GO和KEGG富集分析详细步骤
GO和KEGG富集分析
文章目录
- GO和KEGG富集分析
-
- @[toc]
- 1. 将差异表达结果的基因名称转化为id
- 2. GO富集分析
- 3. GO圈图绘制
- 4. KEGG富集分析
- 5. KEGG圈图绘制
文章目录
- GO和KEGG富集分析
-
- @[toc]
- 1. 将差异表达结果的基因名称转化为id
- 2. GO富集分析
- 3. GO圈图绘制
- 4. KEGG富集分析
- 5. KEGG圈图绘制
1. 将差异表达结果的基因名称转化为id
因为GO和KEGG分析需要用到id,所以这一步需要将基因名字转换为id。具体步骤如下:
-
新建空白文件夹,将差异分析得到的diff.xls复制粘贴到文件夹中
-
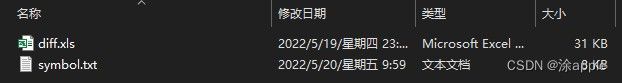
因为在这里只需要diff.xls中的基因名称和logFC两列,所以只复制这两列粘贴到新建的文本文件symbol.txt,如下图所示:
-
新建R语言脚本文件symbol2id.R,代码如下:
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) install.packages("BiocManager") BiocManager::install("org.Hs.eg.db") setwd("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\cptac\\4_name2id") #设置工作目录 library("org.Hs.eg.db") #引用包 rt=read.table("symbol.txt",sep="\t",check.names=F,header=T) #读取文件 genes=as.vector(rt[,1]) entrezIDs <- mget(genes, org.Hs.egSYMBOL2EG, ifnotfound=NA) #找出基因对应的id entrezIDs <- as.character(entrezIDs) out=cbind(rt,entrezID=entrezIDs) write.table(out,file="id.txt",sep="\t",quote=F,row.names=F) -
设置好工作目录之后,打开R软件,运行上述代码即可。运行结束在文件夹中会有id.txt,打开后如下图所示:
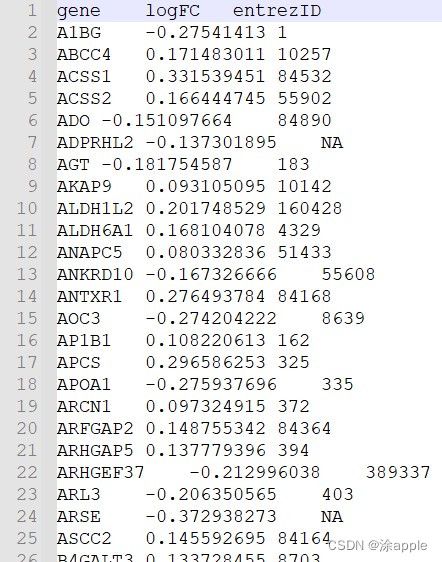
可以看到后面已经有了id这一列了,至此本步骤结束。
2. GO富集分析
GO(gene ontology)是基因本体联合会(Gene Onotology Consortium)所建立的数据库,旨在建立一个适用于各种物种的、对基因和蛋白质功能进行限定和描述的、并能随着研究不断深入而更新的语言词汇标准。GO是多种生物本体语言中的一种,提供了三层结构的系统定义方式,用于描述基因产物的功能。在转录组项目中,GO功能分析一方面给出差异表达转录本的GO功能分类注释;另一方面给出差异表达转录本的GO功能显著性富集分析。
下面介绍GO分析的步骤:
-
将含有基因id的文本文件id.txt复制粘贴到新的文件夹中
-
新建R语言脚本,命名为GO.R,其代码如下:
