Neighbor2Neighbor源码解读
前言
Neighbor2Neighbor属于自监督去噪中算法,通过训练后可以对任意尺寸的图像进行去噪,现在对去噪代码中如何实现任意尺寸图像去噪进行解读。
代码
先贴源码
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
from arch_unet import UNet
import numpy as np
def get_generator():
global operation_seed_counter # 全局变量 在局部变量可以引用全局变量并修改
operation_seed_counter += 1
g_cuda_generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda")
g_cuda_generator.manual_seed(operation_seed_counter)
return g_cuda_generator
class AugmentNoise(object): # 添加噪声的类
def __init__(self, style):
print(style)
if style.startswith('gauss'):
self.params = [
float(p) / 255.0 for p in style.replace('gauss', '').split('_')
]
if len(self.params) == 1:
self.style = "gauss_fix"
elif len(self.params) == 2:
self.style = "gauss_range"
elif style.startswith('poisson'):
self.params = [
float(p) for p in style.replace('poisson', '').split('_')
]
if len(self.params) == 1:
self.style = "poisson_fix"
elif len(self.params) == 2:
self.style = "poisson_range"
def add_train_noise(self, x):
shape = x.shape
if self.style == "gauss_fix":
std = self.params[0]
std = std * torch.ones((shape[0], 1, 1, 1), device=x.device)
noise = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(shape, device=x.device)
torch.normal(mean=0.0,
std=std,
generator=get_generator(),
out=noise)
return x + noise
elif self.style == "gauss_range":
min_std, max_std = self.params
std = torch.rand(size=(shape[0], 1, 1, 1),
device=x.device) * (max_std - min_std) + min_std
noise = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(shape, device=x.device)
torch.normal(mean=0, std=std, generator=get_generator(), out=noise)
return x + noise
elif self.style == "poisson_fix":
lam = self.params[0]
lam = lam * torch.ones((shape[0], 1, 1, 1), device=x.device)
noised = torch.poisson(lam * x, generator=get_generator()) / lam
return noised
elif self.style == "poisson_range":
min_lam, max_lam = self.params
lam = torch.rand(size=(shape[0], 1, 1, 1),
device=x.device) * (max_lam - min_lam) + min_lam
noised = torch.poisson(lam * x, generator=get_generator()) / lam
return noised
def add_valid_noise(self, x):
shape = x.shape
if self.style == "gauss_fix":
std = self.params[0]
return np.array(x + np.random.normal(size=shape) * std,
dtype=np.float32)
elif self.style == "gauss_range":
min_std, max_std = self.params
std = np.random.uniform(low=min_std, high=max_std, size=(1, 1, 1))
return np.array(x + np.random.normal(size=shape) * std,
dtype=np.float32)
elif self.style == "poisson_fix":
lam = self.params[0]
return np.array(np.random.poisson(lam * x) / lam, dtype=np.float32)
elif self.style == "poisson_range":
min_lam, max_lam = self.params
lam = np.random.uniform(low=min_lam, high=max_lam, size=(1, 1, 1))
return np.array(np.random.poisson(lam * x) / lam, dtype=np.float32)
model_path = 'test_dir/unet_gauss25_b4e100r02/2022-03-02-22-24/epoch_model_040.pth' # 导入训练的模型文件
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
net = UNet().to(device)
net.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
net.eval()
noise_adder = AugmentNoise(style='gauss25')
img = Image.open('validation/Kodak/000014.jpg')
im = np.array(img, dtype=np.float32) / 255.0
origin255 = im.copy()
origin255 = origin255.astype(np.uint8)
noisy_im = noise_adder.add_valid_noise(im)
H = noisy_im.shape[0]
W = noisy_im.shape[1]
val_size = (max(H, W) + 31) // 32 * 32
noisy_im = np.pad(
noisy_im,
[[0, val_size - H], [0, val_size - W], [0, 0]],
'reflect')
transformer = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()])
noisy_im = transformer(noisy_im)
noisy_im = torch.unsqueeze(noisy_im, 0)
noisy_im = noisy_im.cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
prediction = net(noisy_im)
prediction = prediction[:, :, :H, :W]
prediction = prediction.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
prediction = prediction.cpu().data.clamp(0, 1).numpy()
prediction = prediction.squeeze()
pred255 = np.clip(prediction * 255.0 + 0.5, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
Image.fromarray(pred255).convert('RGB').save('test1.png')
输入图像
尺寸大小为(408, 310),PIL读入后进行归一化处理。
img = Image.open('validation/Kodak/00001.jpg')
print('img', img.size) # img (408, 310)
im = np.array(img, dtype=np.float32) / 255.0
print('im', im.shape) # im (310, 408, 3)
先对不规则图像进行填充,要求填充的尺寸是32的倍数,否则输入到网络中会报错。在训练的时候是随机裁剪256*256的切片的。
b = torch.rand(1, 3, 255, 255).to('cuda')
a = net(b)
print(a.shape)
![]()
在卷积神经网络中,为了避免因为卷积运算导致输出图像缩小和图像边缘信息丢失,常常采用图像边缘填充技术,即在图像四周边缘填充0,使得卷积运算后图像大小不会缩小,同时也不会丢失边缘和角落的信息。在Python的numpy库中,常常采用numpy.pad()进行填充操作。
val_size = (max(H, W) + 31) // 32 * 32
noisy_im = np.pad(
noisy_im,
[[0, val_size - H], [0, val_size - W], [0, 0]],
'reflect')
上图转自 http://t.zoukankan.com/shuaishuaidefeizhu-p-14179038.html
>>> a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
>>> np.pad(a, (2, 3), 'reflect')
array([3, 2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 3, 2])
个人感觉使用reflect操作,而不是之间的填充0是为了在边缘去噪的时候更平滑一些。镜像填充后的图如下:
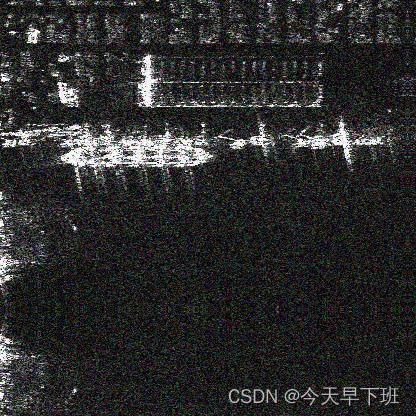

输入网络后,得到预测结果。最后进行裁剪,得到去噪后的图像。
prediction = prediction[:, :, :H, :W]

