Springboot使用Swagger生成API接口文档,但是接口返回值都是Map类型,完美解决办法(前后端分离开发必备)
问题描述
Swagger2没有提供描述返回值的API,导致不能注解map类型的返回值,不能返回Json,也不能描述只返回一个实体类中的部分字段的情况。我们需要自己实现这个功能。
网上找到的思路
实际上我在网上发现有人实现了这个功能,实现的原理是使用第三方jar包生成一个类,这个类里包括返回值里应该有的字段,这些字段使用原生的swagger注解,再让swagger去解析这个类。
这样做的优点是确实把参数信息加入了swagger的缓存中;缺点是需要生成额外的类。
这个思路的链接在这里
https://blog.csdn.net/WOSHITANGWENLE/article/details/87881488
我自己的思路 我采用了另一种思路。我的实现思路是通过搜索’/v2/api-docs’找到了
springfox.documentation.swagger2.web.Swagger2Controller.getDocumentation()
方法,发现其实就是返回了一个Swagger对象(参数信息都存在Swagger对象的definitions属性里)。
swagger又是注入了spring容器中进行管理的,那么就很好说了,直接对这个方法进行切面编程即可,切点就是
springfox.documentation.swagger2.mappers.ServiceModelToSwagger2MapperImpl.mapDocumentation。
这样做的优点是不需要生成额外的类;缺点是没有能把参数信息实际上加入到swagger的缓存里,只是在访问’/v2/api-docs’时修改了返回值而已。
代码实现
下面就我的实现代码了,图省事的小伙伴可以直接贴在项目里。
1、ApiResponseBodyReader
package com.lsp.config.swagger;
import com.fasterxml.classmate.ResolvedType;
import com.google.common.base.Optional;
import com.lsp.entity.Value2;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.models.ModelImpl;
import io.swagger.models.properties.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ResponseMessageBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.schema.ModelRef;
import springfox.documentation.service.ResponseMessage;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spi.service.OperationBuilderPlugin;
import springfox.documentation.spi.service.contexts.OperationContext;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.UUID;
/**
* 注册一个OperationBuilderPlugin
* @author lsp
*/
@Component
public class ApiResponseBodyReader implements OperationBuilderPlugin {
/**
* 是否支持此类DocumentationType
* @param delimiter 当前文档类型
* @return 如果支持当前类型,则返回true
*/
@Override
public boolean supports(DocumentationType delimiter) {
return true;
}
/**
* 如果有需要,可对operationContext执行操作
* @param operationContext 方法上下文
*/
@Override
public void apply(OperationContext operationContext) {
//此方法上有没有ApiResponseObject注解
boolean apiResponseObjectHandle = false;
apiResponseObjectHandle = apiResponseObjectHandle(operationContext);
//若此方法上没有ApiResponseObject注解
if(!apiResponseObjectHandle){
apiResponseFields(operationContext);
}
}
/**
* 处理ApiResponseFields注解
* @param operationContext
*/
private void apiResponseFields(OperationContext operationContext){
Optional optional = operationContext.findAnnotation(ApiResponseFields.class);
if(optional.isPresent() && !isVoid(operationContext)){
ApiResponseFields responseFields = optional.get();
String model_name =responseFields.modelName();
if("".equals(model_name)){
model_name = getModelName(operationContext);
}
String uuid = model_name + "-" + UUID();
String[] fields = responseFields.fields();
Value2 value2 = new Value2<>(model_name, fields);
ModelCache.specified_cache.put(uuid,value2);
addResponseMessage(operationContext,uuid);
}
}
/**
* 处理ApiResponseObject注解
* @param operationContext
* @return 若此方法上有ApiResponseObject注解,则返回true,否则返回false
*/
private boolean apiResponseObjectHandle(OperationContext operationContext){
Optional optional = operationContext.findAnnotation(ApiResponseObject.class);
if(optional.isPresent()){
ApiResponseObject apiResponseObject = optional.get();
ModelImpl model = createModel(apiResponseObject);
String model_name = null;
if(isVoid(operationContext)){
model_name = "Map";
}else{
model_name = getModelName(operationContext);
}
String uuid = model_name + "-" + UUID();
model.setTitle(uuid);
ModelCache.extra_cache.put(uuid,model);
addResponseMessage(operationContext,uuid);