install.packages("colorspace") install.packages("stringi") install.packages("ggplot2") if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) install.packages("BiocManager") BiocManager::install("DOSE") if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) install.packages("BiocManager") BiocManager::install("clusterProfiler") if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) install.packages("BiocManager") BiocManager::install("enrichplot") library("clusterProfiler") library("org.Hs.eg.db") library("enrichplot") library("ggplot2") setwd("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\cptac\\5_GO分析") #设置工作目录 rt=read.table("id.txt",sep="\t",header=T,check.names=F) #读取id.txt文件 rt=rt[is.na(rt[,"entrezID"])==F,] #去除基因id为NA的基因 gene=rt$entrezID #GO富集分析 kk <- enrichGO(gene = gene, OrgDb = org.Hs.eg.db, pvalueCutoff =0.05, qvalueCutoff = 0.05, ont="all", readable =T) write.table(kk,file="GO.txt",sep="\t",quote=F,row.names = F) #保存富集结果 #柱状图 pdf(file="barplot.pdf",width = 10,height = 8) barplot(kk, drop = TRUE, showCategory =10,split="ONTOLOGY") + facet_grid(ONTOLOGY~., scale='free') dev.off() #气泡图 pdf(file="bubble.pdf",width = 10,height = 8) dotplot(kk,showCategory = 10,split="ONTOLOGY",orderBy = "GeneRatio") + facet_grid(ONTOLOGY~., scale='free') dev.off()这里GO分析用到的包为"clusterProfiler",画图用到的包为"enrichplot"。在代码中会设置p值和q值,设置的都是0.05,如果该条件下分析得到的可用基因较少,可将q设置为0,只看p值,但这样准确性也会降低一些。
-
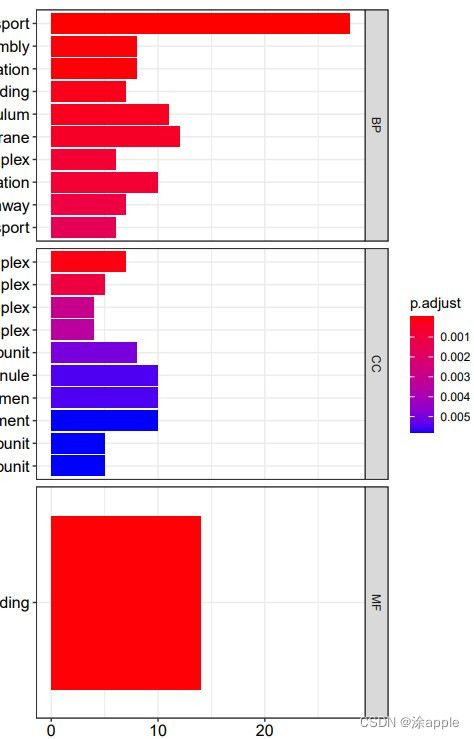
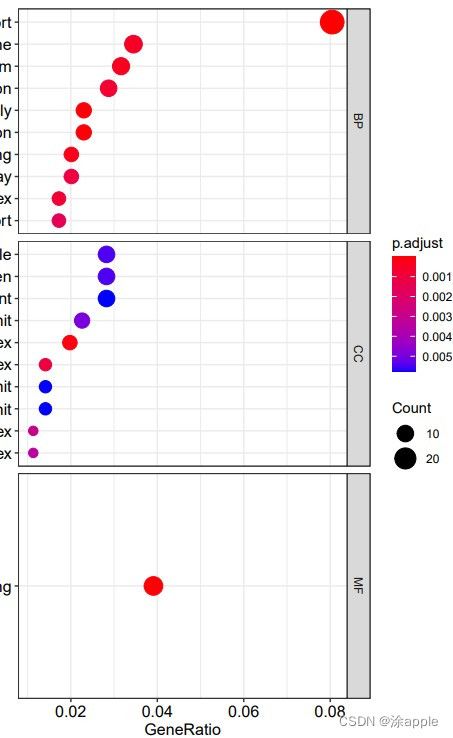
讲一下GO分析得到的文本文件,也就是上面三幅图中的最后一幅图,第一列是GO分析的分类,分别是BP,CC,MF;第二列是GO的id;第三列为对应的描述;第四列为基因背景的比例;第五列为p值,表示富集的显著性;第六列为p值得校正值;第七列为q值;第八列为基因id,也就是基因名称;最后一列就是富集在每个GO上的数目。对于柱状图和气泡图,会分为BP,CC,MF,每个类别颜色越红表示富集程度越高。
3. GO圈图绘制
话不多说,直接上步骤。
-
