nacos配置中心原理
前言
配置文件想必大家都很熟悉,无论什么架构 都离不开配置,虽然spring boot已经大大简化了配置,但如果服务很多 环境也好几个,管理配置起来还是很麻烦,并且每次改完配置都需要重启服务,nacos config出现就解决了这些问题,它把配置统一放到服务进行管理,客户端这边进行有需要的获取,可以实时对配置进行修改和发布
更多SpringCloud源码分析可以点击下方链接:
SpringCloud系列文章
使用教程
1、引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-configartifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
2、安装server端
下载nacos-server-2.0.2.zip 启动即可。
https://github.com/alibaba/nacos/releases/tag/2.0.2
3、在nacos控制台提前配置需要的配置文件
配置文件格式支持text、json、xml、yaml、html、properties,注意spring boot启动支持的配置文件格式只能为yaml或properties格式,其它格式的配置文件需要后续我们自己写代码去获取
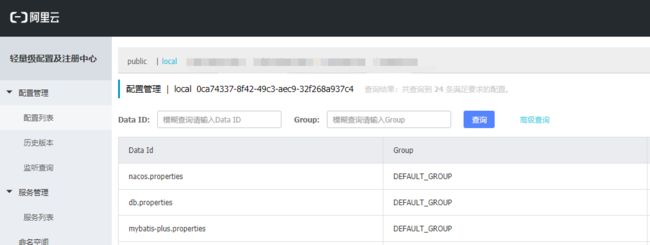
我们来看db.properties也是就数据库配置
data id就是对应配置文件id,group为分组,配置内容就是properties格式的
再来看bootstrap.properties如何引用这个配置文件
spring.application.name=nacos-config
server.port=20200
#命名空间
spring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace=${nacos_register_namingspace:0ca74337-8f42-49c3-aec9-32f268a937c4}
#组名
spring.cloud.nacos.config.group=${spring.application.name}
#文件格式
spring.cloud.nacos.config.file-extension=properties
#nacos server地址
spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr=localhost:8848
#加载配置文件
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[0].data-id=nacos.properties
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[1].data-id=db.properties
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[2].data-id=mybatis-plus.properties
Client端原理分析
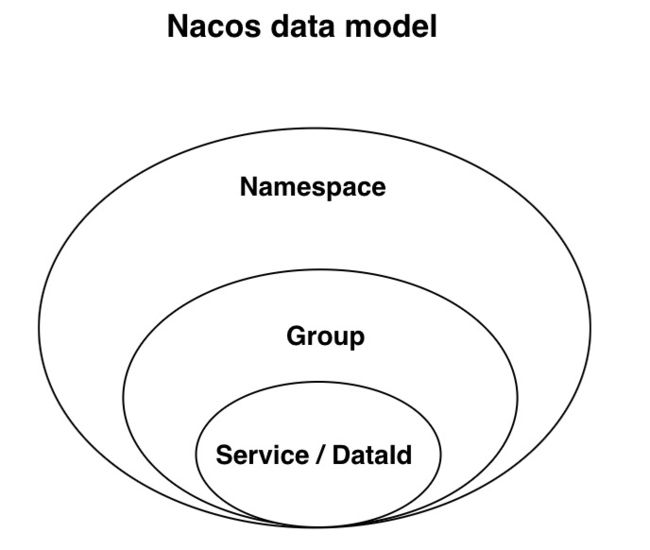
在这里解释下namespace和group的概念,namespace可以用来解决不同环境的问题,group是来管理配置分组的,它们的关系如下图
1、入口
spring boot启动容器如何加载nacos config配置文件
这个配置作用是spring在启动之间准备上下文时会启用这个配置 来导入nacos相关配置文件,为后续容器启动做准备
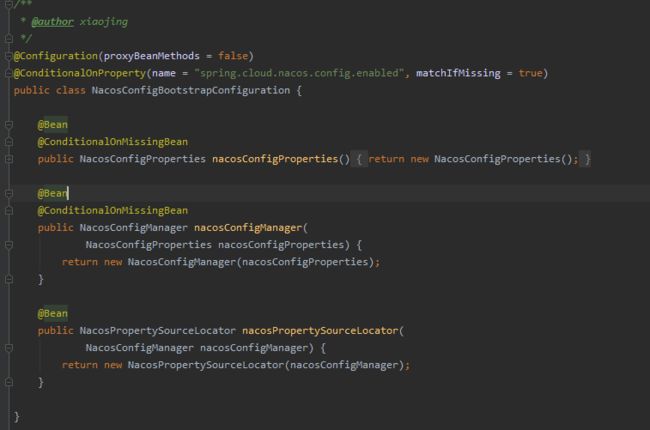
来看NacosConfigBootstrapConfiguration这个配置类
-
1、NacosConfigProperties:对应我们上面在bootstrap.properties中对应的配置信息
-
2、NacosConfigManager: 持有NacosConfigProperties和ConfigService,ConfigService用来查询 发布配置的相关接口
-
3、NacosPropertySourceLocator:它实现了PropertySourceLocator ,spring boot启动时调用PropertySourceLocator.locate(env)用来加载配置信息,下面来看相关源码
2、NacosPropertySourceLocator加载配置
@Order(0)
public class NacosPropertySourceLocator implements PropertySourceLocator {
//.............