return true;
}
return false;
}
private boolean isVoid(OperationContext operationContext){
ResolvedType type = operationContext.getReturnType();
Class aClass = type.getErasedType();
return aClass == void.class;
}
/**
* 获取返回值信息的名字
* @param operationContext
* @return
*/
private String getModelName(OperationContext operationContext){
ResolvedType type = operationContext.getReturnType();
Class aClass = type.getErasedType();
ApiModel apiModel = aClass.getAnnotation(ApiModel.class);
String model_name = null;
if(apiModel != null){
model_name = apiModel.value();
}
if(model_name==null || "".equals(model_name)){
model_name = aClass.getSimpleName();
}
return model_name;
}
/**
* 为operationContext添加状态为200的返ResponseMessage
* @param operationContext
* @param typeName
*/
private void addResponseMessage(OperationContext operationContext,String typeName){
ResponseMessage responseMessage = new ResponseMessageBuilder()
.code(200).responseModel(new ModelRef(typeName))
.build();
HashSet responseMessages = new HashSet<>();
responseMessages.add(responseMessage);
operationContext.operationBuilder().responseMessages(responseMessages);
}
/**
* 生成UUID
* @return
*/
private String UUID(){
return UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
/**
* 根据apiResponseObject注解生成一个ModelImpl
* @param apiResponseObject
* @return
*/
private ModelImpl createModel(ApiResponseObject apiResponseObject){
ModelImpl result = new ModelImpl();
//apiResponseObject的类型指定是object
result.setType("object");
ApiResponseProperty[] properties = apiResponseObject.properties();
for(ApiResponseProperty apiResponseProperty : properties){
String name = apiResponseProperty.name();
String description = apiResponseProperty.description();
String type = apiResponseProperty.type();
Property property = null;
if("string".equalsIgnoreCase(type)){
property = new StringProperty();
}else if("int".equalsIgnoreCase(type)){
property = new IntegerProperty();
}else if("date".equalsIgnoreCase(type)){
property = new DateProperty();
}else if("uuid".equalsIgnoreCase(type)){
property = new UUIDProperty();
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("未支持的类型");
}
property.setDescription(description);
result.property(name,property);
}
return result;
}
} 2、ApiResponseFields
package com.lsp.config.swagger;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ApiResponseFields {
String modelName() default "";
String[] fields();
}3、ApiResponseObject
package com.lsp.config.swagger;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ApiResponseObject {
String name() default "";
String description() default "";
ApiResponseProperty[] properties();
}4、ApiResponseProperty
package com.lsp.config.swagger;
public @interface ApiResponseProperty {
String name();
String description() default "";
String type();
}5、ModelCache
package com.lsp.config.swagger;
import com.lsp.entity.Value2;
import io.swagger.models.Model;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ModelCache {
static Map extra_cache = new HashMap<>();
static Map> specified_cache = new HashMap<>();
} 6、SwaggerAop
package com.lsp.config.swagger;
import io.swagger.models.Model;
import io.swagger.models.ModelImpl;
import io.swagger.models.Swagger;
import io.swagger.models.properties.Property;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
@Aspect
@Component
public class SwaggerAop {
@Pointcut(value = "execution(public * springfox.documentation.swagger2.mappers.ServiceModelToSwagger2MapperImpl.mapDocumentation(..))")