新建R语言脚本文件GOplot.R,脚本文件和GO分析得到的结果放在同一目录下,其代码如下:
install.packages("digest") install.packages("GOplot") library(GOplot) setwd("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\cptac\\6_GO圈图绘制") #设置工作目录 ego=read.table("GO.txt", header = T,sep="\t",check.names=F) #读取kegg富集结果文件 go=data.frame(Category = "All",ID = ego$ID,Term = ego$Description, Genes = gsub("/", ", ", ego$geneID), adj_pval = ego$p.adjust) #读取基因的logFC文件 id.fc <- read.table("id.txt", header = T,sep="\t",check.names=F) genelist <- data.frame(ID = id.fc$gene, logFC = id.fc$logFC) row.names(genelist)=genelist[,1] circ <- circle_dat(go, genelist) termNum = 5 #限定term数目 geneNum = nrow(genelist) #限定蛋白数目 chord <- chord_dat(circ, genelist[1:geneNum,], go$Term[1:termNum]) pdf(file="circ.pdf",width = 11,height = 10.5) GOChord(chord, space = 0.001, #基因之间的间距 gene.order = 'logFC', #按照logFC值对基因排序 gene.space = 0.25, #基因名跟圆圈的相对距离 gene.size = 4, #基因名字体大小 border.size = 0.1, #线条粗细 process.label = 7.5) #term字体大小 dev.off() termCol <- c("#223D6C","#D20A13","#FFD121","#088247","#58CDD9","#7A142C","#5D90BA","#431A3D","#91612D","#6E568C","#E0367A","#D8D155","#64495D","#7CC767") pdf(file="cluster.pdf",width = 11.5,height = 9) GOCluster(circ.gsym, go$Term[1:termNum], lfc.space = 0.2, #倍数跟树间的空隙大小 lfc.width = 1, #变化倍数的圆圈宽度 term.col = termCol[1:termNum], #自定义term的颜色 term.space = 0.2, #倍数跟term间的空隙大小 term.width = 1) #富集term的圆圈宽度 dev.off() -
打开R软件运行上述代码即可。最终即可得到两个圈图,如下图所示:
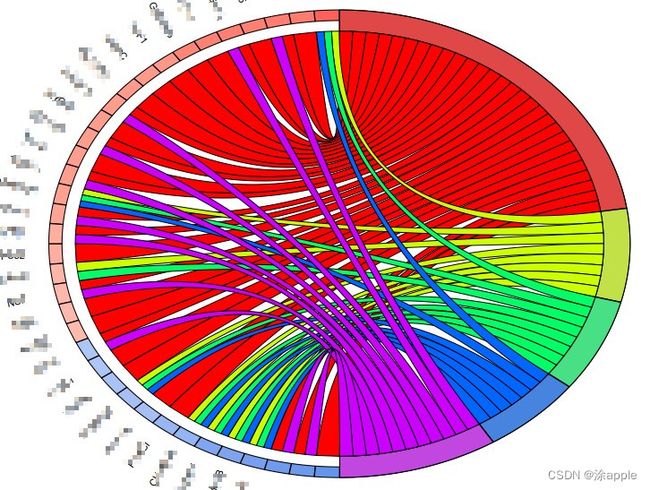
左半圆圈为基因名字,从下到上按照logFC进行排序得,圆圈右半部分为GO的名称,基因与GO之间得连线表示这个基因存在于该GO上。
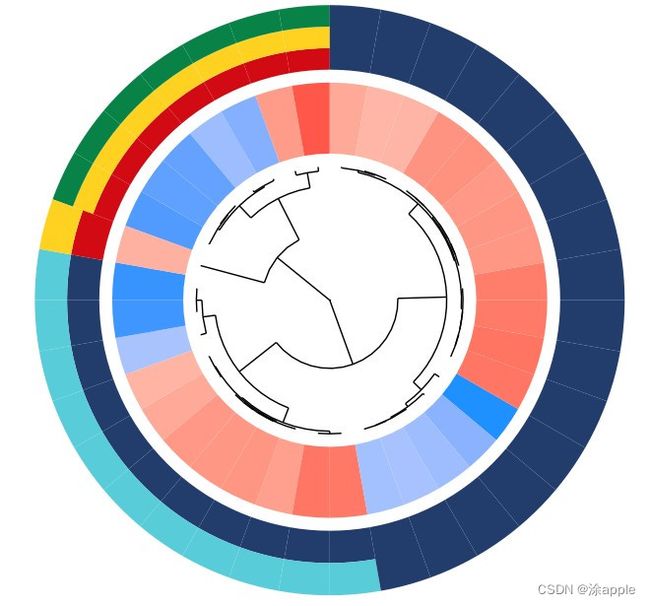