@Override
public PropertySource<?> locate(Environment env) {
nacosConfigProperties.setEnvironment(env);
ConfigService configService = nacosConfigManager.getConfigService();
if (null == configService) {
log.warn("no instance of config service found, can't load config from nacos");
return null;
}
long timeout = nacosConfigProperties.getTimeout();
nacosPropertySourceBuilder = new NacosPropertySourceBuilder(configService,
timeout);
String name = nacosConfigProperties.getName();
String dataIdPrefix = nacosConfigProperties.getPrefix();
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(dataIdPrefix)) {
dataIdPrefix = name;
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(dataIdPrefix)) {
dataIdPrefix = env.getProperty("spring.application.name");
}
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(
NACOS_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
// 加载共享的配置文件 不同指定分组 默认DEFAULT_GROUP,对应配置spring.cloud.nacos.config.sharedDataids=shared_1.properties,shared_2.properties
loadSharedConfiguration(composite);
// 对应spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[0].data-id=nacos.properties的配置
loadExtConfiguration(composite);
// 加载当前应用配置
loadApplicationConfiguration(composite, dataIdPrefix, nacosConfigProperties, env);
return composite;
}
}
下面就从加载当前应用配置看看其原理实现
2、loadApplicationConfiguration()加载当前应用配置
public class NacosPropertySourceBuilder {
//......
/**
* @param dataId Nacos dataId
* @param group Nacos group
*/
NacosPropertySource build(String dataId, String group, String fileExtension,
boolean isRefreshable) {
Map<String, Object> p = loadNacosData(dataId, group, fileExtension);
NacosPropertySource nacosPropertySource = new NacosPropertySource(group, dataId,
p, new Date(), isRefreshable);
NacosPropertySourceRepository.collectNacosPropertySource(nacosPropertySource);
return nacosPropertySource;
}
private Map<String, Object> loadNacosData(String dataId, String group,
String fileExtension) {
String data = null;
try {
//1、 向nacos server拉取配置文件,通过http请求server端的/configs接口获取配置列表。
data = configService.getConfig(dataId, group, timeout);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(data)) {
log.warn(
"Ignore the empty nacos configuration and get it based on dataId[{}] & group[{}]",
dataId, group);
return EMPTY_MAP;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(String.format(
"Loading nacos data, dataId: '%s', group: '%s', data: %s", dataId,
group, data));
}
//2、将获取到的配置数据按格式进行解析保存到一个map缓存中
Map<String, Object> dataMap = NacosDataParserHandler.getInstance()
.parseNacosData(data, fileExtension);
return dataMap == null ? EMPTY_MAP : dataMap;
}
catch (NacosException e) {
log.error("get data from Nacos error,dataId:{}, ", dataId, e);
}
catch (Exception e) {
log.error("parse data from Nacos error,dataId:{},data:{},", dataId, data, e);
}
return EMPTY_MAP;
}
}
至此Nacos Client客户端启动从Nacos Server文件都载入到spring配置文件中来了的过程如上所述。那么Nacos是如何做到动态刷新配置的呢?我们继续往下进行分析一下
3、动态刷新
当nacos config更新后,根据配置中的refresh属性来判断是否刷新配置,配置如下
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[0].refresh=true
首先spring.factories 配置了EnableAutoConfiguration=NacosConfigAutoConfiguration,NacosConfigAutoConfiguration配置类会注入一个NacosContextRefresher,它首先监听了ApplicationReadyEvent,然后注册一个nacos listener用来监听nacos config配置修改后发布一个spring refreshEvent用来刷新配置和应用
public class NacosContextRefresher
implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationReadyEvent>, ApplicationContextAware {
//......
