计算机网络学习笔记(1)
注:本笔记基于对J.F. Kurose的计算机网络课程整理而成,课程链接:
Jim Kurose Homepage![]() https://gaia.cs.umass.edu/kurose_ross/ppt.php
https://gaia.cs.umass.edu/kurose_ross/ppt.php
目录
1.1 Internet and Protocol 互联网和协议
Internet----nuts and bolts view 互联网——底层视角
Internet----Services view 互联网——服务视角
Protocol--协议
1.2 Network Edge 网络边缘
Access networks 网络接入
1. cable-based access 有线网络
2. digital subscriber line (DSL) 数字用户线路
3. home networks 家用网络
4. enterprise networks 企业网络
5. data center networks 数据中心网络
Host 主机
physical media 物理媒介
1. guided media
2. unguided media
1.3 Network Core 互联网核心(非最终,部分概念没太懂)
1. packet switching
Forwarding and routing
2. circuit switching
二者比较(练习题)
Internet Service Providers 网络服务提供
1.1 Internet and Protocol 互联网和协议
Internet----nuts and bolts view 互联网——底层视角
1. devices 使用互联网的设备
2. Packet switches 包/分组交换 将信息进行打包汇总用于交换(不确定)
3. Communication links 互联通道 例如基站、WIFI等用于提供传递信息的渠道
4. Networks 局部网络 各个局部网络进行互联后形成互联网
互联网的关系如图:
汽车,电脑等即设备,圆柱形包代表packet,通过WIFI,基站等实现link,各个network链接后形成internet
Q1
Which of the following descriptions below correspond to a "nuts-and-bolts" view of the Internet?
A. A "network of networks".
B. A platform for building network applications.
C. A place I go for information, entertainment, and to communicate with people.
D. A collection of billions of computing devices, and packet switches interconnected by links.
E. A collection of hardware and software components executing protocols that define the format and the order of messages exchanged between two or more communicating entities, as well as the actions taken on the transmission and/or receipt of a message or other event.
答案:A,D,E
此外,互联网还具有协议(Protocol)和标准(standard)的特性,这里先解释标准
Standard 互联网标准
互联网需要有标准才能被广泛认可并使用,例如一个新的互联网标准被采用之前,应当先向相关机构发送意见征求稿(RFC)征求认可才能投入使用
Internet----Services view 互联网——服务视角
服务视角包含两点
1. applications 将应用提供给用户,我们认为的互联网能够看视频,玩游戏,发邮件...就是这种视角
2. interfaces 服务视角同样包括提供一个程序的界面给用户
Q2
Which of the following descriptions below correspond to a "services" view of the Internet?
A. A collection of billions of computing devices, and packet switches interconnected by links.
B. A collection of hardware and software components executing protocols that define the format and the order of messages exchanged between two or more communicating entities, as well as the actions taken on the transmission and/or receipt of a message or other event.
C. A place I go for information, entertainment, and to communicate with people.
D. A platform for building network applications.
E. A "network of networks".
答案:C,D
Protocol--协议
1. 引入--human protocols
日常生活里向他人询问并得到反馈其实就蕴含着一种协议,问别人:“现在几点?”别人会回答时间,上课的时候学生举手老师就知道学生要问问题,这就是一种协议。
2. Internet protocols
Protocols define the format, order of messages sent and received among network entities, and actions taken on message transmission, receipt
和人类交流类似,其实网络协议就是网络设备进行交流的一种规则
Q3
Which of the following human scenarios involve a protocol?
A. A person reading a book.
