 -0.5 1.5]);title('基带信号');
subplot(312);stairs(t3,code2);axis([0 T/8000*8 -1.5 1.5]);title('双极性基带信号');
subplot(313);plot(t2,s1);axis([0 1/8000*50 -1.5 1.5]);title('载波信号');
%2PSK调制
e_psk=st1.*s1;
%加高斯白噪声
noise=rand(j,1);
psk=e_psk+noise;
%相干解调
x_psk=psk.*s1;%与载波相乘
%低通滤波
[B,A]=butter(4,0.14);
d_psk=filter(B,A,x_psk);
%抽样判决
c_psk=d_psk;
for n=1:len
a=length(find(d_psk((n-1)*50+1:n*50)>0));
b=length(find(d_psk((n-1)*50+1:n*50)<0));
if a>b
c_psk((n-1)*50+1:n*50)=1;
else
c_psk((n-1)*50+1:n*50)=0;
end
end
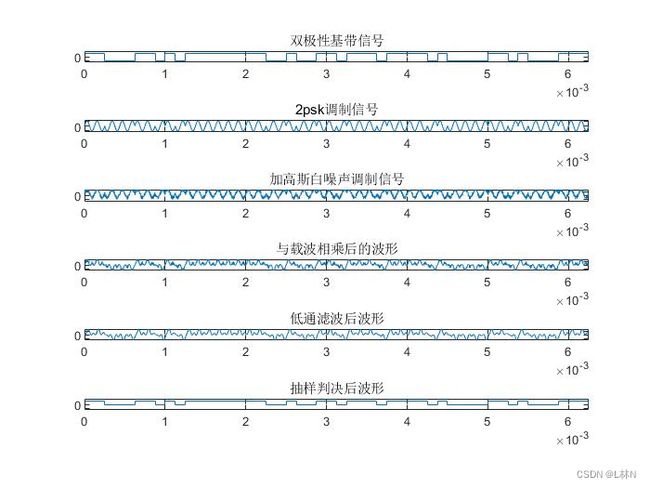
figure(4)
subplot(611);stairs(t2,st1);axis([0 1/8000*50 -1.5 1.5]);title('双极性基带信号');
subplot(612),plot(t2,e_psk);axis([0 1/8000*50 -1.2 1.2]);title('2psk调制信号');
subplot(613),plot(t2,psk);axis([0 1/8000*50 -1.5 1.5]);title('加高斯白噪声调制信号');
subplot(614),plot(t2,x_psk);axis([0 1/8000*50 -1.5 1.5]);title('与载波相乘后的波形');
subplot(615);plot(t2,d_psk);axis([0 1/8000*50 -1.5 1.5]);title('低通滤波后波形');
subplot(616);stairs(t2,c_psk);axis([0 1/8000*50 -1.5 1.5]);title('抽样判决后波形');
%抽样判决后波形-->PCM编码波形
pcm=code2;
for m=1:len
if c_psk((m-1)*50+25)>0.5
pcm(m)=1;
else
pcm(m)=0;
end
end
%误码率
err=0;
for e=1:len
if pcm(e)==code(e)
err=err+0;
else
err=err+1;
end
end
i_err=err/len;
%PCM译码
i_pcm=PCMdecode(pcm,max_xr);
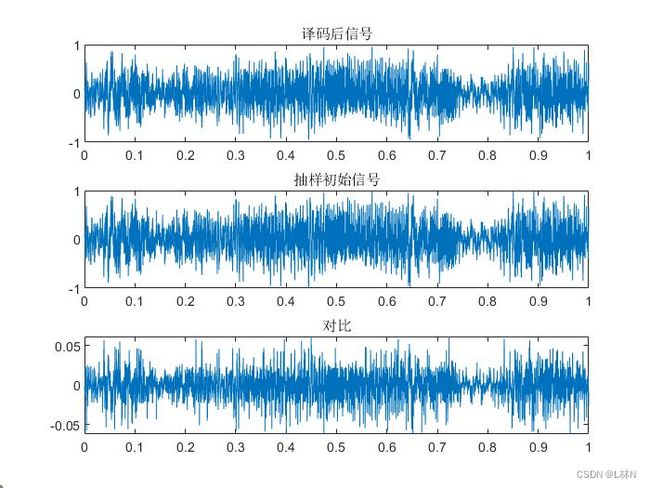
figure(5)
subplot(311);plot(t1,i_pcm);title('译码后信号');
subplot(312);plot(t1,xr1);title('抽样初始信号');
subplot(313);plot(t1,i_pcm-xr1');title('对比');
%播放音乐
sound(i_pcm);
%生成.wav文件
audiowrite('music_cy.wav',i_pcm,8000);
PCMcode.m
function code=PCMcode(S)
z=sign(S); %判断S的正负
MaxS=max(abs(S)); %求S的最大值
S=abs(S/MaxS); %归一化
Q=2048*S; %量化
code=zeros(length(S),8); %代码存储矩阵(全零)
%符号位的判断
for i=1:length(S)
if z(i)>0
code(i,1)=1;
elseif z(i)<0
code(i,1)=0;
end
end
% 段落码判断程序
for i=1:length(S)
if (Q(i)>=128)&&(Q(i)<=2048)
code(i,2)=1; %在第五段与第八段之间,段位码第一位都为"1"
end
if (Q(i)>=32)&&(Q(i)<128)||(Q(i)>=512)&&(Q(i)<=2048)
code(i,3)=1; %在第三四七八段内,段位码第二位为"1"
end
if (Q(i)>=16)&&(Q(i)<32)||(Q(i)>=64)&&(Q(i)<128)||(Q(i)>=256)&&(Q(i)<512)||(Q(i)>=1024)&&(Q(i)<=2048)
code(i,4)=1; %在二四六八段内,段位码第三位为"1"
end
end
N=zeros(length(S),1); %段内码判断程序
for i=1:length(S)
N(i)=bin2dec(num2str(code(i,2:4)))+1; %找到code位于第几段%bin2dec二进制值的字符向量转换为十进制数;num2str转化为字符向量
end
a=[0,16,32,64,128,256,512,1024]; %量化间隔
b=[1,1,2,4,8,16,32,64]; %除以16,得到每段的最小量化间隔
for i=1:length(S)
q=ceil((Q(i)-a(N(i)))/b(N(i))); %求出在段内的位置ceil向上取整
if q==0
code(i,(5:8))=[0,0,0,0]; %如果输入为零则输出"0"
else k=num2str(dec2bin(q-1,4)); %编码段内码为二进制dec2bin把十进制数D转换成二进制形式,二进制位数为4位
code(i,5)=str2num(k(1)); %str2num转化为数值
code(i,6)=str2num(k(2));
code(i,7)=str2num(k(3));
code(i,8)=str2num(k(4));
end
end
code = reshape(code', 1, []);%reshape按列将数据变成一行
end
PCMdecode.m
function s=PCMdecode(encode, max)
encode=(reshape(encode',8,length(encode)/8))';
l=size(encode,1);
a=[0,16,32,64,128,256,512,1024]; %量化间隔
b=[1,1,2,4,8,16,32,64];
c=[0 1.5:15.5];
for i=1:l
x=encode(i,1);
T=bin2dec(num2str(encode(i,(2:4))))+1;
Y=bin2dec(num2str(encode(i,(5:8))));
if Y==0
k(i)=a(T)/2048;
else
k(i)=(a(T)+b(T)*c(Y))/2048;
end
if x==0
s(i)=-k(i);
else
s(i)=k(i);
end
end
s = s*max;
end
结果
《通信原理(第7版)》樊昌信 曹丽娜