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationReadyEvent event) {
// 只注册一次
if (this.ready.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
this.registerNacosListenersForApplications();
}
}
/**
* register Nacos Listeners.
*/
private void registerNacosListenersForApplications() {
// 对应刚才所说的配置 需要配置文件是否需要刷新
if (isRefreshEnabled()) {
for (NacosPropertySource propertySource : NacosPropertySourceRepository
.getAll()) {
if (!propertySource.isRefreshable()) {
continue;
}
String dataId = propertySource.getDataId();
// 注册nacos监听器
registerNacosListener(propertySource.getGroup(), dataId);
}
}
}
private void registerNacosListener(final String groupKey, final String dataKey) {
String key = NacosPropertySourceRepository.getMapKey(dataKey, groupKey);
Listener listener = listenerMap.computeIfAbsent(key,
lst -> new AbstractSharedListener() {
@Override
public void innerReceive(String dataId, String group,
String configInfo) {
refreshCountIncrement();
// 添加刷新记录
nacosRefreshHistory.addRefreshRecord(dataId, group, configInfo);
// 发布一个spring refreshEvent事件 对应监听器为RefreshEventListener 该监听器会完成配置的更新应用
applicationContext.publishEvent(
new RefreshEvent(this, null, "Refresh Nacos config"));
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(String.format(
"Refresh Nacos config group=%s,dataId=%s,configInfo=%s",
group, dataId, configInfo));
}
}
});
try {
configService.addListener(dataKey, groupKey, listener);
}
catch (NacosException e) {
log.warn(String.format(
"register fail for nacos listener ,dataId=[%s],group=[%s]", dataKey,
groupKey), e);
}
}
如上所述nacos config动态刷新就是给所有需要实时更新的配置文件加上一个listener,如果配置有更新applicationContext.publishEvent(new RefreshEvent(this, null, “Refresh Nacos config”));进行更新。
那么nacos config如何知道有配置更新了呢,那么就是接下来讲的动态监听。
4、动态监听
一般来说客户端和服务端数据交互无非就两种方式
pull:客户端主动从服务器拉取数据
push: 由服务端主动向客户端推送数据
这两种模式优缺点各不一样,pull模式需要考虑的是什么时候向服务端拉取数据 可能会存在数据延迟问题,而push模式需要客户端和服务端维护一个长连接 如果客户端较多会给服务端造成压力 但它的实时性会更好
nacos采用的是pull模式,但它作了优化 可以看做是pull+push,客户端会轮询向服务端发出一个长连接请求,这个长连接最多30s就会超时,服务端收到客户端的请求会先判断当前是否有配置更新,有则立即返回
如果没有服务端会将这个请求拿住“hold”29.5s加入队列,最后0.5s再检测配置文件无论有没有更新都进行正常返回,但等待的29.5s期间有配置更新可以提前结束并返回,下面会在源码中讲解具体怎么处理的。
client处理
动态监听的发起是在ConfigService的实现类NacosConfigService的构造方法中,它是对外nacos config api接口,在之前加载配置文件和NacosContextRefresher构造方法中都会获取或创建
通过反射生成NacosConfigService
com.alibaba.nacos.client.config.NacosConfigService
public class ConfigFactory {
public static ConfigService createConfigService(Properties properties) throws NacosException {
try {
Class<?> driverImplClass = Class.forName("com.alibaba.nacos.client.config.NacosConfigService");
Constructor constructor = driverImplClass.getConstructor(Properties.class);
ConfigService vendorImpl = (ConfigService) constructor.newInstance(properties);
return vendorImpl;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new NacosException(NacosException.CLIENT_INVALID_PARAM, e);
}
}
那么看看NacosConfigService里面的逻辑:
/***************************************** NacosConfigService *****************************************/
public class NacosConfigService implements ConfigService {
//构造函数初始化service
public NacosConfigService(Properties properties) throws NacosException {
ValidatorUtils.checkInitParam(properties);
String encodeTmp = properties.getProperty(PropertyKeyConst.ENCODE);
if (StringUtils.isBlank(encodeTmp)) {
this.encode = Constants.ENCODE;
} else {
this.encode = encodeTmp.trim();
}
initNamespace(properties);
// 用来向nacos server发起请求的代理,这里用到了装饰模式
this.agent = new MetricsHttpAgent(new ServerHttpAgent(properties));
