Springboot @Profile使用详解
简介
@Profile这个注解主要是和spring.profile.active这个配置结合使用的,让我们的配置文件使用的更加灵活,比如原来我们写:spring.profile.active=dev,那么整个项目都会使用application-dev.properites下的配置文件,但是如果我们在类或者方法上加上@Profile("dev, prod, xxxx")注解,这样就比较灵活了,比如在一个bean上加上@Profile("prod"),那么这个bean只会在 spring.profile.active=prod的时候才被实例化,以此类推
在项目中,有时我们需要能根据当前环境,动态的激活和切换一系列组件,这个借助 Spring 提供的 @Profile 注解即可实现,下面通过样例进行演示。
@Profile 注解的作用是指定组件在哪个环境的情况下才能被注册到容器中,若不指定,任何环境下都能注册这个组件。
- 加了@Profile 注解的 bean,只有这个环境被激活的时候才能注册到容器中。默认是 default 环境。
- 若 @Profile 注解写在配置类上,只有在指定的环境的时候,整个配置类里面的所有配置才能开始生效。
演示
根据当前环境的不同(dev 或 prod),自动实例化对应的 DataSource
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:/dbconfig.properties"})
public class ProfileBeanConfig implements EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
//数据库连接用户名
@Value(value = "${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
//数据库连接密码
private String password;
//开发环境数据源
@Bean(value = "dataSourceDev")
@Profile(value = "dev")
public DataSource dataSourceDev(@Value("${jdbc.driverClass}") String driverClass)
throws PropertyVetoException {
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
comboPooledDataSource.setUser(this.username);
comboPooledDataSource.setPassword(this.password);
comboPooledDataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass);
comboPooledDataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dev");
return comboPooledDataSource;
}
//生产环境数据源
@Bean(value = "dataSourceProduction")
@Profile("prod")
public DataSource dataSourceProduction(@Value("${jdbc.driverClass}") String driverClass)
throws PropertyVetoException {
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
comboPooledDataSource.setUser(this.username);
comboPooledDataSource.setPassword(this.password);
comboPooledDataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass);
comboPooledDataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/production");
return comboPooledDataSource;
}
}有时候我们会有这样的一个需求,在生产环境或者开发环境我们所看到的功能是不同的,这便需要我们根据配置项来激活不同的功能。
比如一些接口在开发环境中无法调用,那么在开发环境中就需要 mock 数据。因此我们可以写一个 mock 数据接口类,专门供开发环境使用。而生产环境则使用真实的接口调用类,二者通过 @Profile 注解来自动激活生效。
首先我们先定义一个 Service 的接口:
public interface ProductService {
String getProductInfo(Long id);
}接着我们创建两个实现类,分别对应开发环境和生产环境:
@Service
@Profile("dev")
public class MockProductServiceImpl implements ProductService {
@Override
public String getProductInfo(Long id) {
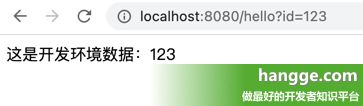
return "这是开发环境数据:" + id;
}
}
@Service
@Profile("prod")
public class ProductServiceImpl implements ProductService {
@Override
public String getProductInfo(Long id) {
//return productResource.getProductInfo(id);
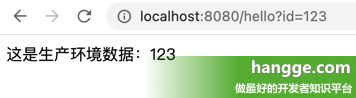
return "这是生产环境数据:" + id;
}
}最后创建一个 Controller 调用 Service 接口:
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(@RequestParam("id") Long id) {
return productService.getProductInfo(id);
}
}开始测试,首先我们编辑 application.properties 文件
spring.profiles.active=dev访问 Controller 接口可以看到调用的是 MockProductServiceImpl 这个 Servcie:
spring.profiles.active=prod访问 Controller 接口可以看到调用的是 ProductServiceImpl 这个 Servcie: