2021SC@SDUSC山东大学软件学院软件工程应用与实践--YOLOV5代码分析(十六)yolo.py-1
2021SC@SDUSC
目录
前言
parse_model函数
Detect类
init方法
forward
make_grid方法
总结
前言
由于分配任务改动,我增加了一篇yolo.py文件的分析。该文件是模型的定义部分,是整个项目的核心部分。
parse_model函数
def parse_model(d, ch): # model_dict, input_channels(3)
LOGGER.info('\n%3s%18s%3s%10s %-40s%-30s' % ('', 'from', 'n', 'params', 'module', 'arguments'))
anchors, nc, gd, gw = d['anchors'], d['nc'], d['depth_multiple'], d['width_multiple']
na = (len(anchors[0]) // 2) if isinstance(anchors, list) else anchors # number of anchors
no = na * (nc + 5) # number of outputs = anchors * (classes + 5)
layers, save, c2 = [], [], ch[-1] # layers, savelist, ch out
for i, (f, n, m, args) in enumerate(d['backbone'] + d['head']): # from, number, module, args
m = eval(m) if isinstance(m, str) else m # eval strings
for j, a in enumerate(args):
try:
args[j] = eval(a) if isinstance(a, str) else a # eval strings
except:
pass
n = n_ = max(round(n * gd), 1) if n > 1 else n # depth gain
if m in [Conv, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, DWConv, MixConv2d, Focus, CrossConv,
BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3SPP, C3Ghost]:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no: # if not output
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
if m in [BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost]:
args.insert(2, n) # number of repeats
n = 1
elif m is nn.BatchNorm2d:
args = [ch[f]]
elif m is Concat:
c2 = sum([ch[x] for x in f])
elif m is Detect:
args.append([ch[x] for x in f])
if isinstance(args[1], int): # number of anchors
args[1] = [list(range(args[1] * 2))] * len(f)
elif m is Contract:
c2 = ch[f] * args[0] ** 2
elif m is Expand:
c2 = ch[f] // args[0] ** 2
else:
c2 = ch[f]
m_ = nn.Sequential(*[m(*args) for _ in range(n)]) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
np = sum([x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()]) # number params
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type, m_.np = i, f, t, np # attach index, 'from' index, type, number params
LOGGER.info('%3s%18s%3s%10.0f %-40s%-30s' % (i, f, n_, np, t, args)) # print
save.extend(x % i for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
layers.append(m_)
if i == 0:
ch = []
ch.append(c2)
return nn.Sequential(*layers), sorted(save)该函数由Model类调用,用于解析模型
参数
d:model_dict,字典形式
ch:记录模型的输出channel,初始为输入channel,即3
d是在Model类中读取了yaml文件后传进来的,字典格式,保存了模型的结构
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 backbone
backbone:
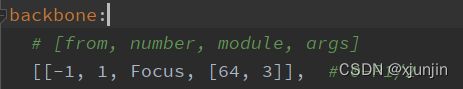
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Focus, [64, 3]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 9, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 1, SPP, [1024, [5, 9, 13]]],
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]上图是yolov5s.yaml文件的内容,yolov5共有四种模型结构,分别是:yolov5s,yolov5m,yolov5l,yolov5x。这几种网络结构只有深度和宽度上的区别,其它的算法内容都是一样的,在源代码里也是默认以yolov5s结构来训练的。
可以看到d定义了nc、anchors、backbone和head等结构,一些如C3,SPP等结构是yolov5自己定义的模块,在common.py文件中有具体定义,这里就不详细介绍这部分内容,具体内容参考组内其他组员的博客。
anchors, nc, gd, gw = d['anchors'], d['nc'], d['depth_multiple'], d['width_multiple']从yaml文件里就可以看出各个值都是多少,anchors为定义好的3个anchor的列表,nc为80,gd为depth_multiple,值为0.33,gw为width_multiple,值为0.5.
na = (len(anchors[0]) // 2) if isinstance(anchors, list) else anchors # number of anchorsna为anchors的数量,anchors[0]为长度为6的列表,即na的值为3.