this.agent.start();
// 客户端的一个工作类,agent作为它的构造传参 可猜想到里面肯定会做一些远程调用
this.worker = new ClientWorker(this.agent, this.configFilterChainManager, properties);
}
/***************************************** ClientWorker *****************************************/
public ClientWorker(final HttpAgent agent, final ConfigFilterChainManager configFilterChainManager,
final Properties properties) {
this.agent = agent;
this.configFilterChainManager = configFilterChainManager;
// Initialize the timeout parameter
init(properties);
// 这个线程池只有一个核心线程 用来执行checkConfigInfo()方法
this.executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1, new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.setName("com.alibaba.nacos.client.Worker." + agent.getName());
t.setDaemon(true);
return t;
}
});
// 其它需要执行线程的地方都交给这个线程池来处理
this.executorService = Executors
.newScheduledThreadPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(), new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.setName("com.alibaba.nacos.client.Worker.longPolling." + agent.getName());
t.setDaemon(true);
return t;
}
});
// 执行一个调用checkConfigInfo()方法的周期性任务,每10ms执行一次,首次执行延迟1ms后执行
this.executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
checkConfigInfo();
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOGGER.error("[" + agent.getName() + "] [sub-check] rotate check error", e);
}
}
}, 1L, 10L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
NacosConfigService构造方法主要创建一个agent 它是用来向nacos server发出请求的,然后又创建了一个clientwoker,它的构造方法创建了两个线程池,第一个线程池只有一个核心线程,它会执行一个周期性任务只用来调用checkconfiginfo()方法,第二个线程是后续由需要执行线程的地方都交给它来执行,下面重点来看checkconfiginfo()方法
/***************************************** ClientWorker *****************************************/
/**
* Check config info.
*/
public void checkConfigInfo() {
// Dispatch taskes.分任务
int listenerSize = cacheMap.get().size();
// Round up the longingTaskCount.向上取整为批数
int longingTaskCount = (int) Math.ceil(listenerSize / ParamUtil.getPerTaskConfigSize());
if (longingTaskCount > currentLongingTaskCount) {
for (int i = (int) currentLongingTaskCount; i < longingTaskCount; i++) {
// The task list is no order.So it maybe has issues when changing.
executorService.execute(new LongPollingRunnable(i));
}
currentLongingTaskCount = longingTaskCount;
}
}
cacheMap:缓存着需要刷新的配置,它是在调用ConfigService 添加监听器方式时会放入,可以自定义监听配置刷新
/***************************************** 自定义监听配置刷新*****************************************/
// 添加一个config监听器,用来监听dataId为ErrorCode,group为DEFAULT_GROUP的config
configService.addListener("ErrorCode","DEFAULT_GROUP",new Listener() {
@Override
public Executor getExecutor() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void receiveConfigInfo(String s) { //当配置更新时会调用监听器该方法
Map<String, Map<String, String>> map = JSON.parseObject(s, Map.class);
// 根据自己的业务需要来处理
}
});
这里采用了一个策略:将cacheMap中的分组,分别创建一个LongPollingRunnable用来监听配置更新,这个LongPollingRunnable就是我们之前所说的长连接任务,来看这个长连接任务
class LongPollingRunnable implements Runnable {
private final int taskId;
public LongPollingRunnable(int taskId) {
this.taskId = taskId;
}
@Override
public void run() {
List<CacheData> cacheDatas = new ArrayList<CacheData>();
List<String> inInitializingCacheList = new ArrayList<String>();
try {
// check failover config
for (CacheData cacheData : cacheMap.get().values()) {
if (cacheData.getTaskId() == taskId) {
cacheDatas.add(cacheData);
try {
// 1、检查本地配置
checkLocalConfig(cacheData);
if (cacheData.isUseLocalConfigInfo()) {