此图为聚类图,内部圆圈为基因或蛋白,颜色表示logFC的大小,内部的一个扇形表示一个基因,如果内部的一个扇形对应着外部的一个颜色的扇形,那么表示该基因只存在于这一个颜色对应的GO里面;如果内部一个扇形对应着外部三个扇形,那么表示内部的这个基因存在于三个GO里面。
4. KEGG富集分析
-
将差异分析得到的含有id的id.txt文件作为输入文件,新建文件夹,将id.txt拷贝到此文件夹下
-
新建R语言脚本文件,更改脚本文件的环境目录,代码如下:
install.packages("colorspace") install.packages("stringi") install.packages("ggplot2") if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) install.packages("BiocManager") BiocManager::install("DOSE") if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) install.packages("BiocManager") BiocManager::install("clusterProfiler") if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) install.packages("BiocManager") BiocManager::install("enrichplot") library("clusterProfiler") library("org.Hs.eg.db") library("enrichplot") library("ggplot2") setwd("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\cptac\\7_KEGG分析") #设置工作目录 rt=read.table("id.txt",sep="\t",header=T,check.names=F) #读取id.txt文件 rt=rt[is.na(rt[,"entrezID"])==F,] #去除基因id为NA的基因 gene=rt$entrezID #kegg富集分析 kk <- enrichKEGG(gene = gene, organism = "hsa", pvalueCutoff =0.05, qvalueCutoff =2) #富集分析 write.table(kk,file="KEGGId.txt",sep="\t",quote=F,row.names = F) #保存富集结果 #柱状图 pdf(file="barplot.pdf",width = 10,height = 7) barplot(kk, drop = TRUE, showCategory = 30) dev.off() #气泡图 pdf(file="bubble.pdf",width = 10,height = 7) dotplot(kk, showCategory = 30,orderBy = "GeneRatio") dev.off() -
KEGG因为数据库更新比较慢,而且分析时需要联网,因此富集到结果就会比较少。
-
运行完之后还会得到KEGGId.txt,里面的需要将里面的id转化为基因名字。因此新建perl脚本文件,代码太长,这里就不展示了。在该文件夹目录下打开powershell窗口,输入命令perl id2symbol.pl,运行完毕之后文件夹目录下就会产生新的含有基因名字的kegg文件,文件名为kegg.txt
-