no = na * (nc + 5) # number of outputs = anchors * (classes + 5)输出的维度,值为anchos*(nc+5),即每一个anchor都要预测一个(nc+5)维的向量,其中‘5'包括了预测框中心点的坐标(x,y)以及宽和高(w,h),还有预测出来的置信度p。
layers, save, c2 = [], [], ch[-1] # layers, savelist, ch out初始化,layers用来保存每一层的网络结构,save记录下所有层结构中from中不是-1的层结构序号,c2保存当前层的输出channel
for i, (f, n, m, args) in enumerate(d['backbone'] + d['head']): # from, number, module, args遍历backbone和head
上图为yaml文件的部分截图,可以看到每一个结构都包含了from、number、module、args,其中from是当前层的输入来自哪些层,number是当前层的次数,module是当前层的网络名称,args为参数。
m = eval(m) if isinstance(m, str) else m # eval strings
for j, a in enumerate(args):
try:
args[j] = eval(a) if isinstance(a, str) else a # eval strings
except:
pass将字符串转为相应的模块或类型,方便后面的操作。
n = n_ = max(round(n * gd), 1) if n > 1 else n # depth gain将n限制在1以内,用以控制深度
if m in [Conv, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, DWConv, MixConv2d, Focus, CrossConv,
BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3SPP, C3Ghost]:如果m是这些模块的话执行
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]c1是当前层的输入维度,c2是当前层的输出维度。
if c2 != no: # if not output
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]更新args,加入当前层的输入维度。
if m in [BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost]:
args.insert(2, n) # number of repeats
n = 1如果m是这些模块,在args的第2个位置插入n,并将n置为1。
elif m is nn.BatchNorm2d:
args = [ch[f]]
elif m is Concat:
c2 = sum([ch[x] for x in f])
elif m is Detect:
args.append([ch[x] for x in f])
if isinstance(args[1], int): # number of anchors
args[1] = [list(range(args[1] * 2))] * len(f)
elif m is Contract:
c2 = ch[f] * args[0] ** 2
elif m is Expand:
c2 = ch[f] // args[0] ** 2
else:
c2 = ch[f]这段代码就是在处理当m是BN层、Concat层、Detect层或Contract层、Expand层时,更改参数,即设置这些模块的输入参数或是获取到当前层的输出维度。
m_ = nn.Sequential(*[m(*args) for _ in range(n)]) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module创建n个当前module
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
np = sum([x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()]) # number params
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type, m_.np = i, f, t, np # attach index, 'from' index, type, number params
LOGGER.info('%3s%18s%3s%10.0f %-40s%-30s' % (i, f, n_, np, t, args)) # print打印当前层的一些信息
save.extend(x % i for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
layers.append(m_)
if i == 0:
ch = []
ch.append(c2)将当前层的模块和输出维度以及结构序号。
总的来说这个函数就是实现从model_dict读取信息,根据model_dict的参数、网络结构等信息创建出一个网络,并返回nn.Sequential供Model使用。
Detect类
class Detect(nn.Module):
stride = None # strides computed during build
onnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameter
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor
self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid
a = torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)
self.register_buffer('anchors', a) # shape(nl,na,2)
self.register_buffer('anchor_grid', a.clone().view(self.nl, 1, -1, 1, 1, 2)) # shape(nl,1,na,1,1,2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment)
def forward(self, x):
z = [] # inference output
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
if not self.training: # inference
if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4] or self.onnx_dynamic:
self.grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny).to(x[i].device)
y = x[i].sigmoid()
if self.inplace:
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
else: # for YOLOv5 on AWS Inferentia https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2953
xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i].view(1, self.na, 1, 1, 2) # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1)
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))
return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
@staticmethod
def _make_grid(nx=20, ny=20):
yv, xv = torch.meshgrid([torch.arange(ny), torch.arange(nx)])
return torch.stack((xv, yv), 2).view((1, 1, ny, nx, 2)).float()该模块用来构建Detect层,将输入的feature map通过卷积操作和相应的公式计算得到我们想要的形状的结果,为计算loss和NMS做准备。
init方法
参数:
nc:预测类别的数量
anchors:3个feature map上所有anchor的大小
ch:3个feature map的channel
属性:
nc:预测的类别数量
no:no=nc+5,是每一个anchor的输出,包括了预测框的位置、置信度和预测类别
nl:detect层的数量
na:anchor的数量
grid :网格
a:有3个feature map,每个feature map都有三个anchor,每个anchor都是(w,h)对
m:卷积网络,输入为ch,输出为no*na,即anchor的数量乘上每个anchor的输出维度。
init方法就是初始化了一些模型的属性
forward
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv得到经过卷积层后的输出,其维度是(bs,255,20,20)。
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()将x从(bs,255,20,20)改为(bs,3,20,20,85),3是有3个anchor,每个anchor的输出维度是85
if not self.training: # inference
if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4] or self.onnx_dynamic:
self.grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny).to(x[i].device)
y = x[i].sigmoid()
if self.inplace:
y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
else: # for YOLOv5 on AWS Inferentia https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2953
xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i].view(1, self.na, 1, 1, 2) # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1)
z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no))将x经过sigmoid激活函数后再加上网格的偏移量得到最终的结果。
make_grid方法
@staticmethod
def _make_grid(nx=20, ny=20):
yv, xv = torch.meshgrid([torch.arange(ny), torch.arange(nx)])
return torch.stack((xv, yv), 2).view((1, 1, ny, nx, 2)).float()这个方法就是返回构造的网格。
总结
本篇博客详细介绍了yolo.py中根据yaml文件构造网络和Detect层的构造,在下一篇将会继续介绍Model类,也就是模型最终的定义部分。