cacheData.checkListenerMd5();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("get local config info error", e);
}
}
}
// 2、向nacos server接口/v1/cs/configs/listener发出一个长连接 30s超时,返回nacos server有更新过的dataIds
List<String> changedGroupKeys = checkUpdateDataIds(cacheDatas, inInitializingCacheList);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(changedGroupKeys)) {
LOGGER.info("get changedGroupKeys:" + changedGroupKeys);
}
for (String groupKey : changedGroupKeys) {
String[] key = GroupKey.parseKey(groupKey);
String dataId = key[0];
String group = key[1];
String tenant = null;
if (key.length == 3) {
tenant = key[2];
}
try {
// 3、向nacos server请求接口/v1/cs/configs获取config最新内容
String[] ct = getServerConfig(dataId, group, tenant, 3000L);
CacheData cache = cacheMap.get().get(GroupKey.getKeyTenant(dataId, group, tenant));
cache.setContent(ct[0]);
if (null != ct[1]) {
cache.setType(ct[1]);
}
LOGGER.info("[{}] [data-received] dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, md5={}, content={}, type={}",
agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant, cache.getMd5(),
ContentUtils.truncateContent(ct[0]), ct[1]);
} catch (NacosException ioe) {
String message = String
.format("[%s] [get-update] get changed config exception. dataId=%s, group=%s, tenant=%s",
agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant);
LOGGER.error(message, ioe);
}
}
// 4、对有变化的config调用对应监听器去处理
for (CacheData cacheData : cacheDatas) {
if (!cacheData.isInitializing() || inInitializingCacheList
.contains(GroupKey.getKeyTenant(cacheData.dataId, cacheData.group, cacheData.tenant))) {
cacheData.checkListenerMd5();
cacheData.setInitializing(false);
}
}
inInitializingCacheList.clear();
// 继续轮询
executorService.execute(this);
} catch (Throwable e) {
// If the rotation training task is abnormal, the next execution time of the task will be punished
LOGGER.error("longPolling error : ", e);
// 发生异常延迟执行
executorService.schedule(this, taskPenaltyTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
}
这个长轮询主要做了4个步骤
- 1、检查本地配置,如果存在本地配置,并且与缓存中的本地配置版本不一样,把本地配置内容更新到缓存,并触发事件,这块源码比较简单,读者跟到源码一读编制
- 2、向nacos server接口/v1/cs/configs/listener发出一个长连接,30s超时,nacos server会返回有变化的dataIds
- 3、根据变化的dataId,从服务端/v1/cs/configs拉取最新的配置内容然后更新到缓存中
- 4、对有变化的配置 触发事件监听器来处理
讲完了nacos client处理流程,再来看服务端这边怎么处理这个长连接的
server处理
服务端长连接接口是/config/listener,对应源码包为config
/****************************************** ConfigController ******************************************/
/**
* The client listens for configuration changes.
*/
@PostMapping("/listener")
@Secured(action = ActionTypes.READ, parser = ConfigResourceParser.class)
public void listener(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setAttribute("org.apache.catalina.ASYNC_SUPPORTED", true);
String probeModify = request.getParameter("Listening-Configs");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(probeModify)) {
LOGGER.warn("invalid probeModify is blank");
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid probeModify");
}
probeModify = URLDecoder.decode(probeModify, Constants.ENCODE);
// 需要检查更新的config信息
Map<String, String> clientMd5Map;
try {
clientMd5Map = MD5Util.getClientMd5Map(probeModify);
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid probeModify");
}
// do long-polling 长连接处理
inner.doPollingConfig(request, response, clientMd5Map, probeModify.length());
}
/****************************************** ConfigServletInner******************************************/
/**
* long polling the config.