至此,KEGG分析完毕
5. KEGG圈图绘制
这里的圈图绘制和上面的GO圈图绘制步骤一样的。话不多说,直接上代码:
install.packages("digest")
install.packages("GOplot")
library(GOplot)
setwd("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\cptac\\8_KEGG圈图绘制") #设置工作目录
ego=read.table("kegg.txt", header = T,sep="\t",check.names=F) #读取kegg富集结果文件
go=data.frame(Category = "All",ID = ego$ID,Term = ego$Description, Genes = gsub("/", ", ", ego$geneID), adj_pval = ego$p.adjust)
#读取基因的logFC文件
id.fc <- read.table("id.txt", header = T,sep="\t",check.names=F)
genelist <- data.frame(ID = id.fc$gene, logFC = id.fc$logFC)
row.names(genelist)=genelist[,1]
circ <- circle_dat(go, genelist)
termNum = 2 #限定term数目
geneNum = nrow(genelist) #限定基因数目
chord <- chord_dat(circ, genelist[1:geneNum,], go$Term[1:termNum])
pdf(file="circ.pdf",width = 10,height = 9.6)
GOChord(chord,
space = 0.001, #基因之间的间距
gene.order = 'logFC', #按照logFC值对基因排序
gene.space = 0.25, #基因名跟圆圈的相对距离
gene.size = 4, #基因名字体大小
border.size = 0.1, #线条粗细
process.label = 7.5) #term字体大小
dev.off()
termCol <- c("#223D6C","#D20A13","#FFD121","#088247","#58CDD9","#7A142C","#5D90BA","#431A3D","#91612D","#6E568C","#E0367A","#D8D155","#64495D","#7CC767")
pdf(file="cluster.pdf",width = 10,height = 9.6)
GOCluster(circ.gsym,
go$Term[1:termNum],
lfc.space = 0.2, #倍数跟树间的空隙大小
lfc.width = 1, #变化倍数的圆圈宽度
term.col = termCol[1:termNum], #自定义term的颜色
term.space = 0.2, #倍数跟term间的空隙大小
term.width = 1) #富集term的圆圈宽度
dev.off()
这里将代码的工作环境更改一下,然后将kegg分析所得到的kegg.txt和之前的id.txt复制到同一目录下,然后打开R软件运行代码即可。得到的圈图如下:
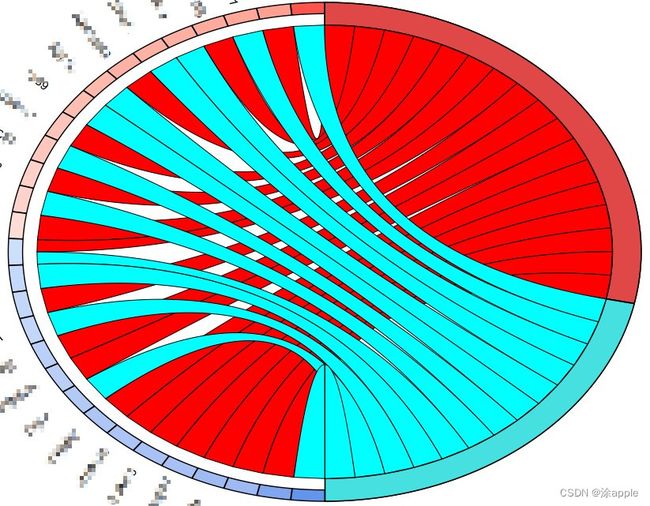
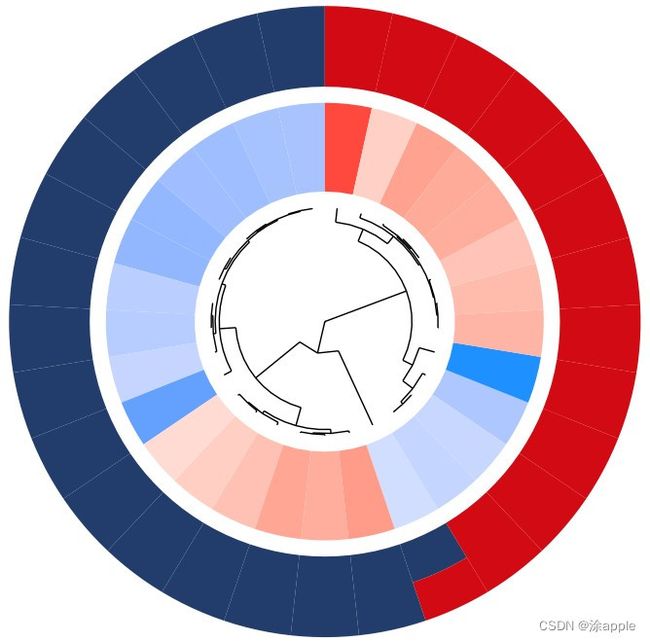
至此,KEGG圈图绘制结束。