B. A person sleeping.
C. A student raising her/his hand to ask a really insightful question, followed by the teaching acknowledging the student, listening carefully to the question, and responding with a clear, insightful answer. And then thanking the student for the question, since teachers love to get questions.
D. Two people introducing themselves to each other.
E. One person asking, and getting, the time to/from another person.
答案:C,D,E
1.2 Network Edge 网络边缘
网络边缘释义:
和上一章了解的内容类似,网络边缘指的其实就是给用户提供服务的设备,有时候也被叫做主机(host)。在数据流中心的服务设备也是网络边缘的一种
本章主要涉及两点内容:网络接入类型和物理网络连线媒介
Access networks 网络接入
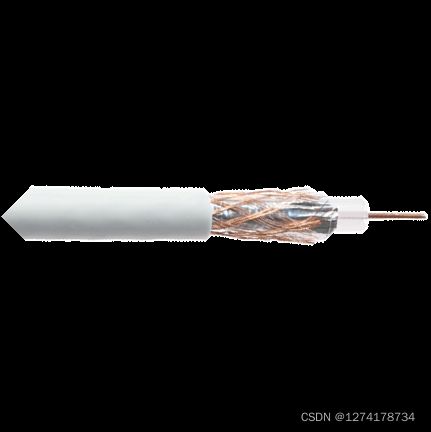
1. cable-based access 有线网络
所有用户通过一条总线接入互联网,总线本身通过FDM技术处理每个用户的需求
frequency division multiplexing (FDM): different channels transmitted in different frequency bands
有线网络采用HFC(hybrid fiber coax),一种结合光纤和同轴电缆的宽带网络实现,这种技术具有不对称性,下行段能够达到40 Mbps – 1.2 Gbps,而上行段仅能达到30-100 Mbps
链接示意图
2. digital subscriber line (DSL) 数字用户线路
通过铜线或者本地电话网提供数字连接的一种技术,数据和声音被分别传输,下行速率可达24-52 Mbps ,上行速率可达3.5-16 Mbps
示意图如下,最重要的特点是设备和电话链接
3. home networks 家用网络
顾名思义,就是我们日常使用的网络,分为WIFI和移动数据两种
Wireless local area networks (WLAN)
一般建设在建筑中或者在建筑周围,传输速率以802.11b/g/n (WiFi)为例,可达11, 54, 450 Mbps。
Wide-area cellular access networks 无线广域网
就是我们常用的移动网络,3G,4G等都是。传输举例在10’s km,速度在10’s Mbps。
4. enterprise networks 企业网络
企业网络通常比较复杂,是有线和无线、交换器和路由器同时存在的混合网络,常见于公司和大学。
主要有两种网络类型:以太网和WIFI。前者有线连接,速度可达100Mbps, 1Gbps, 10Gbps,后者无线连接,速度可达11, 54, 450 Mbps
5. data center networks 数据中心网络
带宽极高,将数百到数千个服务器和网络进行连接(10s to 100s Gbps)
Host 主机
互联网环境中应用主机传递数据包。主机提取应用消息,将其分解成小块(称为包,packet)将包的长度记作L(bits).将主机传递消息的速率记作R,则延迟计算公式如下:
physical media 物理媒介
名词释义:
bit -- 传输数据
physical link -- 数据传输的物理通道
guided media -- 在物理光缆、数据线中传输的信息
unguided media -- 自由传递的数据,例如广播
1. guided media
1. Twisted pair (TP) 雙絞線
每条细线中都含有两条相互缠绕的铜线
2. 同轴电缆 Coaxial cable
双向有线,用于局域网搭建
3. 光纤 Fiber optic cable
几乎没有错误率,速度快,造假贵 (10’s-100’s Gbps)
2. unguided media
效率高 安全性差 只能单向传播 没有铺设成本(不需要导线)
主要有WIFI,广播,卫星通讯等
1.3 Network Core 互联网核心(非最终,部分概念没太懂)
1. packet switching
前文中已经略有提及,主机将消息封装成包进行传输,这里将具体的传输过程进行解释
Forwarding and routing
Forwarding is the local action of moving arriving packets from router’s input link to appropriate router output link
routing is the global action of determining the source-destination paths taken by packets
如上图所示,当数据流进入包时,包通过数据头部相关信息判断其目的地,这就是forwarding的过程。routing则是确定其目的地路线的过程
存储转发 store-and-forward
规则:数据流必须全部存储到包里面以后再转发到接收者设备中
queueing 延迟
就像前面所学的,数据传输是具有延迟的。因此,在多个数据等待传输时就会发生排队现象
loss 丢包
如果排队的包满了,多的包就不会传输,成为丢包
2. circuit switching
这是另一种数据的传递方法,如下图所示:
在需要传输数据时,会把全部的通道打开并分配给要沟通的设备
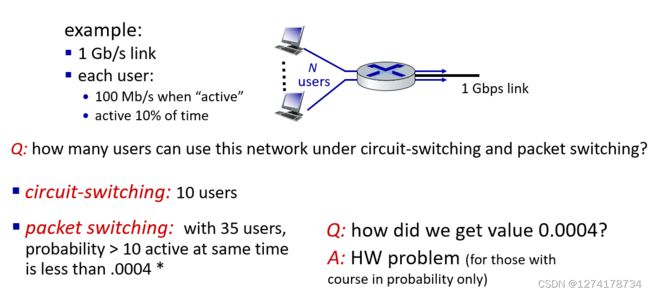
二者比较(练习题)
如题所示,并不是所有用户都会一直用网,所以packet switching 传输功能更好(咋算的)
然而,packet存在丢包,延迟等现象,传输质量不如circuit好
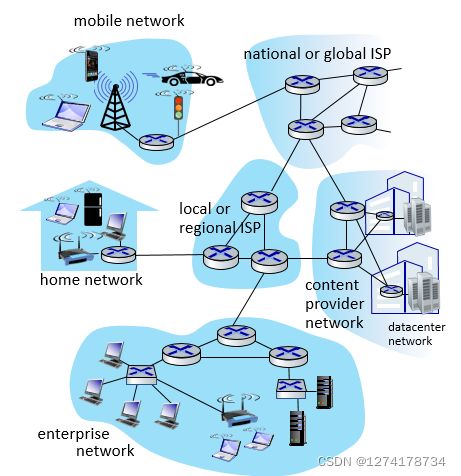
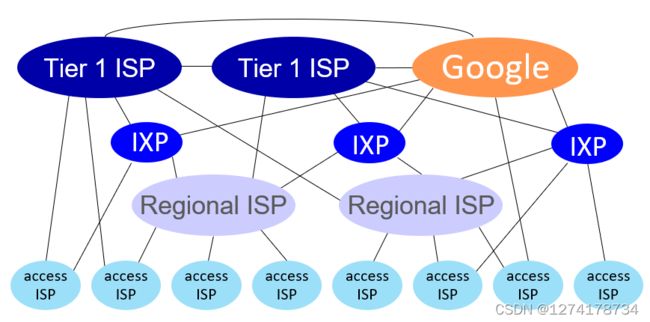
Internet Service Providers 网络服务提供
网络就是通过不同的ISP连接在一起的,目前的网络连接形式:
是一种层层相连的过程,地区互联网通过regional ISP链接,在连接到更大的ISP里面,最终各个ISP之间再通过节点链接
但是有服务商有极大的用户量时