*/
public String doPollingConfig(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Map<String, String> clientMd5Map, int probeRequestSize) throws IOException {
// Long polling.判断是否支持长轮询
if (LongPollingService.isSupportLongPolling(request)) {
// 长轮询处理
longPollingService.addLongPollingClient(request, response, clientMd5Map, probeRequestSize);
return HttpServletResponse.SC_OK + "";
}
// 不支持长轮询,直接与当前配置作比较,返回有变更的配置
List<String> changedGroups = MD5Util.compareMd5(request, response, clientMd5Map);
// Compatible with short polling result.
String oldResult = MD5Util.compareMd5OldResult(changedGroups);
String newResult = MD5Util.compareMd5ResultString(changedGroups);
String version = request.getHeader(Constants.CLIENT_VERSION_HEADER);
if (version == null) {
version = "2.0.0";
}
int versionNum = Protocol.getVersionNumber(version);
// Before 2.0.4 version, return value is put into header.
if (versionNum < START_LONG_POLLING_VERSION_NUM) {
response.addHeader(Constants.PROBE_MODIFY_RESPONSE, oldResult);
response.addHeader(Constants.PROBE_MODIFY_RESPONSE_NEW, newResult);
} else {
request.setAttribute("content", newResult);
}
// Disable cache.
response.setHeader("Pragma", "no-cache");
response.setDateHeader("Expires", 0);
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache,no-store");
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK);
return HttpServletResponse.SC_OK + "";
}
/****************************************** LongPollingService ******************************************/
/**
* Add LongPollingClient.
*
* @param req HttpServletRequest.
* @param rsp HttpServletResponse.
* @param clientMd5Map clientMd5Map.
* @param probeRequestSize probeRequestSize.
*/
public void addLongPollingClient(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse rsp, Map<String, String> clientMd5Map,
int probeRequestSize) {
String str = req.getHeader(LongPollingService.LONG_POLLING_HEADER);
String noHangUpFlag = req.getHeader(LongPollingService.LONG_POLLING_NO_HANG_UP_HEADER);
String appName = req.getHeader(RequestUtil.CLIENT_APPNAME_HEADER);
String tag = req.getHeader("Vipserver-Tag");
int delayTime = SwitchService.getSwitchInteger(SwitchService.FIXED_DELAY_TIME, 500);
// 服务端这边最多处理时长29.5s,需要留0.5s来返回,以免客户端那边超时
long timeout = Math.max(10000, Long.parseLong(str) - delayTime);
if (isFixedPolling()) {
timeout = Math.max(10000, getFixedPollingInterval());
// Do nothing but set fix polling timeout.
} else {
// 不支持长轮询 本地对比返回
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> changedGroups = MD5Util.compareMd5(req, rsp, clientMd5Map);
if (changedGroups.size() > 0) {
generateResponse(req, rsp, changedGroups);
LogUtil.CLIENT_LOG.info("{}|{}|{}|{}|{}|{}|{}", System.currentTimeMillis() - start, "instant",
RequestUtil.getRemoteIp(req), "polling", clientMd5Map.size(), probeRequestSize,
changedGroups.size());
return;
} else if (noHangUpFlag != null && noHangUpFlag.equalsIgnoreCase(TRUE_STR)) {
LogUtil.CLIENT_LOG.info("{}|{}|{}|{}|{}|{}|{}", System.currentTimeMillis() - start, "nohangup",
RequestUtil.getRemoteIp(req), "polling", clientMd5Map.size(), probeRequestSize,
changedGroups.size());
return;
}
}
String ip = RequestUtil.getRemoteIp(req);
// 将http响应交给异步线程,返回一个异步响应上下文, 当配置更新后可以主动调用及时返回,不用非等待29.5s
final AsyncContext asyncContext = req.startAsync();
// AsyncContext.setTimeout() is incorrect, Control by oneself
asyncContext.setTimeout(0L);
// 执行客户端长连接任务,
ConfigExecutor.executeLongPolling(
new ClientLongPolling(asyncContext, clientMd5Map, ip, probeRequestSize, timeout, appName, tag));
}
/****************************************** ClientLongPolling ******************************************/
class ClientLongPolling implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
// 提交一个任务,延迟29.5s执行
asyncTimeoutFuture = ConfigExecutor.scheduleLongPolling(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
getRetainIps().put(ClientLongPolling.this.ip, System.currentTimeMillis());
// Delete subsciber's relations.