public void point(){
}
@Around("point()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
Swagger swagger = (Swagger) proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
Map returnValue = swagger.getDefinitions() ;
returnValue.putAll(ModelCache.extra_cache);
ModelCache.specified_cache.entrySet().forEach(e->{
String key = e.getKey();
String model_name = e.getValue().v1;
String[] fields = e.getValue().v2;
Model model = returnValue.get(model_name);
if(model == null){
throw new RuntimeException("不存在的类型"+model_name);
}
Map properties = model.getProperties();
ModelImpl newModel = new ModelImpl();
newModel.setDescription(model.getDescription());
for(String field : fields){
Property property = properties.get(field);
if(property == null){
throw new RuntimeException("不存在的属性"+field);
}
newModel.property(field,property);
}
returnValue.put(key,newModel);
});
return swagger;
}
} 7、Value2
package com.lsp.entity;
/**
* 存放多个实例的便捷类
*/
public class Value2 {
public final T v1;
public final V v2;
public Value2(T v1, V v2) {
this.v1 = v1;
this.v2 = v2;
}
} 8、使用方法:
package com.lsp.controller;
import com.lsp.config.swagger2.ApiResponseFields;
import com.lsp.config.swagger2.ApiResponseObject;
import com.lsp.config.swagger2.ApiResponseProperty;
import com.lsp.model.IMessage;
import com.lsp.model.Person;
import com.lsp.service.IService;
import io.swagger.annotations.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import springfox.documentation.annotations.ApiIgnore;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@Api(description = "用户接口")
public class IController {
/**
* 查看用户详情
* @param id 用户id
* @return 用户信息
*/
@GetMapping("/select/{id}")
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('ROLE_ADMIN')")
@ApiOperation(value = "查看用户详情",notes = "使用说明")
@ApiResponseFields(fields = {"id","firstName","lastName","email","address"})
public Person select(@ApiParam(name="用户id") @PathVariable int id){
return null;
}
@PutMapping("/put/{id}")
@ApiOperation(value = "更新用户信息",notes = "使用说明")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id",value = "用户id",paramType = "path",dataType = "MAP_>"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "username",value="用户名",paramType = "query",dataType = "string"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "password",value="密码",paramType = "query",dataType = "string")
})
@ApiResponseObject(properties = {
@ApiResponseProperty(name = "username",description = "用户名",type = "string"),
@ApiResponseProperty(name = "email",description = "用户邮箱",type = "string"),
@ApiResponseProperty(name = "address",description = "用户住址",type = "string"),
})
public Map put(@ApiIgnore @PathVariable String id,
@ApiIgnore @RequestParam java.util.Map params){
System.out.println(params);
return null;
}
}
最终效果
启动项目,访问http://127.0.0.1/swagger-ui.html#/。
页面如图:
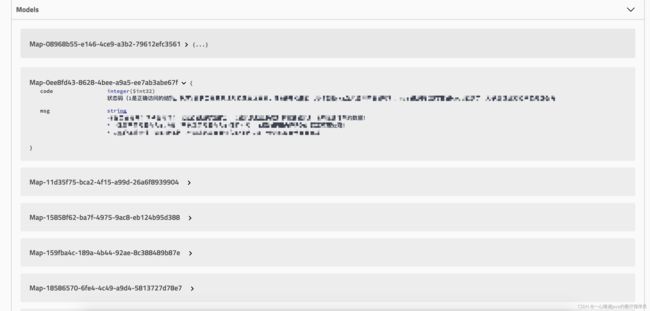
点开Models:
可以看到后缀上加了一串uuid的我使用aop注入的信息,没有uuid后缀的则是swagger自己解析的信息。
增强版swagger:
感觉Swagger功能不够强大?knife4j这款神器了解一下....
Knife4j 接口文档
knife4j是为Java MVC框架集成Swagger生成Api文档的增强解决方案,前身是swagger-bootstrap-ui,取名kni4j是希望她能像一把匕首一样小巧、轻量、并且功能强悍!
knife4j的前身是swagger-bootstrap-ui,为了契合微服务的架构发展,由于原来swagger-bootstrap-ui采用的是后端Java代码+前端Ui混合打包的方式,在微服务架构下显的很臃肿,因此项目正式更名为knife4j。
更名后主要专注的方面
-
前后端Java代码以及前端Ui模块进行分离,在微服务架构下使用更加灵活
-
提供专注于Swagger的增强解决方案,不同于只是改善增强前端Ui部分