allSubs.remove(ClientLongPolling.this);
if (isFixedPolling()) {
// 检查变更配置 并相应
List<String> changedGroups = MD5Util
.compareMd5((HttpServletRequest) asyncContext.getRequest(),
(HttpServletResponse) asyncContext.getResponse(), clientMd5Map);
if (changedGroups.size() > 0) {
sendResponse(changedGroups);
} else {
sendResponse(null);
}
} else {
sendResponse(null);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
LogUtil.DEFAULT_LOG.error("long polling error:" + t.getMessage(), t.getCause());
}
}
}, timeoutTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
allSubs.add(this);
}
}
上面大部分地方都比较好懂,主要解释下ClientLongPolling作用,它首先会提交一个任务,无论配置有没有更新 最终都会进行响应,延迟29.5s执行,然后会把自己添加到一个队列中,之前说过,服务端这边配置有更新后 会找出正在等待配置更新的长连接任务,提前结束这个任务并返回,来看这一步是怎么处理的
/****************************************** LongPollingService ******************************************/
public LongPollingService() {
allSubs = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<ClientLongPolling>();
ConfigExecutor.scheduleLongPolling(new StatTask(), 0L, 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// Register LocalDataChangeEvent to NotifyCenter.
NotifyCenter.registerToPublisher(LocalDataChangeEvent.class, NotifyCenter.ringBufferSize);
// Register A Subscriber to subscribe LocalDataChangeEvent.
NotifyCenter.registerSubscriber(new Subscriber() {
@Override
public void onEvent(Event event) {
if (isFixedPolling()) {
// Ignore.
} else {
if (event instanceof LocalDataChangeEvent) {
LocalDataChangeEvent evt = (LocalDataChangeEvent) event;
ConfigExecutor.executeLongPolling(new DataChangeTask(evt.groupKey, evt.isBeta, evt.betaIps));
}
}
}
@Override
public Class<? extends Event> subscribeType() {
return LocalDataChangeEvent.class;
}
});
}
class DataChangeTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
ConfigCacheService.getContentBetaMd5(groupKey);
// 找出等在该配置的长连接,然后进行提前返回
for (Iterator<ClientLongPolling> iter = allSubs.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
ClientLongPolling clientSub = iter.next();
if (clientSub.clientMd5Map.containsKey(groupKey)) {
// If published tag is not in the beta list, then it skipped.
if (isBeta && !CollectionUtils.contains(betaIps, clientSub.ip)) {
continue;
}
// If published tag is not in the tag list, then it skipped.
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(tag) && !tag.equals(clientSub.tag)) {
continue;
}
getRetainIps().put(clientSub.ip, System.currentTimeMillis());
iter.remove(); // Delete subscribers' relationships.
clientSub.sendResponse(Arrays.asList(groupKey));
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
LogUtil.DEFAULT_LOG.error("data change error: {}", ExceptionUtil.getStackTrace(t));
}
}
}
LongPollingService构造函数中,会注册一个订阅,用来监听LocalDataChangeEvent,当发生该事件时,会执行一个数据变更任务,这个任务就是找出等在配置的长连接,提前返回。
问题: 但是我们在nacos控制台修改一个配置文件进行发布,会调用ConfigController.publishConfig接口,但这个接口发布的是ConfigDataChangeEvent事件。这个跟LocalDataChangeEvent是不是不一样了。
原因:在 ClientLongPolling 任务被提交进入线程池待执行的同时,服务端也通过一个队列 allSubs 保存了所有正在被夯住的轮询请求,这是因为在配置项被夯住的期间内,如果用户通过管理平台操作了配置项变更、或者服务端该节点收到了来自其他节点的 dump 刷新通知,那么都应立即取消夯住的任务,及时通知客户端数据发生了变更。
为了达到这个目的,LongPollingService 类继承自 Event 接口,实际上本身是个事件触发器,需要实现 onEvent 方法,其事件类型是 LocalDataChangeEvent。
因此发布配置更新完整的流程如下:
参考文章
https://www.cnblogs.com/zzz-blogs/p/14249126.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35890572/article/details/112348083
https://www.cnblogs.com/crazymakercircle/p/14231815.html